
Why is ether used as a solvent during Grignard reactions?
Answer
498k+ views
Hint: Let us first understand what a Grignard reagent is. Grignard reagent is Alkyl magnesium halide. It is a popular example of an organometallic reagent. It is named after Victor Grignard and he got the nobel prize in 1912. The Grignard reagent has a general formula of $ RMgX $ where $ R $ is an alkyl or aryl group and $ X $ is halogen. $ C{H_3}MgBr $ is a common example of the Grignard reagent. The Grignard reagent has several important applications in the synthesis of several important organic compounds.
Complete answer:
The polarity of the Grignard reagent is represented as follows-
$ \mathop R\limits^{\delta - } - \mathop {Mg}\limits^{\delta + } X $
There is an electronegativity difference between the Alkyl and the Magnesium atom, the carbon atom is highly nucleophilic and thus the Grignard reagent acts as a strong nucleophile.
The formation of Grignard reagent takes place by the reaction of Haloalkanes and small bits of Magnesium in a flask. The reaction is represented as follows-
$ RX + Mg\xrightarrow{{Ether}}RMgX $
This reaction takes place in the presence of ether as a solvent. An example of such ether may be diethyl ether. The reaction is performed in extremely dry conditions since the Grignard reagent reacts with water.
Following are the reasons why ether is used-
(A)Absence of acidic proton in the ether-
Ether is an aprotic solvent (i.e. do not give any acidic proton) that does not react with the Grignard reagent. Grignard reagent is basic in nature. In the case of polar solvent like water, Grignard reagent reacts and forms alkanes as follows-
$ RMgX + {H_2}O \to RH + MgX\left( {OH} \right) $
The Halogenated solvents like chloroform and chlorobenzene can also not be used since they undergo magnesium-Halogen exchange.
Thus Grignard reagent is extremely stable in the presence of ether and ether prevents the formation of alkanes or alkenes or alkynes from the Grignard reagent.
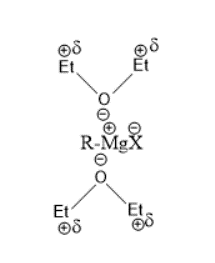
(B)Formation of stable complex that aids stability and solubility-
Ether is also used as a solvent since it reacts with Grignard reagents forming a stable complex. The Magnesium-halogen bond is ionic and solvates the carbon-oxygen bond of ether thus forming a stable complex and increases the ability of the Grignard reagent to react. Thus we see that the Grignard reagent is soluble in ether.
The complex is shown as under-
Note:
We see that we cannot use polar solvents like water and alcohol in the Grignard reaction and neither do we use halogenated solvents and so we use anhydrous ethers. However other than ether we can also THF (tetrahydrofuran) as a solvent. Benzene or any other non-polar alkane also makes the possibility for the solvent however these are not used because these are not soluble in the Grignard reagent.
Complete answer:
The polarity of the Grignard reagent is represented as follows-
$ \mathop R\limits^{\delta - } - \mathop {Mg}\limits^{\delta + } X $
There is an electronegativity difference between the Alkyl and the Magnesium atom, the carbon atom is highly nucleophilic and thus the Grignard reagent acts as a strong nucleophile.
The formation of Grignard reagent takes place by the reaction of Haloalkanes and small bits of Magnesium in a flask. The reaction is represented as follows-
$ RX + Mg\xrightarrow{{Ether}}RMgX $
This reaction takes place in the presence of ether as a solvent. An example of such ether may be diethyl ether. The reaction is performed in extremely dry conditions since the Grignard reagent reacts with water.
Following are the reasons why ether is used-
(A)Absence of acidic proton in the ether-
Ether is an aprotic solvent (i.e. do not give any acidic proton) that does not react with the Grignard reagent. Grignard reagent is basic in nature. In the case of polar solvent like water, Grignard reagent reacts and forms alkanes as follows-
$ RMgX + {H_2}O \to RH + MgX\left( {OH} \right) $
The Halogenated solvents like chloroform and chlorobenzene can also not be used since they undergo magnesium-Halogen exchange.
Thus Grignard reagent is extremely stable in the presence of ether and ether prevents the formation of alkanes or alkenes or alkynes from the Grignard reagent.
(B)Formation of stable complex that aids stability and solubility-
Ether is also used as a solvent since it reacts with Grignard reagents forming a stable complex. The Magnesium-halogen bond is ionic and solvates the carbon-oxygen bond of ether thus forming a stable complex and increases the ability of the Grignard reagent to react. Thus we see that the Grignard reagent is soluble in ether.
The complex is shown as under-

Note:
We see that we cannot use polar solvents like water and alcohol in the Grignard reaction and neither do we use halogenated solvents and so we use anhydrous ethers. However other than ether we can also THF (tetrahydrofuran) as a solvent. Benzene or any other non-polar alkane also makes the possibility for the solvent however these are not used because these are not soluble in the Grignard reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




