
Enlist the basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Recombinant DNA technology is the technology of producing the required organism or the host cell with the desired DNA from the two different genes. This method is used mainly to produce new varieties and combinations that are useful to the humankind.
Complete Answer:
The basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology includes
(1) The donor is taken and the genome is isolated from it. Donor is defined as the cells from which the gene is ken for the purpose of isolation.
(2) The isolated DNA is cut using the molecular scissors. Molecular scissors are the enzyme used to cut the DNA at the required sites. Commonly the restriction endonuclease is used as the molecular scissor to cleave DNA. These protein enzymes are obtained from the bacteria.
(3) The fragmented DNA is taken and the screening is done to obtain the desired gene.
(4) The cloning vector is defined as the stable DNA in an organism in which the foreign DNA is inserted for the cloning. Here plasmids, cosmid and phage DNA are mostly used as the cloning vector. The fragmented DNA is inserted into it.
(5) Placing the cloning vector along with the fragmented foreign DNA into the required host cell or organism.
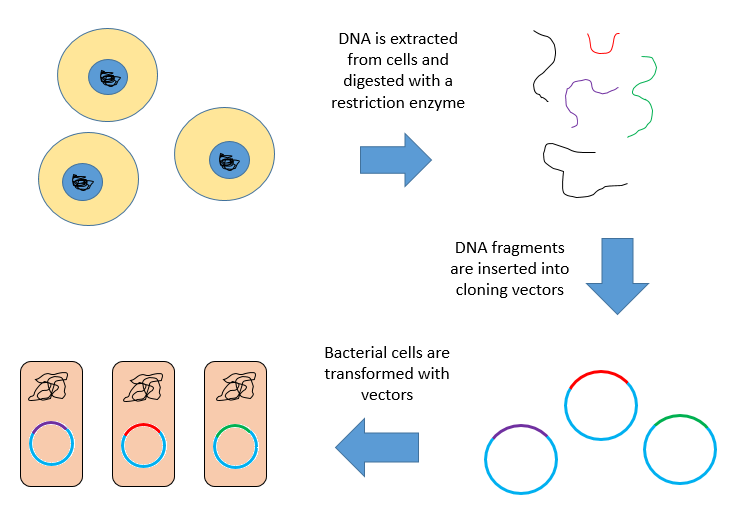
(6) The host cells grow with the new inserted DNA and they develop and cultured to produce multiple copies with the desired foreign DNA.
(7) The copies or clones obtained from this process are used to develop the suitable organisms with the desired DNA and to express the desired characters.
Note: This method is mainly used in the medical field to produce vaccines and the drugs and protein therapies like insulin etc. It is also used in the treatment of haemophilia. But it also has some disadvantages like destruction of the native varieties.
Complete Answer:
The basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology includes
(1) The donor is taken and the genome is isolated from it. Donor is defined as the cells from which the gene is ken for the purpose of isolation.
(2) The isolated DNA is cut using the molecular scissors. Molecular scissors are the enzyme used to cut the DNA at the required sites. Commonly the restriction endonuclease is used as the molecular scissor to cleave DNA. These protein enzymes are obtained from the bacteria.
(3) The fragmented DNA is taken and the screening is done to obtain the desired gene.
(4) The cloning vector is defined as the stable DNA in an organism in which the foreign DNA is inserted for the cloning. Here plasmids, cosmid and phage DNA are mostly used as the cloning vector. The fragmented DNA is inserted into it.
(5) Placing the cloning vector along with the fragmented foreign DNA into the required host cell or organism.

(6) The host cells grow with the new inserted DNA and they develop and cultured to produce multiple copies with the desired foreign DNA.
(7) The copies or clones obtained from this process are used to develop the suitable organisms with the desired DNA and to express the desired characters.
Note: This method is mainly used in the medical field to produce vaccines and the drugs and protein therapies like insulin etc. It is also used in the treatment of haemophilia. But it also has some disadvantages like destruction of the native varieties.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




