
Explain stereoisomerism in tartaric acid. How many optical isomers are possible for tartaric acid? What are the differences between meso tartaric acid and racemic mixture?
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: Stereoisomers are defined as the molecules having the similar bond connectivity but different molecular configuration. Stereoisomers are of two types: optical and geometrical isomers.
Complete Solution :
Compounds which have the same structure but different spatial arrangements are known as stereoisomers and this phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism.
The structure of tartaric acid is mentioned below:
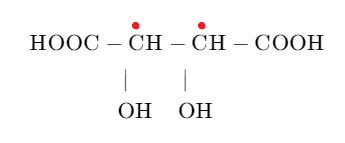
If we analyse the structure, we can see that there are two asymmetric carbon atoms so using the formulae ${{2}^{n}}$ formula where n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms, we can calculate the number of stereoisomers.
Number of stereoisomers$={{2}^{2}}=4$
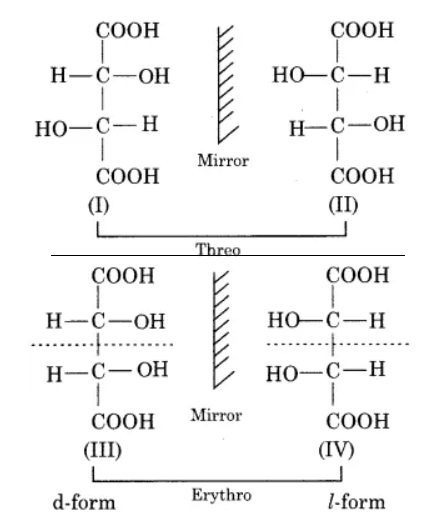
Compounds (I) and (II) are mirror images of each other and they are known as enantiomers but in the meso form. There is a place of symmetry present in tartaric acid. Tartaric acid shows three isomeric forms one of which is optically inactive and the other two are optically active i.e. d (+) and I or (-).
- Difference between meso tartaric acid and racemic mixture is mentioned below:
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Meso tartaric acid cannot be separated into two different forms whereas racemic mixture can be separated into two forms.
- To identify the geometrical isomerism we need to restrict the rotation of the carbon-carbon double bond and if there is presence of carbon-carbon double bond then we can check for the possibility of geometrical isomers.
Complete Solution :
Compounds which have the same structure but different spatial arrangements are known as stereoisomers and this phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism.
The structure of tartaric acid is mentioned below:

If we analyse the structure, we can see that there are two asymmetric carbon atoms so using the formulae ${{2}^{n}}$ formula where n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms, we can calculate the number of stereoisomers.
Number of stereoisomers$={{2}^{2}}=4$

Compounds (I) and (II) are mirror images of each other and they are known as enantiomers but in the meso form. There is a place of symmetry present in tartaric acid. Tartaric acid shows three isomeric forms one of which is optically inactive and the other two are optically active i.e. d (+) and I or (-).
- Difference between meso tartaric acid and racemic mixture is mentioned below:
| Meso tartaric acid | Racemic mixture |
| The angle of optical rotation of meso tartaric acid is 0 degree. | The optical rotation of racemic mixture is also 0 degree. |
| Melting point = 140 degree centigrade. | Melting point = 260 degree centigrade. |
| This is optically inactive due to internal compensation. | This is optically inactive due to external compensation. |
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Meso tartaric acid cannot be separated into two different forms whereas racemic mixture can be separated into two forms.
- To identify the geometrical isomerism we need to restrict the rotation of the carbon-carbon double bond and if there is presence of carbon-carbon double bond then we can check for the possibility of geometrical isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




