
Explain the elementary idea of an oscillator with the help of a block diagram.
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint:An oscillator is an electronic device that generates an AC signal from a DC source. Continuous oscillations are the basis of the working of an oscillator. It provides output even when no input is applied to it.
Complete step by step answer:
An amplifier and a feedback network with frequency-determining components are required by an oscillator. When a component of the output of an amplifier is coupled with the input of the amplifier, it is called feedback. When the feedback sample is out of phase with the Input, it is called negative feedback. When the feedback sample is in phase with the input, it is called positive feedback. For an oscillator, positive feedback is required. The block diagram of an oscillator is shown below.
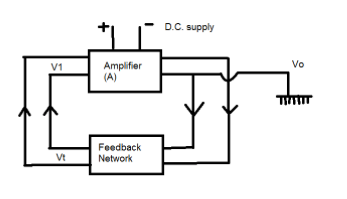
The voltage gain of a complete system is given by
${A_f} = \dfrac{A}{{1 - A\beta }}$ where ${A_f}$ is the voltage gain with feedback, A is voltage gain without feedback, and $\beta $
is the feedback factor.
If for some frequency the value of $A\beta = 1$, then the system gain becomes equal to infinity and the circuit begins to oscillate at that frequency. This condition is called the Barkhausen criterion for sustained oscillations.
The frequency of oscillations depends on the RC or LC combinations which are used in a feedback network. A wide range of frequencies generates the electrical noise in the circuit when the power supply connected to the oscillator is turned on, but the condition $A\beta = 1$ is satisfied only for a particular frequency and the oscillator oscillates at that frequency.
Note: Oscillators are widely used in many circuits such as amplitude and frequency modulating circuits, in superheterodyne receivers, etc. These are used to produce clock signals. It has many applications as it is used in RADAR, radio transmitters, smartphones, and microwave ovens.
Complete step by step answer:
An amplifier and a feedback network with frequency-determining components are required by an oscillator. When a component of the output of an amplifier is coupled with the input of the amplifier, it is called feedback. When the feedback sample is out of phase with the Input, it is called negative feedback. When the feedback sample is in phase with the input, it is called positive feedback. For an oscillator, positive feedback is required. The block diagram of an oscillator is shown below.

The voltage gain of a complete system is given by
${A_f} = \dfrac{A}{{1 - A\beta }}$ where ${A_f}$ is the voltage gain with feedback, A is voltage gain without feedback, and $\beta $
is the feedback factor.
If for some frequency the value of $A\beta = 1$, then the system gain becomes equal to infinity and the circuit begins to oscillate at that frequency. This condition is called the Barkhausen criterion for sustained oscillations.
The frequency of oscillations depends on the RC or LC combinations which are used in a feedback network. A wide range of frequencies generates the electrical noise in the circuit when the power supply connected to the oscillator is turned on, but the condition $A\beta = 1$ is satisfied only for a particular frequency and the oscillator oscillates at that frequency.
Note: Oscillators are widely used in many circuits such as amplitude and frequency modulating circuits, in superheterodyne receivers, etc. These are used to produce clock signals. It has many applications as it is used in RADAR, radio transmitters, smartphones, and microwave ovens.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




