
Explain refraction of light and lateral shift using a rectangular glass slab with figure.
Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint: Learn the definition of refraction then learn what happens when the light travels from denser to rarer medium or rarer to denser medium. Learn how to draw perpendicular and parallel lines.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction of light and lateral shift using a rectangular glass slab,
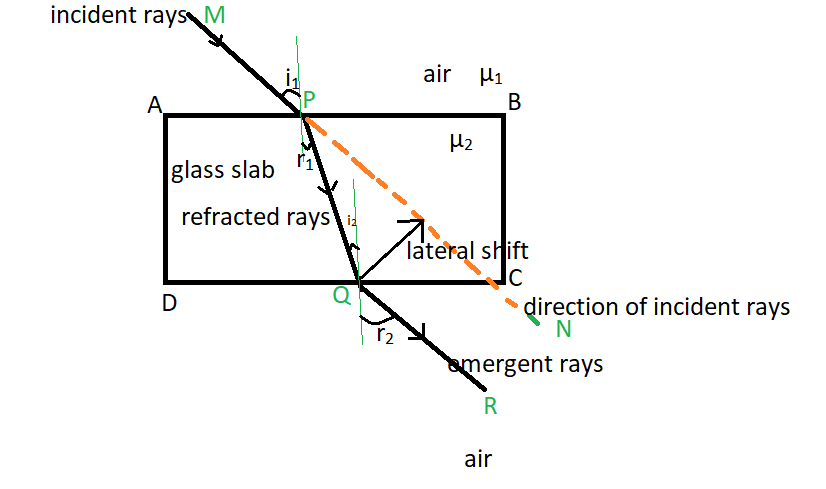
In case of rectangular slab, light first travels from air to glass and then back from glass to air. So there are two refractions. First, the ray of light travels from air to glass. Hence, it travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. So the first refracted ray bends towards normal.
After first refraction, the ray of light travels from glass to air. Hence it travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. So the second refracted ray also called emergent ray bends away from normal.
Now, for getting lateral shift, we extend the original incidence ray and bring it towards emergent ray. Here, we can observe that the original ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. The angle made by the emergent ray with the normal is called the angle of emergence. And the perpendicular distance between the original incidence ray and emergent ray is called lateral shift.
Note: Refraction – when a light ray is incident on a surface separating two transparent media, the ray bends at the time of changing the medium. The angle of incidence i and the angle of refraction r follow Snell’s law
\[\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}}\]
Where $v_1$ and $v_2$ are speeds of light in media 1 and 2 respectively and $µ_1$, $µ_2$ are refractive indices of media 1 and 2 respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction of light and lateral shift using a rectangular glass slab,

In case of rectangular slab, light first travels from air to glass and then back from glass to air. So there are two refractions. First, the ray of light travels from air to glass. Hence, it travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. So the first refracted ray bends towards normal.
After first refraction, the ray of light travels from glass to air. Hence it travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. So the second refracted ray also called emergent ray bends away from normal.
Now, for getting lateral shift, we extend the original incidence ray and bring it towards emergent ray. Here, we can observe that the original ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. The angle made by the emergent ray with the normal is called the angle of emergence. And the perpendicular distance between the original incidence ray and emergent ray is called lateral shift.
Note: Refraction – when a light ray is incident on a surface separating two transparent media, the ray bends at the time of changing the medium. The angle of incidence i and the angle of refraction r follow Snell’s law
\[\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}}\]
Where $v_1$ and $v_2$ are speeds of light in media 1 and 2 respectively and $µ_1$, $µ_2$ are refractive indices of media 1 and 2 respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




