
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Ursa Major is a constellation in the northern sky consisting of a large number of stars. It is mainly known for seven of its main stars. These stars form a ladle like structure. The two stars Dubhe and Merak among the seven stars can be used to navigate the Pole star.
Complete answer:
First, locate and observe the Ursa Major constellation. There you can find the following seven stars: Dubhe, Merak, Phecda, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar and Alkaid. All these stars appear to form a spoon/ladle like shape as shown in the figure.
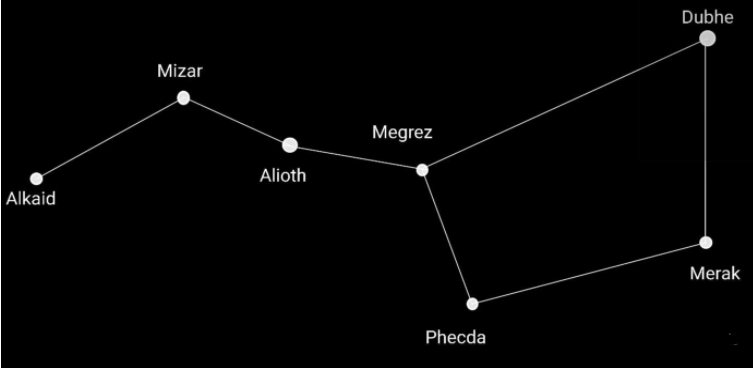
The first three are on the handle of the imaginary ladle, and the rest four are on the bowl of the imaginary ladle. Consider the last two stars on the right side of the quadrilateral, Dubhe and Merak. Imagine a line passing through these two stars. Extend this line in the upward direction, that is from Merak to Dubhe. A star will coincide with this extended imaginary line, it will be a faint star. This star will be your Pole Star.
Therefore, the Pole Star can be located with the help of Ursa Major by extending the line joining the two stars Dubhe and Merak.
Additional Information:
The Ursa Major is also known as the Great Bear. The stars Dubhe and Merak are the pointer stars as we have seen that the position of the Pole Star can be determined using them. The Pole Star is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Minor. Ursa Minor is a constellation. It is similar to the Ursa Major constellation.
Note:
Keep in mind the main seven stars of the Ursa major which are mentioned above as well as in the diagram. While looking for the last two stars, remember to look for the quadrilateral having the stars Megrez, Phecda, Merak and Dubhe, and not the stars on the handle. The imaginary line before extending it should only have two stars, Dubhe and Merak.
Complete answer:
First, locate and observe the Ursa Major constellation. There you can find the following seven stars: Dubhe, Merak, Phecda, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar and Alkaid. All these stars appear to form a spoon/ladle like shape as shown in the figure.

The first three are on the handle of the imaginary ladle, and the rest four are on the bowl of the imaginary ladle. Consider the last two stars on the right side of the quadrilateral, Dubhe and Merak. Imagine a line passing through these two stars. Extend this line in the upward direction, that is from Merak to Dubhe. A star will coincide with this extended imaginary line, it will be a faint star. This star will be your Pole Star.
Therefore, the Pole Star can be located with the help of Ursa Major by extending the line joining the two stars Dubhe and Merak.
Additional Information:
The Ursa Major is also known as the Great Bear. The stars Dubhe and Merak are the pointer stars as we have seen that the position of the Pole Star can be determined using them. The Pole Star is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Minor. Ursa Minor is a constellation. It is similar to the Ursa Major constellation.
Note:
Keep in mind the main seven stars of the Ursa major which are mentioned above as well as in the diagram. While looking for the last two stars, remember to look for the quadrilateral having the stars Megrez, Phecda, Merak and Dubhe, and not the stars on the handle. The imaginary line before extending it should only have two stars, Dubhe and Merak.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




