
Explain Liebermann's nitroso reaction with at least one example.
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Liebermann's nitroso reaction can be used as a test to distinguish secondary ($2{}^\circ $) aliphatic or aromatic amines containing a nitroso group. Liebermann's reagent is composed of 10 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) and 1 g of potassium nitrate ($KN{{O}_{2}}$).
Complete answer:
The reaction between a phenol and concentrated sulfuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) along with sodium nitrate ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$) given a product that has a deep blue or green color.
When this product obtained is diluted with water, it further turns into a red-colored solution.
This red-colored solution can be restored to its original deep blue or green color in the presence of alkaline sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or alkaline potassium hydroxide (KOH).
This process is known as Liebermann's nitroso reactions.
For example,
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow[excess\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O]{NaN{{O}_{2}}}\operatorname{Re}d\xrightarrow[excess]{NaOH}Blue\]
Its mechanism is as follows
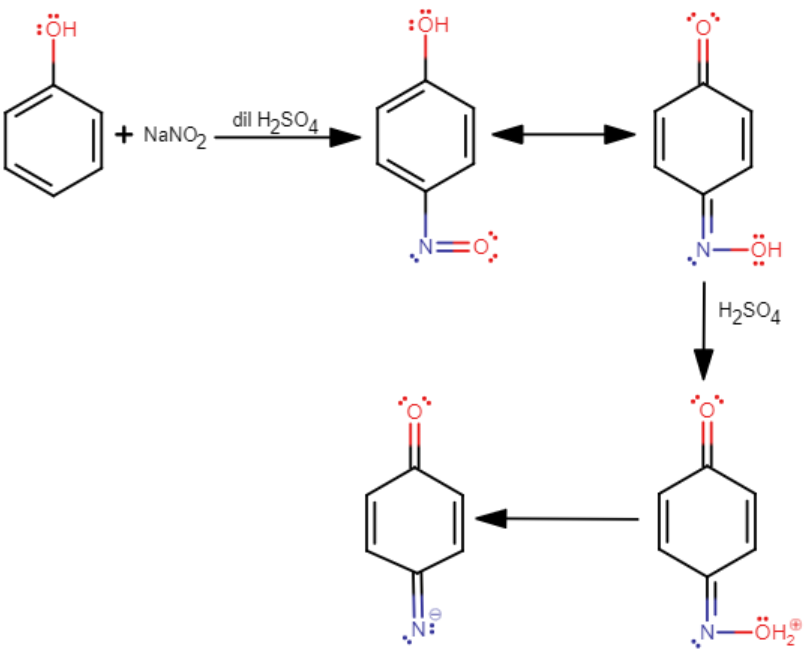
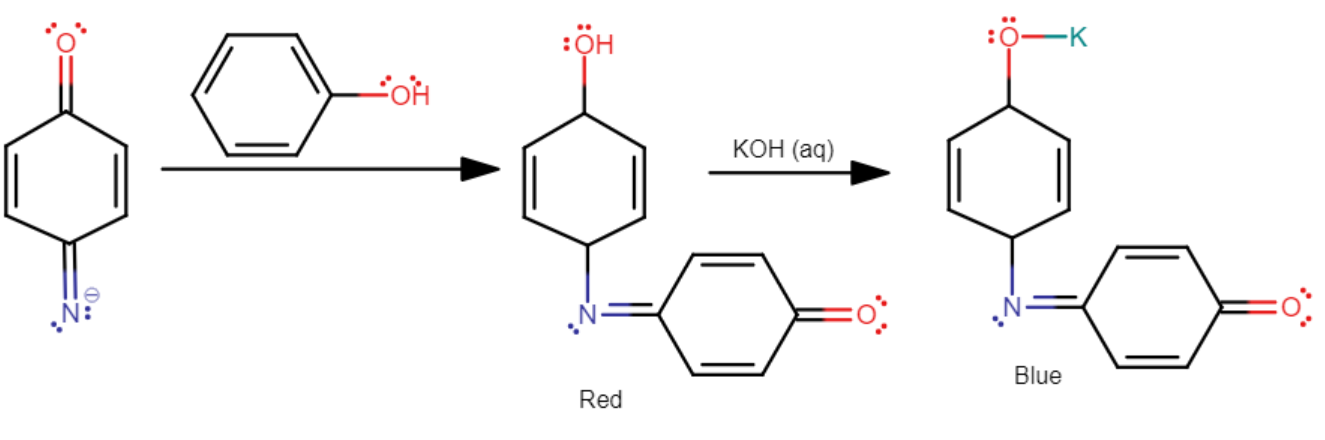
It should be noted that Liebermann's nitroso reaction is a test that is given only by secondary ($2{}^\circ $) aliphatic or aromatic amines. Upon treatment with nitric acid ($HN{{O}_{3}}$), the secondary ($2{}^\circ $) aliphatic or aromatic amine is converted into a nitroso amine. This nitroso amine, upon warming with phenol and concentrated sulfuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) forms a red or brown color which first changes to blue, and then to green.
Upon dilution, the color changes to red, and upon further treatment with alkali, the color changes to violet or greenish-blue.
Note:
It should be noted that the test is performed by adding a drop of colorless and clear reagent to a small amount of substance that is scraped off. The analysis of the color of the resulting mixture obtained and the time taken for it to become apparent can help us determine the result.
Complete answer:
The reaction between a phenol and concentrated sulfuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) along with sodium nitrate ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$) given a product that has a deep blue or green color.
When this product obtained is diluted with water, it further turns into a red-colored solution.
This red-colored solution can be restored to its original deep blue or green color in the presence of alkaline sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or alkaline potassium hydroxide (KOH).
This process is known as Liebermann's nitroso reactions.
For example,
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow[excess\text{ }{{H}_{2}}O]{NaN{{O}_{2}}}\operatorname{Re}d\xrightarrow[excess]{NaOH}Blue\]
Its mechanism is as follows


It should be noted that Liebermann's nitroso reaction is a test that is given only by secondary ($2{}^\circ $) aliphatic or aromatic amines. Upon treatment with nitric acid ($HN{{O}_{3}}$), the secondary ($2{}^\circ $) aliphatic or aromatic amine is converted into a nitroso amine. This nitroso amine, upon warming with phenol and concentrated sulfuric acid (${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) forms a red or brown color which first changes to blue, and then to green.
Upon dilution, the color changes to red, and upon further treatment with alkali, the color changes to violet or greenish-blue.
Note:
It should be noted that the test is performed by adding a drop of colorless and clear reagent to a small amount of substance that is scraped off. The analysis of the color of the resulting mixture obtained and the time taken for it to become apparent can help us determine the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




