
Explain the alkylation of aniline.
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: Aniline possesses nitrogen having lone pair of electrons which behaves as a nucleophile. And the reaction of aniline with haloalkanes, which is called alkylation, forms substituted anilines by the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
Aniline belongs to a class of aromatic amine in which $-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ group is directly attached to the aromatic benzene ring system. The nitrogen present in aniline and other aromatic amines is bearing a lone pair of electrons which behaves as a nucleophile and thus aniline undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Alkylation is the reaction of aniline with haloalkanes which results in the formation of substituted aromatic amine. Aniline reacts with haloalkane and produces a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary ammonium salt.
The products are formed by the substitution of hydrogen from aniline to an alkyl group. The reaction involved is shown below:
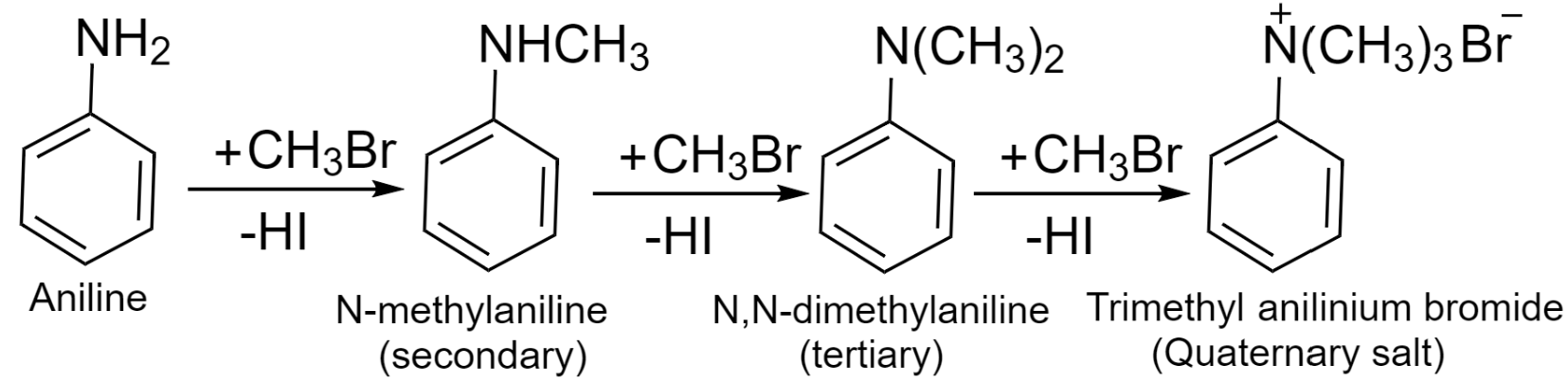
Additional information:
Due to the resonance (+R) effect of $-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ , }-\text{NHR , }-\text{N}{{\text{R}}_{2}}$ groups, the electron density at ortho and para positions of benzene ring increases, and thus aromatic amines can also undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Note:
The aromatic amines are less basic than the aliphatic amines but more basic than water. On reaction with mineral acids, these compounds form their respective salts. Also, the original amines can be regenerated from their salts by treating them with alkalis.
Complete answer:
Aniline belongs to a class of aromatic amine in which $-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ group is directly attached to the aromatic benzene ring system. The nitrogen present in aniline and other aromatic amines is bearing a lone pair of electrons which behaves as a nucleophile and thus aniline undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Alkylation is the reaction of aniline with haloalkanes which results in the formation of substituted aromatic amine. Aniline reacts with haloalkane and produces a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary ammonium salt.
The products are formed by the substitution of hydrogen from aniline to an alkyl group. The reaction involved is shown below:

Additional information:
Due to the resonance (+R) effect of $-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ , }-\text{NHR , }-\text{N}{{\text{R}}_{2}}$ groups, the electron density at ortho and para positions of benzene ring increases, and thus aromatic amines can also undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Note:
The aromatic amines are less basic than the aliphatic amines but more basic than water. On reaction with mineral acids, these compounds form their respective salts. Also, the original amines can be regenerated from their salts by treating them with alkalis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




