
Explain the conduction of nerve impulse through a nerve fiber.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The information is passing through a nerve fiber in the form of electric conduction. This is possible because the neuron membrane is present in a polarized state. A disturbance in this state begins the conduction of electrical impulses.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let us now understand how a neuron is polarized. This happens because the ion channels present on the neural membrane are more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions. This causes a difference in the concentration of both the ions outside and inside the neuron (concentration gradient). There is a net positive charge outside and a net negative charge inside the neuron. This leads to the formation of electrical potential difference across the membrane and is known as resting potential.
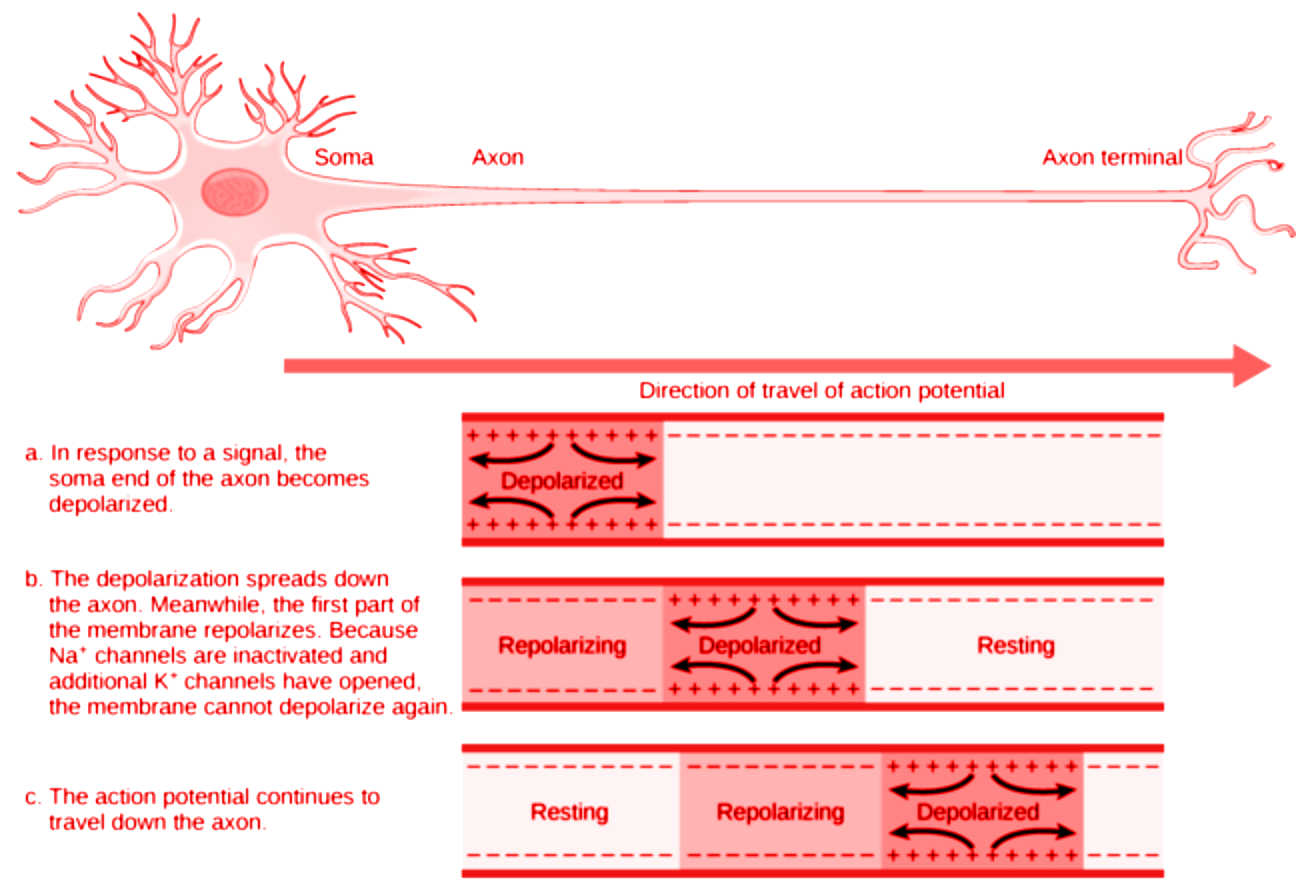
When a stimulus is applied, the polarity at that site of the axon is reversed i.e. the outer side becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged and is known as depolarization. The electrical potential difference produced at this site is known as an action potential or a nerve impulse.
Now, because the polarity of the rest of the axon did not change there is still a net positive charge on the outside and net negative charge on the inside along the rest of the axon. This causes a flow of charges from the depolarized region to the polarized region. This keeps happening along the entire length of the axon until the end is reached.
Note:
- Myelinated nerve fibers have Schwann cells around them, which form a myelin sheath around the axon. Two adjacent myelin sheaths are separated by gaps called nodes of Ranvier.
- Nerve conduction in myelinated nerves is much much faster than the eclectic impulse just from one node to another instead of traveling the entire neuron.
- Impulse conduction across two different neurons is done through the synapse.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let us now understand how a neuron is polarized. This happens because the ion channels present on the neural membrane are more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions. This causes a difference in the concentration of both the ions outside and inside the neuron (concentration gradient). There is a net positive charge outside and a net negative charge inside the neuron. This leads to the formation of electrical potential difference across the membrane and is known as resting potential.

When a stimulus is applied, the polarity at that site of the axon is reversed i.e. the outer side becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged and is known as depolarization. The electrical potential difference produced at this site is known as an action potential or a nerve impulse.
Now, because the polarity of the rest of the axon did not change there is still a net positive charge on the outside and net negative charge on the inside along the rest of the axon. This causes a flow of charges from the depolarized region to the polarized region. This keeps happening along the entire length of the axon until the end is reached.
Note:
- Myelinated nerve fibers have Schwann cells around them, which form a myelin sheath around the axon. Two adjacent myelin sheaths are separated by gaps called nodes of Ranvier.
- Nerve conduction in myelinated nerves is much much faster than the eclectic impulse just from one node to another instead of traveling the entire neuron.
- Impulse conduction across two different neurons is done through the synapse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




