
Explain the mechanism of action of hydroiodic acid on 3-methylbutan-2-ol.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Reaction of hydrogen halide with alcohol gives the alkyl halide and water as products and it is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The reaction takes place with the formation of the carbocation as an intermediate. Here, halide ion is acting as nucleophile attacks on the electropositive center that is carbocation formed as intermediates in the reaction. Here, the stability of the carbocation formed decides the nature of the product.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, in the question alcohol has given is 3-methylbutan-2-ol is secondary alcohol that reacts with hydrogen iodide by SN1 reaction mechanism.
The reaction is completed in three steps which are given as follows:
Step 1: Protonation of alcohol by acid.

Here, we can see that alcohol is pronated to form an intermediate as shown above.
Step 2: Formation of carbocation

Here, the formed intermediate removes water molecules and forms carbocation as an intermediate. Here, secondary carbocation is formed.
Step 3: Formation of product
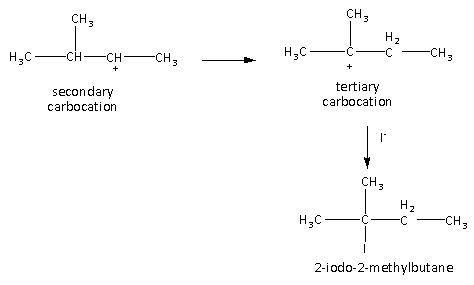
Here, the secondary carbocation undergoes rearrangement and forms a more stable tertiary carbocation. The tertiary carbocation is then attacked by a nucleophile and the final product 2-iodo-2-methyl butane is formed.
Thus, the action of the hydroiodic acid on 3-methylbutan-2-ol gives 2-iodo-2-methylbutane as a product.
Note:
i) The secondary alcohols in reaction with hydroiodic acid undergo the reaction through the SN2 mechanism.
ii) The reactivity order for alcohols with hydrohalic acid is as follows:
Tertiary> secondary>primary
iii) It indicates tertiary alcohols more radially undergo the reaction compared to secondary and primary.
iv) The stability order of the carbocation is as follows:
Tertiary> secondary> primary
v) The order indicates tertiary carbocation is favored compared to secondary which is favored compared to the primary.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, in the question alcohol has given is 3-methylbutan-2-ol is secondary alcohol that reacts with hydrogen iodide by SN1 reaction mechanism.
The reaction is completed in three steps which are given as follows:
Step 1: Protonation of alcohol by acid.

Here, we can see that alcohol is pronated to form an intermediate as shown above.
Step 2: Formation of carbocation

Here, the formed intermediate removes water molecules and forms carbocation as an intermediate. Here, secondary carbocation is formed.
Step 3: Formation of product

Here, the secondary carbocation undergoes rearrangement and forms a more stable tertiary carbocation. The tertiary carbocation is then attacked by a nucleophile and the final product 2-iodo-2-methyl butane is formed.
Thus, the action of the hydroiodic acid on 3-methylbutan-2-ol gives 2-iodo-2-methylbutane as a product.
Note:
i) The secondary alcohols in reaction with hydroiodic acid undergo the reaction through the SN2 mechanism.
ii) The reactivity order for alcohols with hydrohalic acid is as follows:
Tertiary> secondary>primary
iii) It indicates tertiary alcohols more radially undergo the reaction compared to secondary and primary.
iv) The stability order of the carbocation is as follows:
Tertiary> secondary> primary
v) The order indicates tertiary carbocation is favored compared to secondary which is favored compared to the primary.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




