
Explain hybridization of central atoms in NH3.
Answer
610.8k+ views
- Hint: $N{H_3}$ is known as Ammonia. It has Nitrogen as the central atom with three Hydrogens around it attached with a sigma bond and a lone pair on Nitrogen.
Complete step by step answer:
The central atom in Ammonia, i.e. Nitrogen is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. It is a gas at normal conditions and is known as Azane. The molecular weight of Ammonia is 17 g/mol. It is a colourless alkaline gas.
Starting with the Lewis dot structure of Ammonia, Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and each hydrogen has 1 valence electron. So, the total valence electrons are 8. Hydrogen always goes on the outside, so Nitrogen is the central atom. After the three valence electrons of Nitrogen have bonded with three Hydrogens, we still have two valence electrons left, which make up one lone pair of Nitrogen.
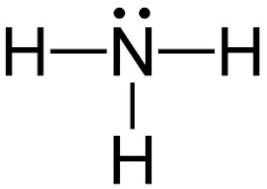
To understand the hybridization of Nitrogen in ammonia, we need to look into the configuration of nitrogen. Nitrogen in its ground state has configuration $1{s^2}2{s^2}2p{}^3$
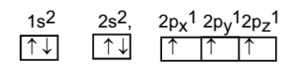
During hybridization, one s orbital and 3 p orbitals of nitrogen hybridize to form four hybrid orbitals having equal energy levels, thus making its hybridization $s{p^3}$. Half three filled $s{p^3}$ orbitals of nitrogen form a bond with three hydrogens. The fourth fully filled hybridized orbital holds the lone pair of nitrogen.
Ammonia has pyramidal or distorted tetrahedral structure due to the repulsive lone pair – bond pair interaction. Also, the bond angle in ammonia is less than standard $109^\circ 73'$ due to the same reason. The bond angle is $107^\circ$.
Note: A student might not consider the lone pair of nitrogen in the hybridization of the central atom of Ammonia. The answer in that case would come out to be $s{p^2}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The central atom in Ammonia, i.e. Nitrogen is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. It is a gas at normal conditions and is known as Azane. The molecular weight of Ammonia is 17 g/mol. It is a colourless alkaline gas.
Starting with the Lewis dot structure of Ammonia, Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and each hydrogen has 1 valence electron. So, the total valence electrons are 8. Hydrogen always goes on the outside, so Nitrogen is the central atom. After the three valence electrons of Nitrogen have bonded with three Hydrogens, we still have two valence electrons left, which make up one lone pair of Nitrogen.

To understand the hybridization of Nitrogen in ammonia, we need to look into the configuration of nitrogen. Nitrogen in its ground state has configuration $1{s^2}2{s^2}2p{}^3$

During hybridization, one s orbital and 3 p orbitals of nitrogen hybridize to form four hybrid orbitals having equal energy levels, thus making its hybridization $s{p^3}$. Half three filled $s{p^3}$ orbitals of nitrogen form a bond with three hydrogens. The fourth fully filled hybridized orbital holds the lone pair of nitrogen.
Ammonia has pyramidal or distorted tetrahedral structure due to the repulsive lone pair – bond pair interaction. Also, the bond angle in ammonia is less than standard $109^\circ 73'$ due to the same reason. The bond angle is $107^\circ$.
Note: A student might not consider the lone pair of nitrogen in the hybridization of the central atom of Ammonia. The answer in that case would come out to be $s{p^2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




