
Example of a typical homopolysaccharide is
(a) Lignin
(b) Starch
(c) Inulin
(d) Suberin
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: Homopolysaccharides are those polysaccharides that are composed of only one type of sugar monomer or monosaccharides. These monomers react with other monomers to form polymers.
Complete answer
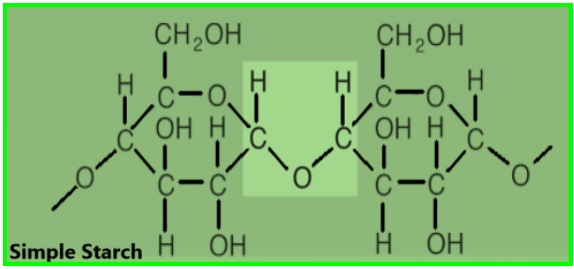
Starch, glucose, and glycogen are examples of typical homopolysaccharides. Starch is mostly produced by green plants to store energy. Since starch is that type of polysaccharides, which is made up of the only same type of sugar monomer or monosaccharides, that is why it is also called homopolysaccharides. Every unit of monosaccharides is held together by a glycosidic bond and the long-chain is linked or joined in α 1,4 linkages.
The basic molecular formula of starch is $ \left( { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 } \right) { n }$
Additional Information:
-Lignin is the class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae.
-Inulin is found during a big variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, including wheat, onions, bananas, leeks, artichokes, and asparagus.IT is a starchy substance.
-An inert impermeable waxy substance present in the cell walls of corky tissues is called suberin.
So, the correct answer is,’ starch’.
Note:
1. Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules are made up of large numbers of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. It is a white solid at room temperature and does not dissolve in cold water.
2. A chemical bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to a different group, which can or might not be another carbohydrate is named as glycosidic bond.
3. Starch can also be used to make products such as glue, paste, and new types of bio-batteries.
4. Food that contains starch in them is a good source of energy and the main origin of a variety of nutrients in our diet. e.g, potato, rice, corn, etc are rich sources of starch.
Complete answer
Starch, glucose, and glycogen are examples of typical homopolysaccharides. Starch is mostly produced by green plants to store energy. Since starch is that type of polysaccharides, which is made up of the only same type of sugar monomer or monosaccharides, that is why it is also called homopolysaccharides. Every unit of monosaccharides is held together by a glycosidic bond and the long-chain is linked or joined in α 1,4 linkages.
The basic molecular formula of starch is $ \left( { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 } \right) { n }$

Additional Information:
-Lignin is the class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae.
-Inulin is found during a big variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, including wheat, onions, bananas, leeks, artichokes, and asparagus.IT is a starchy substance.
-An inert impermeable waxy substance present in the cell walls of corky tissues is called suberin.
So, the correct answer is,’ starch’.
Note:
1. Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules are made up of large numbers of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. It is a white solid at room temperature and does not dissolve in cold water.
2. A chemical bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to a different group, which can or might not be another carbohydrate is named as glycosidic bond.
3. Starch can also be used to make products such as glue, paste, and new types of bio-batteries.
4. Food that contains starch in them is a good source of energy and the main origin of a variety of nutrients in our diet. e.g, potato, rice, corn, etc are rich sources of starch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




