
Explain alternation of generation in Bryophytes.
Answer
537.8k+ views
Hint: The alternation of multicellular diploid and haploid forms in the life cycle of the organism is known as the alternation of genes. In 1851, Hofmeister first gave this process.
Complete answer:
In bryophytes, when the two generations are morphologically different, then the type of alternation of generations is known as heteromorphic.
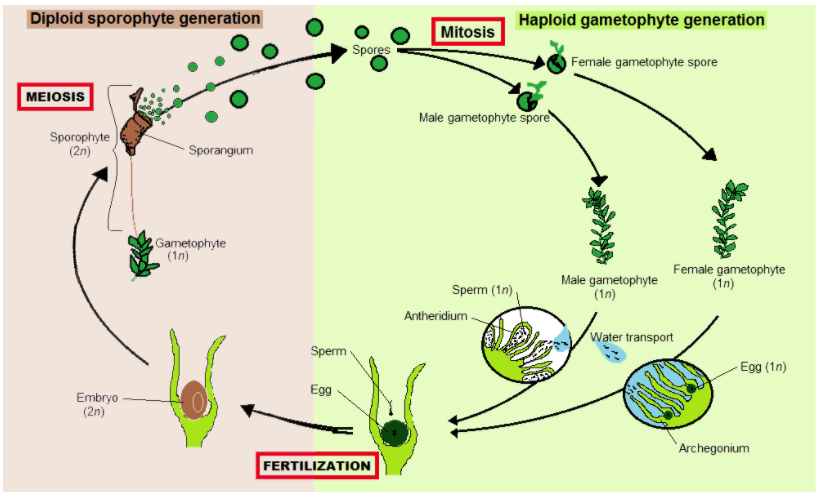
The haploid phase (n) is known as the gametophyte or sexual generation. It has the sexual reproductive organs which produce gametes, i.e., antherozoids and eggs. With the result of gametic fusion, a zygote is formed, which is the sporophyte. This is the diploid phase (2n). This sporophyte produces spores that always germinate and form gametophytes.
During the formation of spores, the spore mother cells(SMCs) divide meiotically and haploid spores are produced. The beginning of the haploid phase is marked by the production of spores. The spores then germinate and produce the gametophyte or haploid phase. The spores germinate and produce gametophytes that bear sex organs.
Ultimately the gametic fusion takes place, zygote is formed. It is diploid (2n). This is the beginning of the sporophytic or diploid phase. This way, the sporophyte generation intervenes between fertilization (syngamy) and meiosis (reduction division); and gametophyte generation intervenes between meiosis and fertilization.
The gametophytic phase is a conspicuous and longer-lived phase of the life cycle. The gametophyte generation of the bryophyte is usually perennial and photosynthetically independent of the sporophyte, which forms an intimate interconnection with the gametophytic tissue, especially at the base, or foot, of the sporophyte.
Note: Bryophyte, a nonvascular seedless plant, which includes three divisions, namely, mosses (division Bryophyta), hornworts (division Anthocerotophyta), and liverworts (division Marchantiophyta). ‘Metagenesis’ or ‘heterogenesis’, are the types of alternation of generation. The two phases, or generations, are often morphologically and chromosomally distinct.
Complete answer:
In bryophytes, when the two generations are morphologically different, then the type of alternation of generations is known as heteromorphic.

The haploid phase (n) is known as the gametophyte or sexual generation. It has the sexual reproductive organs which produce gametes, i.e., antherozoids and eggs. With the result of gametic fusion, a zygote is formed, which is the sporophyte. This is the diploid phase (2n). This sporophyte produces spores that always germinate and form gametophytes.
During the formation of spores, the spore mother cells(SMCs) divide meiotically and haploid spores are produced. The beginning of the haploid phase is marked by the production of spores. The spores then germinate and produce the gametophyte or haploid phase. The spores germinate and produce gametophytes that bear sex organs.
Ultimately the gametic fusion takes place, zygote is formed. It is diploid (2n). This is the beginning of the sporophytic or diploid phase. This way, the sporophyte generation intervenes between fertilization (syngamy) and meiosis (reduction division); and gametophyte generation intervenes between meiosis and fertilization.
The gametophytic phase is a conspicuous and longer-lived phase of the life cycle. The gametophyte generation of the bryophyte is usually perennial and photosynthetically independent of the sporophyte, which forms an intimate interconnection with the gametophytic tissue, especially at the base, or foot, of the sporophyte.
Note: Bryophyte, a nonvascular seedless plant, which includes three divisions, namely, mosses (division Bryophyta), hornworts (division Anthocerotophyta), and liverworts (division Marchantiophyta). ‘Metagenesis’ or ‘heterogenesis’, are the types of alternation of generation. The two phases, or generations, are often morphologically and chromosomally distinct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




