
How many enol structures of the 3-hexanone are possible?
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: In chemistry, carbon is a very versatile element which has a tetravalent structure which means it can attach to mostly four elements at a time, but it also shows a wide variety of bond structure ranging from the single bond, double bond, and triple bond. All these bonds take different types of strengths and exist with different electrons that are in participation.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon is a very different element. It is the element that makes the most of organic chemistry. It reacts with many types of elements and forms various products. It is the element that forms compounds with many types of bonds which give it different properties. Organic chemistry is also filled with the phenomenon which grants various properties to the element. One such effect is keto-enol tautomerism.
It is the phenomenon in which the ketonic group of a chemical compound rearranges itself and transforms into enol form. Enol is the representation of the ene means double bond and ‘ol’ represents the alcohol group. The ketone group is delocalized with the adjacent carbon atom and forms the enol structure.
When we see the structure of 3- hexanone we see that it can form into 4 enol structures.
The 4 structures occur in the pair of 2 pairs of geometrical isomers.
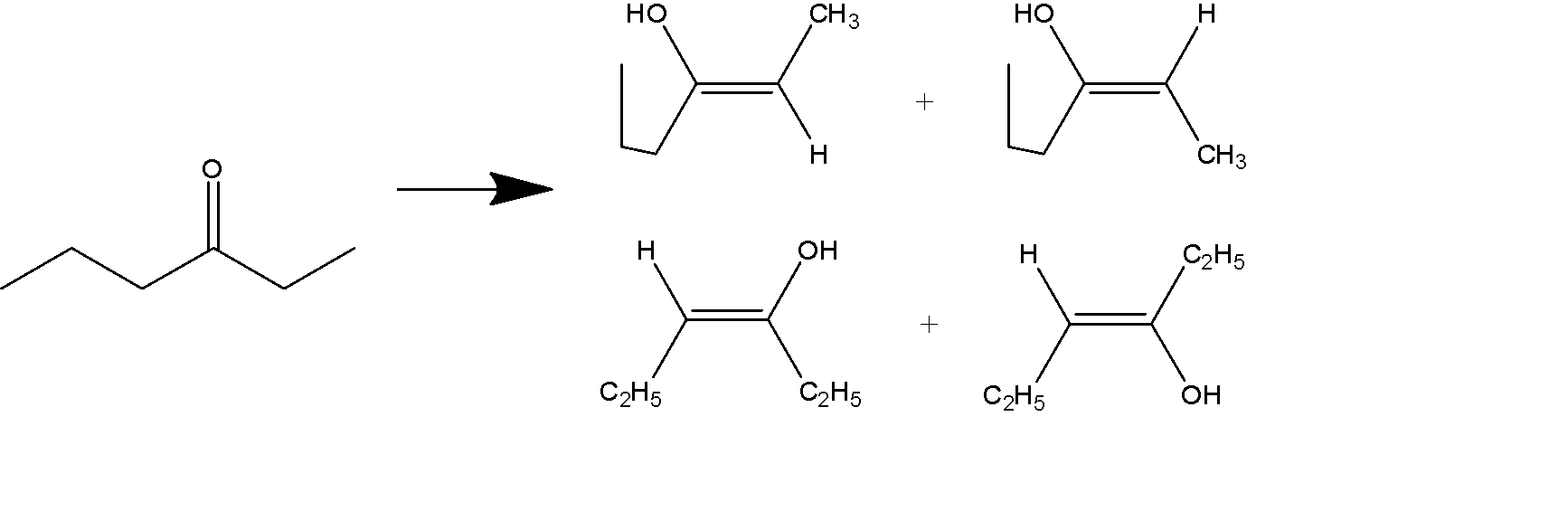
Note: This ketone tautomerism is the result of the delocalization of the carbon bonds to gain higher stability.
Apart from the ketone group, there are other functional groups too that help us categorize the vast number of organic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbon is a very different element. It is the element that makes the most of organic chemistry. It reacts with many types of elements and forms various products. It is the element that forms compounds with many types of bonds which give it different properties. Organic chemistry is also filled with the phenomenon which grants various properties to the element. One such effect is keto-enol tautomerism.
It is the phenomenon in which the ketonic group of a chemical compound rearranges itself and transforms into enol form. Enol is the representation of the ene means double bond and ‘ol’ represents the alcohol group. The ketone group is delocalized with the adjacent carbon atom and forms the enol structure.
When we see the structure of 3- hexanone we see that it can form into 4 enol structures.
The 4 structures occur in the pair of 2 pairs of geometrical isomers.

Note: This ketone tautomerism is the result of the delocalization of the carbon bonds to gain higher stability.
Apart from the ketone group, there are other functional groups too that help us categorize the vast number of organic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




