
How do you evaluate the equation $arc\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$?
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: We explain the function $arc\tan \left( x \right)$. We express the inverse function of tan in the form of $arc\tan \left( x \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}x$. We draw the graph of $arc\tan \left( x \right)$ and the line $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to find the intersection point as the solution.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given expression is the inverse function of the trigonometric ratio tan.
The arcus function represents the angle which on ratio tan gives the value.
So, $arc\tan \left( x \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}x$. If $arc\tan \left( x \right)=\alpha $ then we can say $\tan \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\tan \alpha =x$ will be $n\pi +\alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $arc\tan \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio tan we have $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}\le arc\tan \left( x \right)\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
The graph of the function is
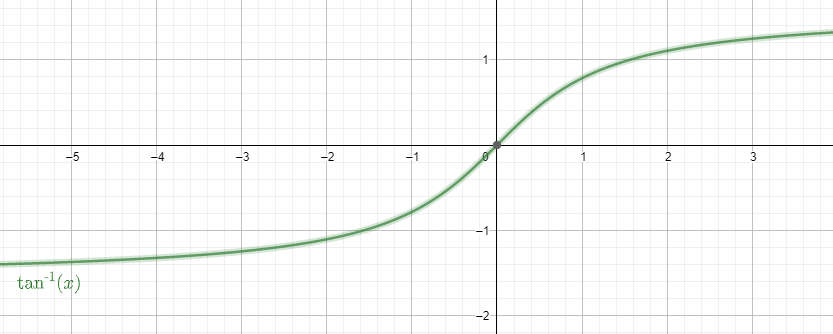
$arc\tan \left( x \right)=\alpha $ gives the angle $\alpha $ behind the ratio.
We now place the value of $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ in the function of $arc\tan \left( x \right)$.
Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $arc\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\theta $. This gives $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. The value of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ is close to 1.57. Putting the value in the graph of $arc\tan \left( x \right)$, we get $\theta =1.003$.
For this we take the line of $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $arc\tan \left( x \right)$.
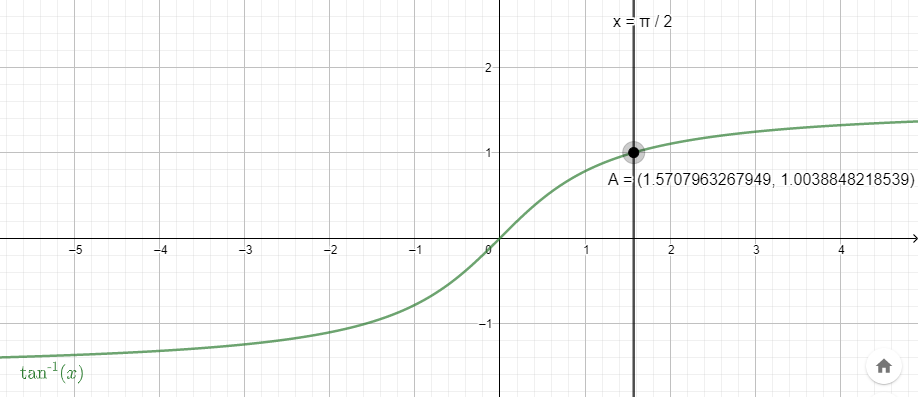
We get the value of y coordinates as 1.003.
Therefore, the value of $arc\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is 1.003.
Note: First note that the value $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ looks suspiciously like it was intended to be an angle but the argument of the $arc\tan \left( x \right)$ function is not an angle. The representation will be the right-angle triangle with base 2 and height $\pi $ and the angle being $\theta $.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given expression is the inverse function of the trigonometric ratio tan.
The arcus function represents the angle which on ratio tan gives the value.
So, $arc\tan \left( x \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}x$. If $arc\tan \left( x \right)=\alpha $ then we can say $\tan \alpha =x$.
Each of the trigonometric functions is periodic in the real part of its argument, running through all its values twice in each interval of $2\pi $.
The general solution for that value where $\tan \alpha =x$ will be $n\pi +\alpha ,n\in \mathbb{Z}$.
But for $arc\tan \left( x \right)$, we won’t find the general solution. We use the principal value. For ratio tan we have $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}\le arc\tan \left( x \right)\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
The graph of the function is

$arc\tan \left( x \right)=\alpha $ gives the angle $\alpha $ behind the ratio.
We now place the value of $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ in the function of $arc\tan \left( x \right)$.
Let the angle be $\theta $ for which $arc\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\theta $. This gives $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. The value of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ is close to 1.57. Putting the value in the graph of $arc\tan \left( x \right)$, we get $\theta =1.003$.
For this we take the line of $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and see the intersection of the line with the graph $arc\tan \left( x \right)$.

We get the value of y coordinates as 1.003.
Therefore, the value of $arc\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is 1.003.
Note: First note that the value $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ looks suspiciously like it was intended to be an angle but the argument of the $arc\tan \left( x \right)$ function is not an angle. The representation will be the right-angle triangle with base 2 and height $\pi $ and the angle being $\theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




