
Explain how to graph sinusoidal functions.
Answer
549k+ views
Hint: A sinusoidal function is a function which consists of a smooth and repetitive oscillation. It comes from “sine”, as the sine function is also a smooth and repetitive oscillation. There are many everyday things which can be represented by this function. For example, a vibrating guitar string, a bouncing spring, swinging pendulum etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To graph sinusoidal functions there is a standard form i.e,
\[y = A\sin \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{B}(x - C) + D} \right)\]
Where, A, B, C, D are constants and if these constants are specified then we can draw an accurate graph easily.
From the equation$y = D$, draw a horizontal line, this line divides the graph\[y = A\sin \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{B}(x - C) + D} \right)\] symmetrically.
From the equation, $y = D + A$, draw a horizontal line and on this line the maximum value will lie and from the equation $y = D - A$, draw a horizontal line and on this line the minimum value will lie.
The distance between the two successive maxima and the two successive minima is termed as the period B. Therefore, the distance between the maxima and the minima is $\dfrac{1}{2}B$.
Now, plot the point $(C,D)$and now there are three places in the graph which crosses the mean line i.e, $\left( {C,D} \right),\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right),\left( {C + B,D} \right)$.
Between the point $\left( {C,D} \right)$and$\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right)$, there is a maxima at point $\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{4}B,D + A} \right)$. Similarly, there is a minima i.e. $\left( {C + \dfrac{3}{4}B,D - A} \right)$, between the point $\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right)$ and$\left( {C + B,D} \right)$. The sinusoidal graph is indicated as,
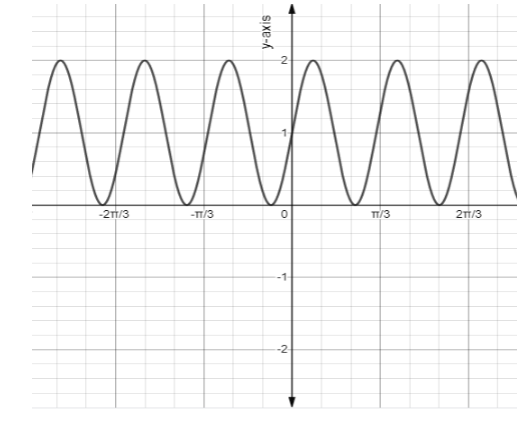
Note: On the domain$C \leqslant x \leqslant C + B$, we can graph sinusoidal functions by connecting the points that are described. Once we know, the part of a graph, it shows that the function is periodic and the pattern repeats at intervals i.e, $C + B \leqslant x \leqslant C + 2B,C - B \leqslant x \leqslant C,$etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To graph sinusoidal functions there is a standard form i.e,
\[y = A\sin \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{B}(x - C) + D} \right)\]
Where, A, B, C, D are constants and if these constants are specified then we can draw an accurate graph easily.
From the equation$y = D$, draw a horizontal line, this line divides the graph\[y = A\sin \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{B}(x - C) + D} \right)\] symmetrically.
From the equation, $y = D + A$, draw a horizontal line and on this line the maximum value will lie and from the equation $y = D - A$, draw a horizontal line and on this line the minimum value will lie.
The distance between the two successive maxima and the two successive minima is termed as the period B. Therefore, the distance between the maxima and the minima is $\dfrac{1}{2}B$.
Now, plot the point $(C,D)$and now there are three places in the graph which crosses the mean line i.e, $\left( {C,D} \right),\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right),\left( {C + B,D} \right)$.
Between the point $\left( {C,D} \right)$and$\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right)$, there is a maxima at point $\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{4}B,D + A} \right)$. Similarly, there is a minima i.e. $\left( {C + \dfrac{3}{4}B,D - A} \right)$, between the point $\left( {C + \dfrac{1}{2}B,D} \right)$ and$\left( {C + B,D} \right)$. The sinusoidal graph is indicated as,

Note: On the domain$C \leqslant x \leqslant C + B$, we can graph sinusoidal functions by connecting the points that are described. Once we know, the part of a graph, it shows that the function is periodic and the pattern repeats at intervals i.e, $C + B \leqslant x \leqslant C + 2B,C - B \leqslant x \leqslant C,$etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




