
Explain the terms of polymer and monomer.
Answer
618k+ views
Hint:
Poly – Many.
Mono – One.
Mer – A share.
The etymologies of these two words suffice as quite effective hints in this case.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let’s go through each of these terms one at a time to help you understand each of them better
Polymer:
A polymer is a large molecule/macromolecule which is a combination of many smaller molecules also known as monomers. 103−107u is the range of the molar mass of a polymer.
It is possible to find polymers naturally in plants and animals. These polymers are referred to as natural polymers. The polymers that are man-made however are known as synthetic polymers.
Different polymers have a number of unique physical and chemical properties due to which they find usage in everyday life.
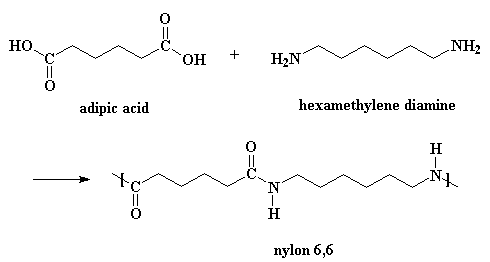
Examples: Nylon 6,6 which is made up of monomers adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.
Monomers:
A monomer is defined as a simple molecule with two or more binding sites through which it forms covalent linkages with other monomer molecules to form the macromolecule.
Monomers are thus building blocks of polymers. Only those simple molecules with two or more bonding sites can act as monomers.
Examples: Alkenes ($R-CH=CH-R$, where R stands for an alkyl group), vinyl chloride (${{H}_{2}}C=CHCl$) and adipic acid (structure seen in the polymer example)
NOTE: It is very important to know the distinction between monomers and polymers to be able to answer this question correctly. Also, to ensure that you give a brilliant answer, make sure that it is rife with examples, as is seen in the above solution.
Poly – Many.
Mono – One.
Mer – A share.
The etymologies of these two words suffice as quite effective hints in this case.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let’s go through each of these terms one at a time to help you understand each of them better
Polymer:
A polymer is a large molecule/macromolecule which is a combination of many smaller molecules also known as monomers. 103−107u is the range of the molar mass of a polymer.
It is possible to find polymers naturally in plants and animals. These polymers are referred to as natural polymers. The polymers that are man-made however are known as synthetic polymers.
Different polymers have a number of unique physical and chemical properties due to which they find usage in everyday life.
Examples: Nylon 6,6 which is made up of monomers adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.

Monomers:
A monomer is defined as a simple molecule with two or more binding sites through which it forms covalent linkages with other monomer molecules to form the macromolecule.
Monomers are thus building blocks of polymers. Only those simple molecules with two or more bonding sites can act as monomers.
Examples: Alkenes ($R-CH=CH-R$, where R stands for an alkyl group), vinyl chloride (${{H}_{2}}C=CHCl$) and adipic acid (structure seen in the polymer example)
NOTE: It is very important to know the distinction between monomers and polymers to be able to answer this question correctly. Also, to ensure that you give a brilliant answer, make sure that it is rife with examples, as is seen in the above solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




