
Explain magnetic separation process of ores with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Magnetic separation is the technique useful for few minerals such as ferromagnetic and paramagnetic. Ferromagnetic substances are the substances strongly affected by magnetic fields. Paramagnetic substances are the substances less affected by magnetic fields.
Complete step by step answer:
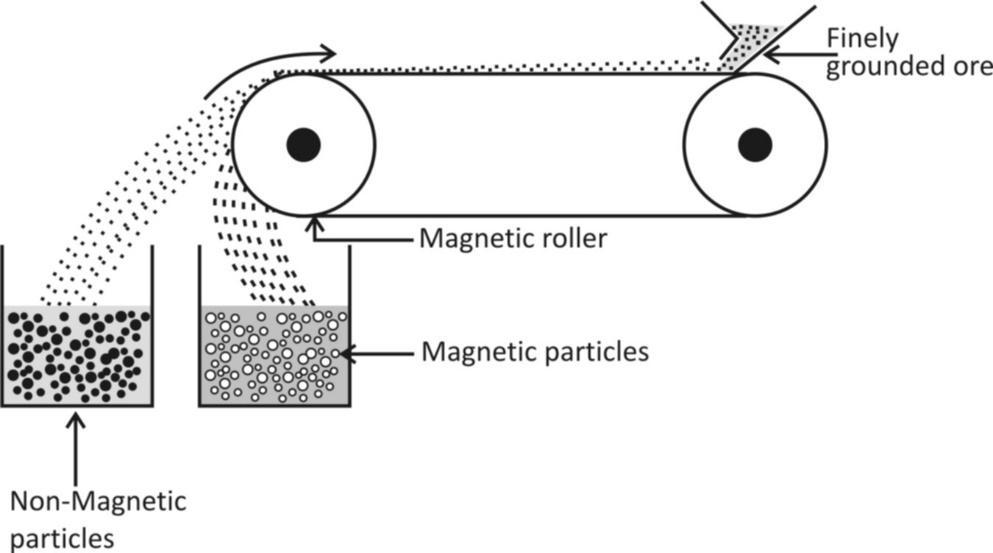
Construction –
An electromagnetic separator requires a leather or brass belt that moves over two rollers one of the roller encloses magnet in it.
Working –
(1) Slowly drop finely grounded particles on the moving belt at one end.
(2) Start rolling the moving belt with the help of two rollers.
(3) The non – magnetic particles of the ore are not attracted by the magnet and flats to do a separate heap at a distance.
(4) The magnetic particles of the ore clings to the belt for a longer distance and forms another heap near the magnet.
Conclusion – the magnetic particles and non – magnetic particles can be finely separated with the help of magnetic property i.e. magnetic attraction.
Example – Non – magnetic tin oxide (SnO) can be separated from magnetic $FeW{O_4}$ present in the ore cassiterite by magnetic separation process.
Note:
The magnetic separation ore is used in scrap yards. Magnetic operation was developed in $1970$with new technologies these new technologies of magnetic separation included magnetic pulleys, overhead magnets and magnetic drums. These technologies are used in the recycling industry.
This technique is also used in industries to remove metal contaminants from product streams. Magnetic separation is also used in dairy, grain and milling, plastics, food, chemical, oils, textile and many more industries, magnetic separation is also used in situations where pollution needs to be controlled in chemical processing as well as the benefaction of non – ferrous low grade ores.
Complete step by step answer:

Construction –
An electromagnetic separator requires a leather or brass belt that moves over two rollers one of the roller encloses magnet in it.
Working –
(1) Slowly drop finely grounded particles on the moving belt at one end.
(2) Start rolling the moving belt with the help of two rollers.
(3) The non – magnetic particles of the ore are not attracted by the magnet and flats to do a separate heap at a distance.
(4) The magnetic particles of the ore clings to the belt for a longer distance and forms another heap near the magnet.
Conclusion – the magnetic particles and non – magnetic particles can be finely separated with the help of magnetic property i.e. magnetic attraction.
Example – Non – magnetic tin oxide (SnO) can be separated from magnetic $FeW{O_4}$ present in the ore cassiterite by magnetic separation process.
Note:
The magnetic separation ore is used in scrap yards. Magnetic operation was developed in $1970$with new technologies these new technologies of magnetic separation included magnetic pulleys, overhead magnets and magnetic drums. These technologies are used in the recycling industry.
This technique is also used in industries to remove metal contaminants from product streams. Magnetic separation is also used in dairy, grain and milling, plastics, food, chemical, oils, textile and many more industries, magnetic separation is also used in situations where pollution needs to be controlled in chemical processing as well as the benefaction of non – ferrous low grade ores.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




