
Explain the hybridization involved in $PC{l_5}$ molecules.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:As we all know that hybridization is the mixing of two atomic orbitals to give a degenerated new orbital and orbitals that are fully filled and half-filled can participate in this process. Phosphorus belong to p-block elements having electronic configuration as $n{s^2}n{p^3}$ and it forms $PC{l_5}$ with chlorine having electronic configuration $n{s^2}n{p^5}$.
Complete answer:
As we know that the concept of hybridization depends upon the mixing of two atomic orbitals having similar energies to give a degenerated new orbital or we can say that hybridization is the result of formation of a hybrid orbital formed by mixing of two atomic orbitals for redistribution of their energy and orbitals that are fully filled and half-filled can participate in this process. During mixing, the orbitals with same energy are mixed together such as the mixing of one s and one p-orbital or two s and two p-orbitals or one s or one d-orbital etc. and can be named as $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d,s{p^3}{d^2}$ etc.
Considering our molecule, using Valence Bond Theory let us first write the configurations of both elements:
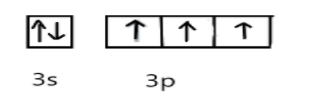
In ground state, the electronic configuration of phosphorus is, P= $3{s^2}3{p^3}$ and Cl=$3{s^2}3{p^5}$
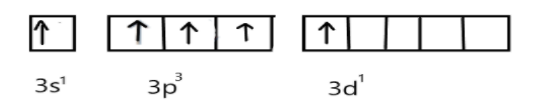
In excited state, under the conditions of bond formation electron in s-orbitals get unpaired and one electron will be promoted to vacant d-orbital as shown:
Now, these five singly occupied orbitals will overlap with the 3pz-orbitals of five chlorine atoms and form five σ-bonds between P-C:
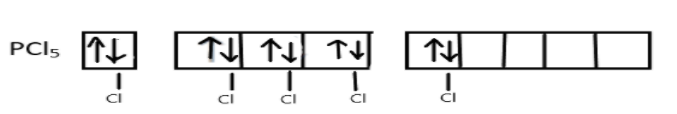
Hence, the final result will be a $s{p^3}d$ hybridized molecule $PC{l_5}$ involving one s, three p and one d-orbital. The geometry of this molecule is trigonal bipyramidal, three of the hybrid orbitals lie in a horizontal plane at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ to one another and other two orbitals will lie in a vertical plane at right angle to the horizontal orbitals.
Note:
The hybrid state of some atoms like $I{F_5},S{F_4},ClO_3^ - $ can be easily found using the formula: $X = SA + \dfrac{1}{2}(G - V) $ where SA is the number of atoms surrounding the central atom, G is valence electrons of central atom and V is valency of central atom.
Complete answer:
As we know that the concept of hybridization depends upon the mixing of two atomic orbitals having similar energies to give a degenerated new orbital or we can say that hybridization is the result of formation of a hybrid orbital formed by mixing of two atomic orbitals for redistribution of their energy and orbitals that are fully filled and half-filled can participate in this process. During mixing, the orbitals with same energy are mixed together such as the mixing of one s and one p-orbital or two s and two p-orbitals or one s or one d-orbital etc. and can be named as $sp,s{p^2},s{p^3},s{p^3}d,s{p^3}{d^2}$ etc.
Considering our molecule, using Valence Bond Theory let us first write the configurations of both elements:
In ground state, the electronic configuration of phosphorus is, P= $3{s^2}3{p^3}$ and Cl=$3{s^2}3{p^5}$

In excited state, under the conditions of bond formation electron in s-orbitals get unpaired and one electron will be promoted to vacant d-orbital as shown:

Now, these five singly occupied orbitals will overlap with the 3pz-orbitals of five chlorine atoms and form five σ-bonds between P-C:

Hence, the final result will be a $s{p^3}d$ hybridized molecule $PC{l_5}$ involving one s, three p and one d-orbital. The geometry of this molecule is trigonal bipyramidal, three of the hybrid orbitals lie in a horizontal plane at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ to one another and other two orbitals will lie in a vertical plane at right angle to the horizontal orbitals.
Note:
The hybrid state of some atoms like $I{F_5},S{F_4},ClO_3^ - $ can be easily found using the formula: $X = SA + \dfrac{1}{2}(G - V) $ where SA is the number of atoms surrounding the central atom, G is valence electrons of central atom and V is valency of central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




