
Explain the electrolysis of water?
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: The electrolysis of water is the dissociation of a water molecule into oxygen and hydrogen gas due to the passage of current through it. This method is also called ‘water-splitting’.
Complete step by step answer:
Pure water is a poor conductor of electricity. So a salt-like NaCl is added. Then the current is passed. Water splits into ions. Hydrogen is liberated at the cathode while oxygen is liberated at the anode.
Electrolysis of water is the splitting of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas when an electric current is passed through the water.
An electrical power source is connected to two electrodes or two plates which are placed in the water. Hydrogen will be liberated at the cathode (the negatively charged electrode), and oxygen will be liberated at the anode (the positively charged electrode). The amount of hydrogen generated is double the amount of oxygen, and both are proportional to the total electrical charge produced by the solution.
There is a simple setup for electrolysis of water.
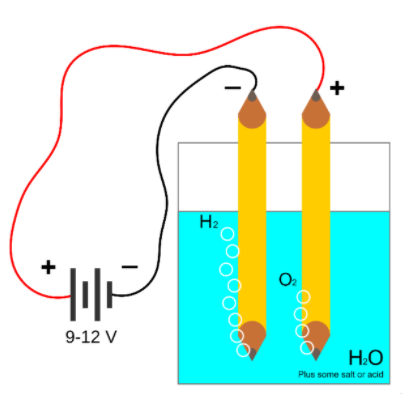
Additional information:
An electric cell is a device in which a constant potential difference is maintained between the two conductors (or terminals) either by chemical reaction or by mechanical action. Inside an electric cell, either chemical energy or mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy, which is used to maintain the constant potential difference between the terminals. When connected in a circuit, an electric cell drives charges in an external circuit, constituting the electric current. Hence, the electric cell is the source of electric current in the circuit, it is also called a Battery.
A cell essentially consists of two terminals. Terminals at higher potential are called positive terminal while another terminal at lower potential is called the negative terminal. The ability of an electric cell to drive charges in a circuit is called e.m.f. of the cell.
Electric cells are of two kinds: (1) primary cell and (2) Secondary cell.
1. Primary cell: These are the cells that provide current as a result of chemical reaction, but cannot be recharge that is, a chemical reaction is irreversible. Simple voltaic cells, Leclanche cell, Daniel cell, dry cell are the primary cells.
2. Secondary cell: These cells are the cells that can be recharged after use. Thus, as a result of a reversible reaction, the electrical energy can be stored in it. The lead accumulator, Ni-Fe, or alkali accumulator is the secondary cell.
The E.M.F of a cell is defined as the work done in carrying a unit positive charge through the complete circuit including the charge flow inside the cell. Emf (Electromotive force) depends on the nature of the electrolyte, metal of the electrodes, and temperature of the electrolyte.
Note:
This technique of water electrolysis can be used to make the hydrogen gas which is the main component to make the hydrogen fuel.
The water electrolysis technique is used to provide oxygen in space stations.
Complete step by step answer:
Pure water is a poor conductor of electricity. So a salt-like NaCl is added. Then the current is passed. Water splits into ions. Hydrogen is liberated at the cathode while oxygen is liberated at the anode.
Electrolysis of water is the splitting of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas when an electric current is passed through the water.
An electrical power source is connected to two electrodes or two plates which are placed in the water. Hydrogen will be liberated at the cathode (the negatively charged electrode), and oxygen will be liberated at the anode (the positively charged electrode). The amount of hydrogen generated is double the amount of oxygen, and both are proportional to the total electrical charge produced by the solution.
There is a simple setup for electrolysis of water.

Additional information:
An electric cell is a device in which a constant potential difference is maintained between the two conductors (or terminals) either by chemical reaction or by mechanical action. Inside an electric cell, either chemical energy or mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy, which is used to maintain the constant potential difference between the terminals. When connected in a circuit, an electric cell drives charges in an external circuit, constituting the electric current. Hence, the electric cell is the source of electric current in the circuit, it is also called a Battery.
A cell essentially consists of two terminals. Terminals at higher potential are called positive terminal while another terminal at lower potential is called the negative terminal. The ability of an electric cell to drive charges in a circuit is called e.m.f. of the cell.
Electric cells are of two kinds: (1) primary cell and (2) Secondary cell.
1. Primary cell: These are the cells that provide current as a result of chemical reaction, but cannot be recharge that is, a chemical reaction is irreversible. Simple voltaic cells, Leclanche cell, Daniel cell, dry cell are the primary cells.
2. Secondary cell: These cells are the cells that can be recharged after use. Thus, as a result of a reversible reaction, the electrical energy can be stored in it. The lead accumulator, Ni-Fe, or alkali accumulator is the secondary cell.
The E.M.F of a cell is defined as the work done in carrying a unit positive charge through the complete circuit including the charge flow inside the cell. Emf (Electromotive force) depends on the nature of the electrolyte, metal of the electrodes, and temperature of the electrolyte.
Note:
This technique of water electrolysis can be used to make the hydrogen gas which is the main component to make the hydrogen fuel.
The water electrolysis technique is used to provide oxygen in space stations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




