
Explain the structure and function of plasmodesmata with help of diagram?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Plasmodesmata are the bridge of cytoplasm between every living cell. Plasmodesmata progress individualistic in various lineages, and species include members of the Charophyceae, Charales, Coleochaetales and Phaeophyceae (algae), embryophytes (plants)
Complete answer:
Plasmodesmata are cytoplasmic bridges which develop in the pores of their cell walls.
Two kinds of plasmodesmata are present: primary plasmodesmata (formed during cell division) and secondary plasmodesmata (form between mature cells).
Primary plasmodesmata formation occurs when fractions of the endoplasmic reticulum are treed across the middle lamella as a new cytomembrane is synthesized between two newly divided plant cells. These eventually become the protoplasmic connections between cells. At the formation site, the wall is not thickened further, and depressions or thin areas are understood as pits which are formed in the walls. Pits ordinarily combine between adjacent cells.Plasmodesmatafit into existing cell walls between non-dividing cells are secondary plasmodesmata.
Correct answer:
Function: Intercellular communication, transport protein, and transport molecules between near plants.
Structure:
They are made up of a protoplasmic continuum called symplast.
Apoplasm:A non-living component of the plant body formed by cell wall and intercellular spaces called apoplasm.
Diameter of plasmodesmata is 40-50 nm and it issimple, branched and roughly cylindrical.
There is space between the desmotubule and plasma membrane which contains 8-10 microchannels.
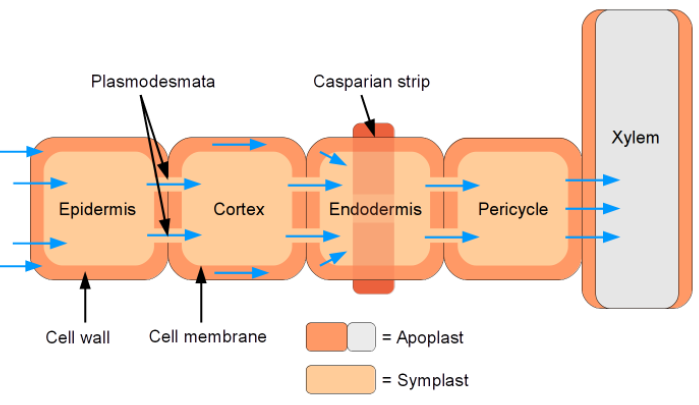
Note: Plasmodesmata form channels for controlled passage of small-sized particles between adjacent cells as well as the transfer of some specific signals. Plasma membrane lines the plasmodesmata and encloses tubular extension of the endoplasmic reticulum known as desmotubule.
Complete answer:
Plasmodesmata are cytoplasmic bridges which develop in the pores of their cell walls.
Two kinds of plasmodesmata are present: primary plasmodesmata (formed during cell division) and secondary plasmodesmata (form between mature cells).
Primary plasmodesmata formation occurs when fractions of the endoplasmic reticulum are treed across the middle lamella as a new cytomembrane is synthesized between two newly divided plant cells. These eventually become the protoplasmic connections between cells. At the formation site, the wall is not thickened further, and depressions or thin areas are understood as pits which are formed in the walls. Pits ordinarily combine between adjacent cells.Plasmodesmatafit into existing cell walls between non-dividing cells are secondary plasmodesmata.
Correct answer:
Function: Intercellular communication, transport protein, and transport molecules between near plants.
Structure:
They are made up of a protoplasmic continuum called symplast.
Apoplasm:A non-living component of the plant body formed by cell wall and intercellular spaces called apoplasm.
Diameter of plasmodesmata is 40-50 nm and it issimple, branched and roughly cylindrical.
There is space between the desmotubule and plasma membrane which contains 8-10 microchannels.

Note: Plasmodesmata form channels for controlled passage of small-sized particles between adjacent cells as well as the transfer of some specific signals. Plasma membrane lines the plasmodesmata and encloses tubular extension of the endoplasmic reticulum known as desmotubule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




