
Explain the working of the lac operon with diagrammatic representation.
Answer
603.6k+ views
Hint: Operon refers to a set of functional genes (Transcription unit) required for the production of enzymes. They have a single promoter region. In operon the genes encode proteins that allow the bacteria to use lactose as an energy source.
Complete Answer:
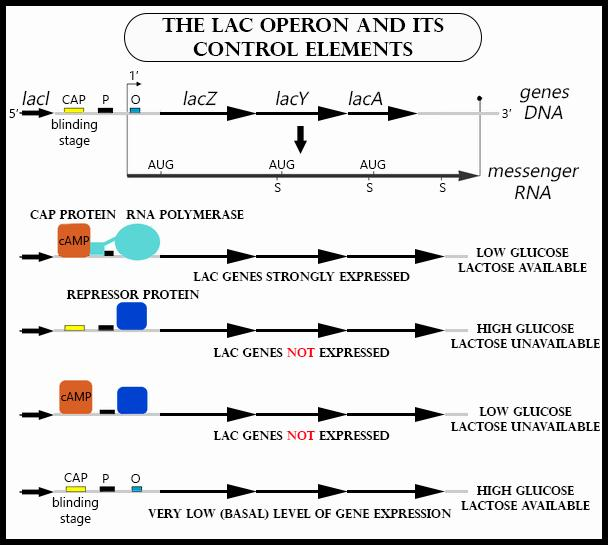
The concept of Lac operon was given by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod. Lac operon is an operon present predominantly in the prokaryotes like E. coli. It was the first gene regulatory process to be discovered in bacteria. It is associated with the regulation of lactose i.e. transport and metabolism.
-It consists of an operator, promoter, three structural genes, z, y, a, and a terminator.
-The three structural genes lacZ, lacY, lacA code for beta-galactosidase, galactoside permease, and galactoside acetyltransferase, respectively.
-The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region (at 3’ end of template strand) and moves downstream, forming the desirable protein.
-The enzyme beta-galactosidase is responsible for the breakdown of disaccharide lactose into glucose and galactose. Permease is a cell membrane protein responsible for the entry of lactose into the cell. Acetyltransferase is responsible for the transfer of the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to beta galactoside.
-The operon is active only in the presence of lactose.
Note: -Jacob and Monad were awarded the Nobel prize for the discovery of Lac operon in 1965.
-The lac operon remains in ‘off’ position. It means that the operon is negatively inducible due to the presence of a repressor gene i.e. ‘I’ gene. The depression molecule blocks the action of RNA polymerase. The repressor molecule can be removed only by an operator protein (coded by a gene ‘o’).
-The operator present in Lac operon is ‘Allolactose’.
Complete Answer:
The concept of Lac operon was given by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod. Lac operon is an operon present predominantly in the prokaryotes like E. coli. It was the first gene regulatory process to be discovered in bacteria. It is associated with the regulation of lactose i.e. transport and metabolism.
-It consists of an operator, promoter, three structural genes, z, y, a, and a terminator.
-The three structural genes lacZ, lacY, lacA code for beta-galactosidase, galactoside permease, and galactoside acetyltransferase, respectively.
-The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region (at 3’ end of template strand) and moves downstream, forming the desirable protein.
-The enzyme beta-galactosidase is responsible for the breakdown of disaccharide lactose into glucose and galactose. Permease is a cell membrane protein responsible for the entry of lactose into the cell. Acetyltransferase is responsible for the transfer of the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to beta galactoside.
-The operon is active only in the presence of lactose.

Note: -Jacob and Monad were awarded the Nobel prize for the discovery of Lac operon in 1965.
-The lac operon remains in ‘off’ position. It means that the operon is negatively inducible due to the presence of a repressor gene i.e. ‘I’ gene. The depression molecule blocks the action of RNA polymerase. The repressor molecule can be removed only by an operator protein (coded by a gene ‘o’).
-The operator present in Lac operon is ‘Allolactose’.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




