
Explain with the help of a suitable example polar covalent bond.
Answer
606k+ views
Hint: Polar covalent bonding is a type of chemical bond where a pair of electrons are unequally shared between two atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been asked to explain polar covalent bonds with a suitable example.
So, let us first discuss the polar covalent bond.
Polar bond-
So, polar covalent bond is a bond which takes place when two different atoms are linked to each other by a covalent bond. In this type of bonding, a chemical bond where a pair of electrons are unequally shared between the atoms. The shared electron pair will not be in the centre just because the bonding atoms differ in electronegativities.
Example of polar covalent bond-
The water molecule shows polar bonding, the water molecule has chemical formula, ${H_2}O$
Now here slightly positive charges are developed in hydrogen atoms and slightly negative charge developed in oxygen atoms as oxygen is more electronegativity than the hydrogen atom. Thus, opposite poles are developed in the molecule.
Refer the figure below to understand the charge distribution-
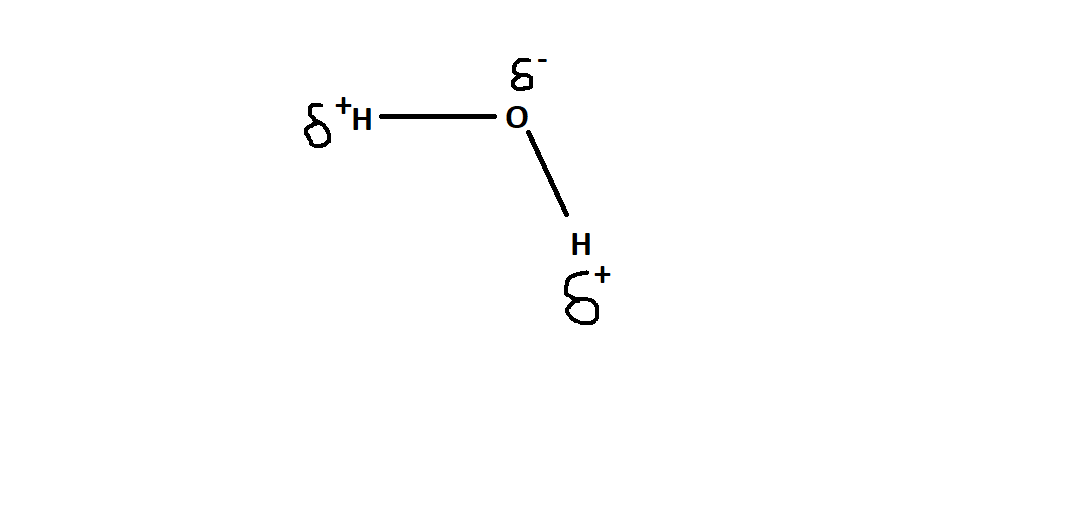
As you can see the above structure has a slight positive charge on hydrogen atoms and a slight negative charge on oxygen atom, hence the bond pair lies towards oxygen atom.
Another example of polar bonding is hydrogen chloride (HCl) molecule. The bonding of hydrogen and chlorine atoms leans more towards Cl atoms because Cl is more electronegative in nature than the hydrogen. Hence, the shared pair of electrons lies not exactly in between the bond but lean towards chlorine. Due to this reason, Cl atoms acquire a slight negative charge, and H atoms acquire slight positive charge.
Refer to the structure below to understand better-
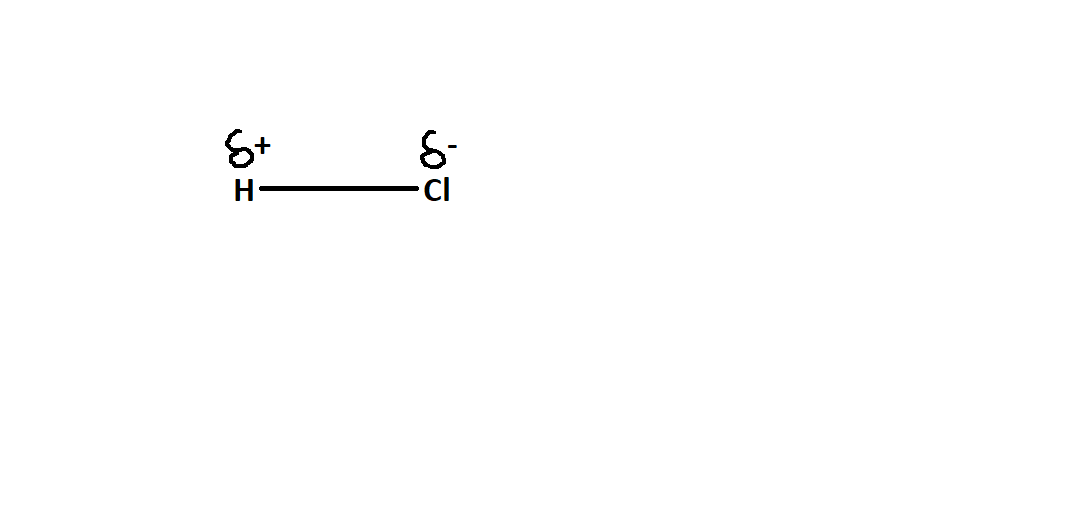 The above structure shows that there is slightly positive charge on hydrogen atom and negative charge on chlorine atom due to its high electronegativity.
