
Explain the function of the cranium.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: The skull is a major part of the axial skeleton system. It is a flat hard bone curved to hold the brain inside it. The brain is the most sensitive and important organ of the body which needs to be protected against environmental shocks. All vertebrates have a cranium which forms their head portion.
Complete answer: The cranium is the bony structure present in the vertebrate organism at the top of their axial skeleton. It forms the head part of the body. The cranium supports the face and the brain. Cranium’s main function is to hold and protect the brain. The cranium is made up of flat bones that consist of fossae, foramina, sinuses, and processes. The sinuses are cavities in the skull. The main function of the cranium is to protect the brain from any possible injuries. The brain is the most sensitive organ of the body which needs to be protected from external stresses.
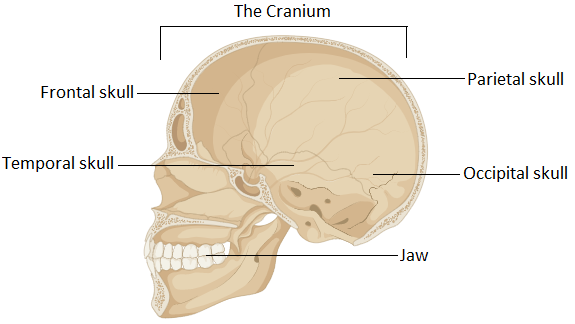
The cranium consists of cranial fluid beneath it which covers the brain. This fluid is able to absorb shock. The main four parts of the cranium are occipital, frontal, parietal, and temporal. Each cranial bone is joined together by sutures that are specialized joints. At birth, the cranium is composed of 44 bones that fuse together into solid bones with development. The sutures stay separated until adulthood and only joint at the adult stage. This allows our brain to grow continuously up to 20 years of age. With age, the cranium becomes harder and stronger. If we will not have a strong cranium we will be vulnerable to traumatic brain injuries.
Note: The cavities in the skull are responsible for the extension of various Brain structures towards different body parts. The dorsal cavity of the skull helps to connect the brain stem of the brain and the cervical section of the spinal cord. It is present at the base of the cranium.
Complete answer: The cranium is the bony structure present in the vertebrate organism at the top of their axial skeleton. It forms the head part of the body. The cranium supports the face and the brain. Cranium’s main function is to hold and protect the brain. The cranium is made up of flat bones that consist of fossae, foramina, sinuses, and processes. The sinuses are cavities in the skull. The main function of the cranium is to protect the brain from any possible injuries. The brain is the most sensitive organ of the body which needs to be protected from external stresses.

The cranium consists of cranial fluid beneath it which covers the brain. This fluid is able to absorb shock. The main four parts of the cranium are occipital, frontal, parietal, and temporal. Each cranial bone is joined together by sutures that are specialized joints. At birth, the cranium is composed of 44 bones that fuse together into solid bones with development. The sutures stay separated until adulthood and only joint at the adult stage. This allows our brain to grow continuously up to 20 years of age. With age, the cranium becomes harder and stronger. If we will not have a strong cranium we will be vulnerable to traumatic brain injuries.
Note: The cavities in the skull are responsible for the extension of various Brain structures towards different body parts. The dorsal cavity of the skull helps to connect the brain stem of the brain and the cervical section of the spinal cord. It is present at the base of the cranium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




