
Explain Gattermann Reaction.
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint : Gattermann reaction is used in the synthesis of aromatic compounds. Aromatic aldehyde and aromatic halide can be obtained from this reaction. It is also known as Gattermann formylation or Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis. This reaction is named after German Chemist Ludwig Gattermann. This reaction is similar to the Friedel Craft reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Examples of Gattermann Reaction-
$1.$ Chlorobenzene or bromobenzene can be obtained from benzene diazonium chloride by treating it with $Cu/HCl$ or $Br/HCl$ respectively. The yield of the product is approximately $40\% $. The reaction of formation of chlorobenzene and bromobenzene is given below;
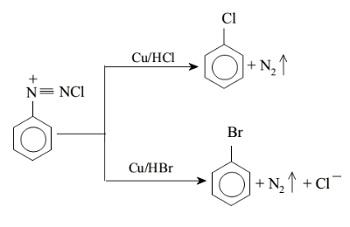
The yield in the Sandmeyer reaction is better than the Gattermann reaction. This reaction is a variation of the Sandmeyer reaction where copper chloride is replaced with copper powder. Thus the replacement leads to formation of aryl halide very easily. The yield is reduced under mild conditions in the Sandmeyer reaction.
$2.$ Hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of a catalyst such as $AlC{l_3}$ gives an aromatic compound. This reaction is a substitution type reaction. The reaction is given below;
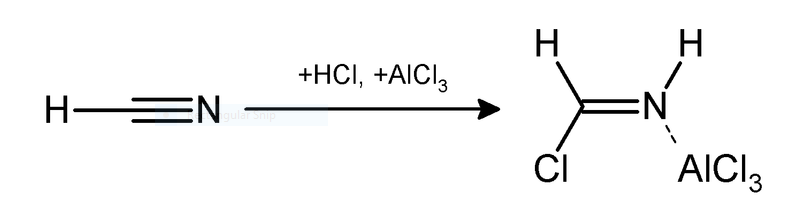
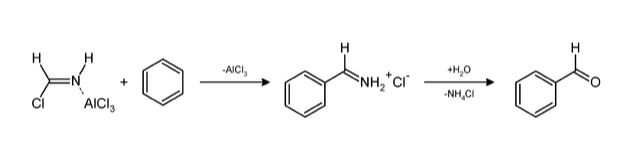
Applications of Gattermann Reaction- It is used in the formation of chlorobenzene and bromobenzene. Products of this reaction are used in pharmaceuticals, agriculture and medicine such as benzaldehydes and haloarenes etc. It is useful in formation of benzaldehydes and aromatic halides.
Note : Hence we have learned about the Gattermann reaction and its applications. It is a kind of substitution reaction where electrophile attacks on benzene ring and by substituting components product is formed. This is a very famous reaction which is always used in the synthesis or preparation of aromatic halides.
Complete step by step solution:
Examples of Gattermann Reaction-
$1.$ Chlorobenzene or bromobenzene can be obtained from benzene diazonium chloride by treating it with $Cu/HCl$ or $Br/HCl$ respectively. The yield of the product is approximately $40\% $. The reaction of formation of chlorobenzene and bromobenzene is given below;

The yield in the Sandmeyer reaction is better than the Gattermann reaction. This reaction is a variation of the Sandmeyer reaction where copper chloride is replaced with copper powder. Thus the replacement leads to formation of aryl halide very easily. The yield is reduced under mild conditions in the Sandmeyer reaction.
$2.$ Hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of a catalyst such as $AlC{l_3}$ gives an aromatic compound. This reaction is a substitution type reaction. The reaction is given below;


Applications of Gattermann Reaction- It is used in the formation of chlorobenzene and bromobenzene. Products of this reaction are used in pharmaceuticals, agriculture and medicine such as benzaldehydes and haloarenes etc. It is useful in formation of benzaldehydes and aromatic halides.
Note : Hence we have learned about the Gattermann reaction and its applications. It is a kind of substitution reaction where electrophile attacks on benzene ring and by substituting components product is formed. This is a very famous reaction which is always used in the synthesis or preparation of aromatic halides.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




