
Explain Friedel-Craft alkylation of chlorobenzene. Give an equation.
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint : An alkyl group can be added to a benzene molecule by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction called the Friedel‐Crafts alkylation reaction. One example is the addition of a methyl group to a benzene ring. The mechanism for this reaction begins with the generation of a methyl carbocation from methyl bromide.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring with the help of a carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a method of generating alkyl benzenes by using alkyl halides as reactants.
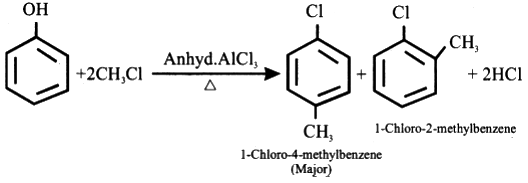
A Lewis acid catalyst such as $ FeC{l_3} $ or $ AlC{l_3} $ is employed in this reaction in order to form a carbocation by facilitating the removal of the halide. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Additional Information:
Mechanism:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction proceeds via a three-step mechanism.
Step 1
The Lewis acid catalyst ( $ AlC{l_3} $ ) undergoes a reaction with the alkyl halide, resulting in the formation of an electrophilic carbocation.
Step 2
The carbocation proceeds to attack the aromatic ring, forming a cyclohexadienyl cation as an intermediate. The aromaticity of the arene is temporarily lost due to the breakage of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Step 3
The deprotonation of the intermediate leads to the reformation of the carbon-carbon double bond, restoring aromaticity to the compound. This proton goes on to form hydrochloric acid, regenerating the $ AlC{l_3} $ catalyst.
Note :
Friedel craft alkylation will undergo that aromatic compound, which is electron-rich. As it is the electrophilic substitution reaction. But, since the carbo-cations formed by aryl and vinyl halides are extremely unstable, they cannot be used in this reaction. And also the presence of a deactivating group on the aromatic ring can lead to the deactivation of the catalyst due to the formation of complexes.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group. This is done through an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring with the help of a carbocation. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a method of generating alkyl benzenes by using alkyl halides as reactants.

A Lewis acid catalyst such as $ FeC{l_3} $ or $ AlC{l_3} $ is employed in this reaction in order to form a carbocation by facilitating the removal of the halide. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction.
Additional Information:
Mechanism:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction proceeds via a three-step mechanism.
Step 1
The Lewis acid catalyst ( $ AlC{l_3} $ ) undergoes a reaction with the alkyl halide, resulting in the formation of an electrophilic carbocation.
Step 2
The carbocation proceeds to attack the aromatic ring, forming a cyclohexadienyl cation as an intermediate. The aromaticity of the arene is temporarily lost due to the breakage of the carbon-carbon double bond.
Step 3
The deprotonation of the intermediate leads to the reformation of the carbon-carbon double bond, restoring aromaticity to the compound. This proton goes on to form hydrochloric acid, regenerating the $ AlC{l_3} $ catalyst.
Note :
Friedel craft alkylation will undergo that aromatic compound, which is electron-rich. As it is the electrophilic substitution reaction. But, since the carbo-cations formed by aryl and vinyl halides are extremely unstable, they cannot be used in this reaction. And also the presence of a deactivating group on the aromatic ring can lead to the deactivation of the catalyst due to the formation of complexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