The above structure shows that there is slightly positive charge on hydrogen atom and negative charge on chlorine atom due to its high electronegativity.
Note – Whenever such types of questions appear, then first explain what does it mean by polar bonding and what compounds form polar bonds. In polar bonds slightly positive charge appears on the atom which is less electronegative and slightly negative charge appears on the more electronegative atom. As mentioned in the solution, about ${H_2}O$ molecule and $HCl$ molecule and polar bonding is explained with these examples and their structure is also shown.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been asked to explain polar covalent bonds with a suitable example.
So, let us first discuss the polar covalent bond.
Polar bond-
So, polar covalent bond is a bond which takes place when two different atoms are linked to each other by a covalent bond. In this type of bonding, a chemical bond where a pair of electrons are unequally shared between the atoms. The shared electron pair will not be in the centre just because the bonding atoms differ in electronegativities.
Example of polar covalent bond-
The water molecule shows polar bonding, the water molecule has chemical formula, ${H_2}O$
Now here slightly positive charges are developed in hydrogen atoms and slightly negative charge developed in oxygen atoms as oxygen is more electronegativity than the hydrogen atom. Thus, opposite poles are developed in the molecule.
Refer the figure below to understand the charge distribution-

As you can see the above structure has a slight positive charge on hydrogen atoms and a slight negative charge on oxygen atom, hence the bond pair lies towards oxygen atom.
Another example of polar bonding is hydrogen chloride (HCl) molecule. The bonding of hydrogen and chlorine atoms leans more towards Cl atoms because Cl is more electronegative in nature than the hydrogen. Hence, the shared pair of electrons lies not exactly in between the bond but lean towards chlorine. Due to this reason, Cl atoms acquire a slight negative charge, and H atoms acquire slight positive charge.
Refer to the structure below to understand better-
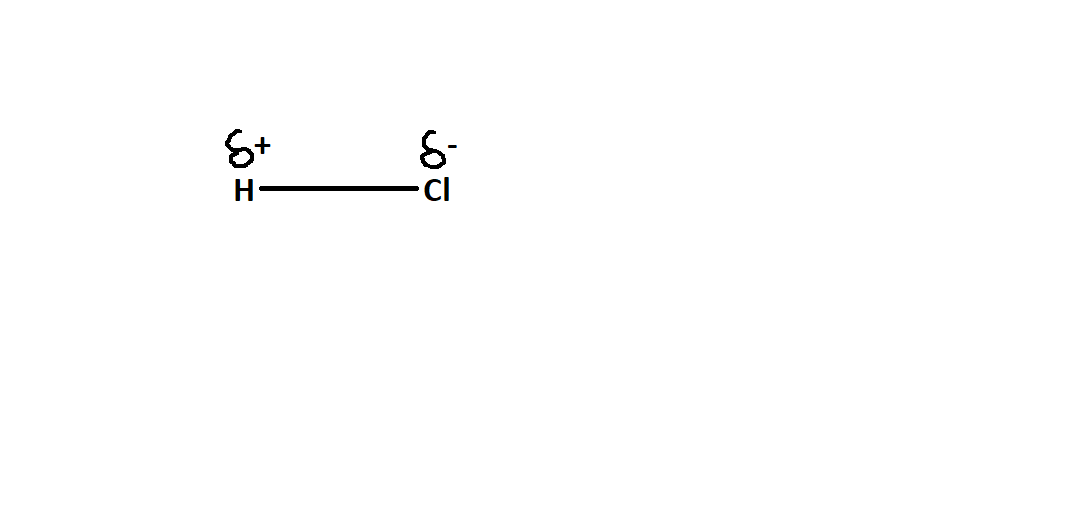
Note – Whenever such types of questions appear, then first explain what does it mean by polar bonding and what compounds form polar bonds. In polar bonds slightly positive charge appears on the atom which is less electronegative and slightly negative charge appears on the more electronegative atom. As mentioned in the solution, about ${H_2}O$ molecule and $HCl$ molecule and polar bonding is explained with these examples and their structure is also shown.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




