
Explain the structure of glycogen.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Glycogen is a polysaccharide and a polymer of glucose. It is stored in animal tissues e.g. liver adipose tissue, muscles, etc. When required it is broken down to provide energy.
Complete answer:Glycogen is a common homo-polysaccharide. It is a branched polymer of glucose (monosaccharide).
The glucose molecules are aligned in a linear fashion and they are linked by α(1🡪4) glycosidic bond. After every 8-10 glucose residues, a branch occurs.
The branch is different because, in it, the glucose residues are linked with α(1🡪6) glycosidic bond.
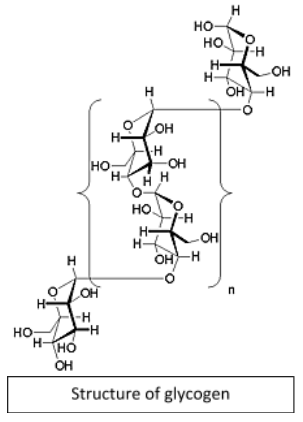
Glycogen can be broken down into glucose when required. It happens in the process called glycogenolysis. Here, the bonds in between the glucose residues get hydrolyzed; these residues are then used for respiration pathways to yield energy.
In simple words, glycogen is a branched homopolysaccharide of α-D-glucose linked by α(1 $\to$ 4) glycosidic bonds.
Note: Glycogen is an analogue of the starch in plants (found as their stored material). There are approximately 2000 to 6000 glucose residues in a glycogen molecule. Each glycogen granule has a central protein- glycogenin.
Complete answer:Glycogen is a common homo-polysaccharide. It is a branched polymer of glucose (monosaccharide).
The glucose molecules are aligned in a linear fashion and they are linked by α(1🡪4) glycosidic bond. After every 8-10 glucose residues, a branch occurs.
The branch is different because, in it, the glucose residues are linked with α(1🡪6) glycosidic bond.

Glycogen can be broken down into glucose when required. It happens in the process called glycogenolysis. Here, the bonds in between the glucose residues get hydrolyzed; these residues are then used for respiration pathways to yield energy.
In simple words, glycogen is a branched homopolysaccharide of α-D-glucose linked by α(1 $\to$ 4) glycosidic bonds.
Note: Glycogen is an analogue of the starch in plants (found as their stored material). There are approximately 2000 to 6000 glucose residues in a glycogen molecule. Each glycogen granule has a central protein- glycogenin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




