
Explain the structure of chloroplast. Accompany with a neat labeled diagram.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis and are present in photosynthetic plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. They also carry out a number of other functions, such as fatty acid synthesis, some amino acid synthesis, and the immune response.
Complete answer:
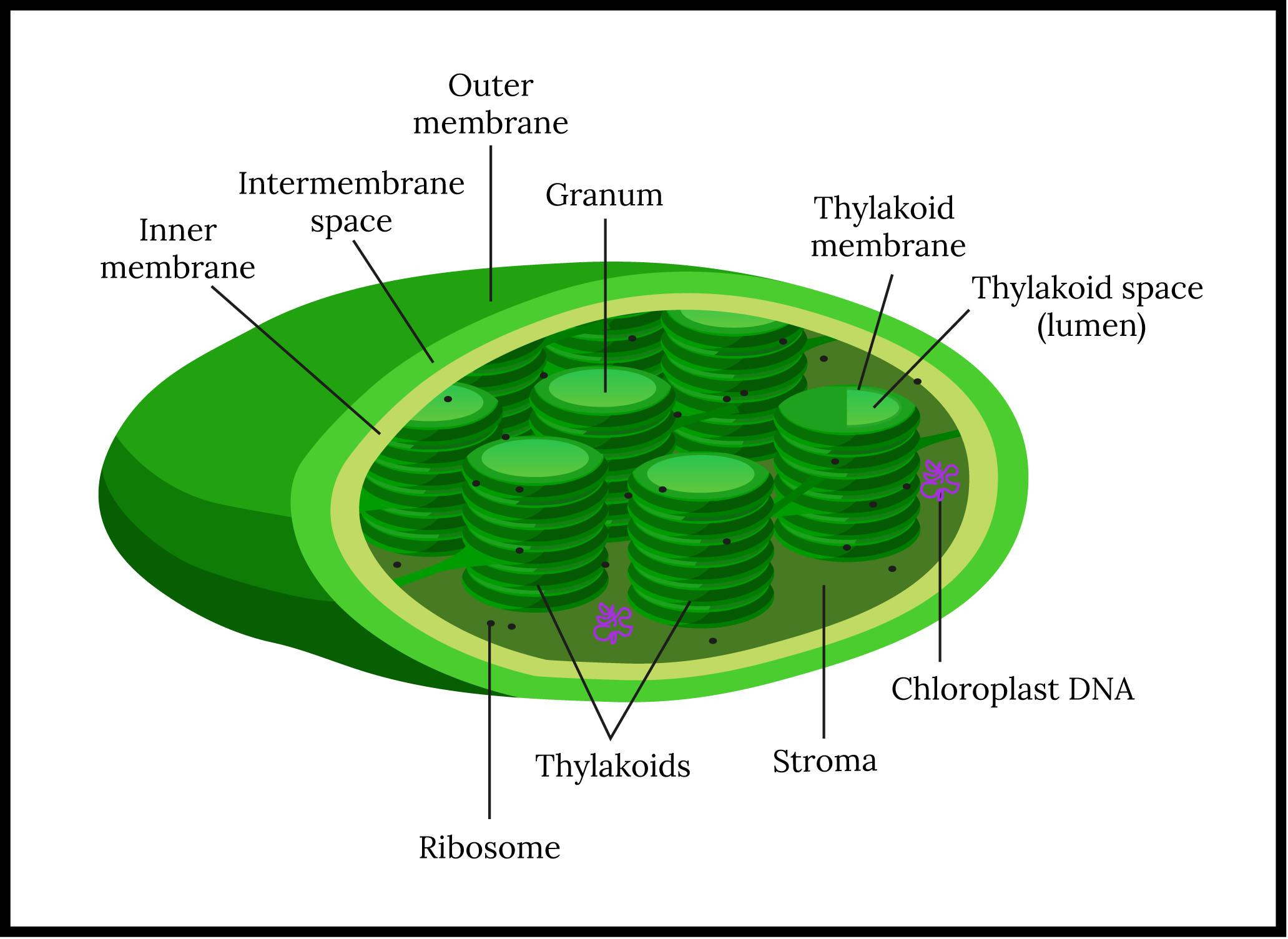
- Chloroplasts are free-moving, membrane-bound plastids present in photosynthetic organisms such as plants.
- They can be found in the mesophyll cells of plant leaves. They are plano convex or biconvex shaped in higher plants.
-Chloroplast consists of an inner and outer membrane to form an envelope, with an empty intermediate space in between. The inner membrane regulates the passage of materials in and out of the chloroplast.
-Individual thylakoid discs are stacked on top of each other known as a granum (plural: grana).
-Stroma is the colorless matrix that surrounds the grana in the chloroplast. It is the site for Calvin cycle reactions and chloroplast DNA replication. It is alkaline and aqueous in nature.
-The grana are connected to each other by lamellae or stroma thylakoids.
-Certain plants contain an organelle called the peripheral reticulum that is an additional set of membranous tubules. They are formed from tiny vesicles budding off from the inner membrane.
-Chloroplasts also provide a site for metabolic reactions to form membrane lipids, isoprenoids, tetrapyrroles, starch, and hormones.
-Chloroplasts have their own DNA, known as ctDNA.
Note: - Some algae like glaucophytes have a peptidoglycan layer between their inner and outer chloroplast membranes.
- In some ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants and some algae, the chloroplasts contain free-floating thylakoids.
- The thylakoid membrane is also a site for ATP synthesis.
- Photosynthetic pigments present in the thylakoid for green plants are chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids (carotene and xanthophylls), and plastoquinone.
- Chloroplasts contain 10-100 grana.
Complete answer:

- Chloroplasts are free-moving, membrane-bound plastids present in photosynthetic organisms such as plants.
- They can be found in the mesophyll cells of plant leaves. They are plano convex or biconvex shaped in higher plants.
-Chloroplast consists of an inner and outer membrane to form an envelope, with an empty intermediate space in between. The inner membrane regulates the passage of materials in and out of the chloroplast.
-Individual thylakoid discs are stacked on top of each other known as a granum (plural: grana).
-Stroma is the colorless matrix that surrounds the grana in the chloroplast. It is the site for Calvin cycle reactions and chloroplast DNA replication. It is alkaline and aqueous in nature.
-The grana are connected to each other by lamellae or stroma thylakoids.
-Certain plants contain an organelle called the peripheral reticulum that is an additional set of membranous tubules. They are formed from tiny vesicles budding off from the inner membrane.
-Chloroplasts also provide a site for metabolic reactions to form membrane lipids, isoprenoids, tetrapyrroles, starch, and hormones.
-Chloroplasts have their own DNA, known as ctDNA.
Note: - Some algae like glaucophytes have a peptidoglycan layer between their inner and outer chloroplast membranes.
- In some ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants and some algae, the chloroplasts contain free-floating thylakoids.
- The thylakoid membrane is also a site for ATP synthesis.
- Photosynthetic pigments present in the thylakoid for green plants are chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids (carotene and xanthophylls), and plastoquinone.
- Chloroplasts contain 10-100 grana.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




