
Explain the formation of calcium chloride with the help of electron dot structure.
Answer
504.9k+ views
Hint: Compounds which are formed by complete transfer on one or more electrons from electropositive atom to electronegative element forms an ionic compound. Lewis symbols are used to express the valence electrons of atoms as a dot.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know atomic number of calcium is $ \left( {20} \right) $ , so its electronic configuration according to Aufbau’s principle will be $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2} $ . From the electronic configuration we clearly see that the calcium atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. So, if calcium loses its two electrons then it will attain the noble gas configuration.
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine atom is $ \left( {17} \right) $ , so its electronic configuration according to Aufbau’s principle will be $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5} $ . From the electronic configuration we clearly see that the chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outermost shell. So, a chlorine atom requires one more electron to attain noble gas configuration.
When a calcium atom reacts with two atoms of chlorine, each chlorine atom gains one electron from the calcium atom and forms the ionic compound.
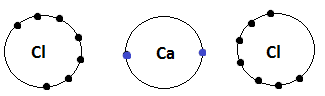
When calcium donates its electrons to chlorine atoms it become positive in nature while chlorine atom become negative in nature as $ \left[ {C{a^{ + 2}}} \right] $ and $ \left[ {2C{l^ - }} \right] $ .
So, formation of calcium chloride with the help of electron dot structure is expressed as –:
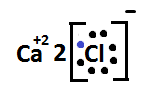
When we write the chemical formula of calcium chloride it will become $ CaC{l_2} $ .
Note:
Calcium chloride is an example of ionic compound and shows good electrical conductivity only in aqueous state or in its molten state when it breaks down into its constituents’ ions. Dots shown in any Lewis structure are equivalent to valence electrons of atoms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know atomic number of calcium is $ \left( {20} \right) $ , so its electronic configuration according to Aufbau’s principle will be $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2} $ . From the electronic configuration we clearly see that the calcium atom has two electrons in its outermost shell. So, if calcium loses its two electrons then it will attain the noble gas configuration.
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine atom is $ \left( {17} \right) $ , so its electronic configuration according to Aufbau’s principle will be $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5} $ . From the electronic configuration we clearly see that the chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outermost shell. So, a chlorine atom requires one more electron to attain noble gas configuration.
When a calcium atom reacts with two atoms of chlorine, each chlorine atom gains one electron from the calcium atom and forms the ionic compound.

When calcium donates its electrons to chlorine atoms it become positive in nature while chlorine atom become negative in nature as $ \left[ {C{a^{ + 2}}} \right] $ and $ \left[ {2C{l^ - }} \right] $ .
So, formation of calcium chloride with the help of electron dot structure is expressed as –:

When we write the chemical formula of calcium chloride it will become $ CaC{l_2} $ .
Note:
Calcium chloride is an example of ionic compound and shows good electrical conductivity only in aqueous state or in its molten state when it breaks down into its constituents’ ions. Dots shown in any Lewis structure are equivalent to valence electrons of atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




