
Explain the formation of ${O_2}$ molecule using molecular orbital theory.
Answer
526.4k+ views
Hint: Draw molecular orbital diagram for oxygen molecule. Then, count the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital and antibonding molecular orbital. After that count the bond order by using the following formula.
Bond Order = $\dfrac{{{\text{Number of electrons in bonding - Number of electrons in antibonding}}}}{2}$
The bond order will tell us the number of bonds that will be formed between two atoms of oxygen molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
The molecular orbital theory is a widely accepted theory for describing the electronic structure of molecules.
The formation of oxygen molecule can be given as –
We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as –
$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$
One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons.
The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as –
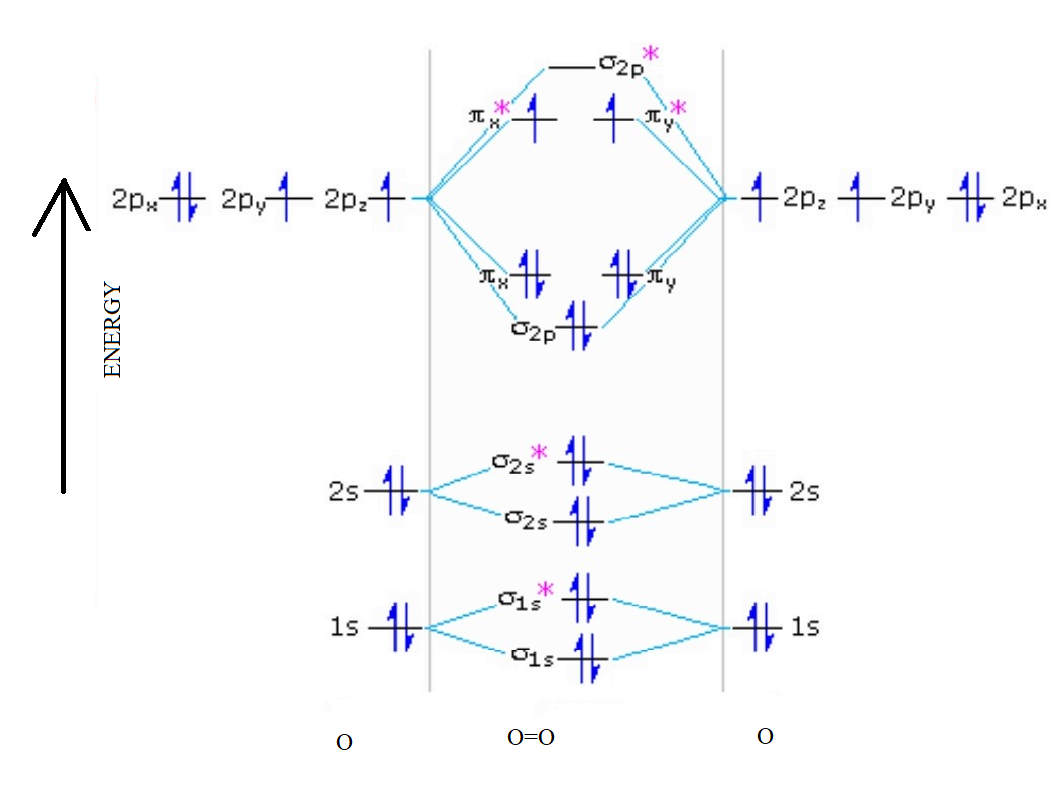
From the diagram, the electronic configuration of oxygen molecule can be written as -
${O_2}$ :- $\sigma 1{s^2}{\sigma ^*}1{s^2}\sigma 2{s^2}{\sigma ^*}2{s^2}\sigma 2{p^2}\Pi 2p_x^2\Pi 2p_y^2{\Pi ^*}2p_x^1{\Pi ^*}2p_y^1$
Now, we can calculate the bond order.
We know the formula for bond order is:-
Bond Order = $\dfrac{{{\text{Number of electrons in bonding - Number of electrons in antibonding}}}}{2}$
Thus, Bond Order = $\dfrac{{10 - 6}}{2}$
Bond Order =2
Thus, the oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is $\sigma $bond and one $\Pi $ bond.
The two electrons in ${\Pi ^*}2p_x^1$ and ${\Pi ^*}2p_y^1$ orbitals are unpaired. So, the oxygen molecule is paramagnetic in nature due to the presence of these two unpaired electrons.
Note: There are two types of molecular orbital diagrams. The rest of the diagram is the same. The change occurs in two at the point of the splitting of p- orbitals. This should be taken care of so that we choose the right splitting.
Bond Order = $\dfrac{{{\text{Number of electrons in bonding - Number of electrons in antibonding}}}}{2}$
The bond order will tell us the number of bonds that will be formed between two atoms of oxygen molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
The molecular orbital theory is a widely accepted theory for describing the electronic structure of molecules.
The formation of oxygen molecule can be given as –
We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as –
$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$
One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons.
The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as –

From the diagram, the electronic configuration of oxygen molecule can be written as -
${O_2}$ :- $\sigma 1{s^2}{\sigma ^*}1{s^2}\sigma 2{s^2}{\sigma ^*}2{s^2}\sigma 2{p^2}\Pi 2p_x^2\Pi 2p_y^2{\Pi ^*}2p_x^1{\Pi ^*}2p_y^1$
Now, we can calculate the bond order.
We know the formula for bond order is:-
Bond Order = $\dfrac{{{\text{Number of electrons in bonding - Number of electrons in antibonding}}}}{2}$
Thus, Bond Order = $\dfrac{{10 - 6}}{2}$
Bond Order =2
Thus, the oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is $\sigma $bond and one $\Pi $ bond.
The two electrons in ${\Pi ^*}2p_x^1$ and ${\Pi ^*}2p_y^1$ orbitals are unpaired. So, the oxygen molecule is paramagnetic in nature due to the presence of these two unpaired electrons.
Note: There are two types of molecular orbital diagrams. The rest of the diagram is the same. The change occurs in two at the point of the splitting of p- orbitals. This should be taken care of so that we choose the right splitting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




