
What is emission and absorption spectra?. Explain the different types of emission and absorption spectra with examples? (Diagram not necessary )
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: When whit light is passed through the prism we get a spectrum of light. This band of light having different colors is called the continuous spectrum i.e. all the wavelengths of light in the visible region are formed. When a rarefied gas is heated it emits some radiation having only few wavelengths of the continuous spectrum .Similarly when the white light is passed through the rarefied gas it only emits radiation other than the ones when the gas was heated. This spectrum obtained is accordingly classified into emission and absorption spectra.
Complete solution:
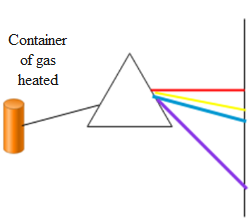
In the above diagram we can see that when the container containing a gas is heated it emits radiation of a particular wavelength in the visible spectrum. This is because the electrons in their orbits gain energy when heated. But electrons possessing energy are highly unstable. Hence they again come back to their initial orbit thereby releasing energy in the form of visible radiation. The electrons only emit particular radiation of a particular wavelength because the electrons exist only in permitted orbits. Hence when the electrons make transition from one energy state to another they do not give radiations of all the possible wavelengths corresponding to the visible spectrum. They only emit those radiations which correspond to the transitions. This spectrum of light obtained is called the emission spectrum.
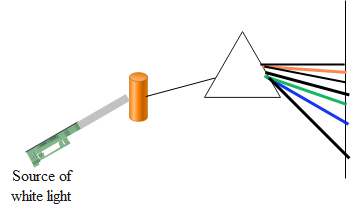
Similarly when the source of white light is put on the rarefied gas, the wavelengths of light which were emitted when the gas was heated, the gas now absorbs the energy in the form of the visible radiations. The gas absorbs only those radiations which corresponds to the possible transition due to the permitted orbits of the electrons in an atom. Since the radiations are absorbed by the gas and result in a formation of spectrum, this is termed as absorption spectrum.
The permitted energy state in an atom for an electron is given by,
${{E}_{N}}=\dfrac{-13.6{{\left( Z \right)}^{2}}}{{{N}^{2}}}$ ,where Z is the atomic number of the electrons and N is the permitted energy state for an electron in a particular atom. Since the permitted energy states of individual atoms are different, the corresponding transitions resulting in emission of radiations will be different. This will result in the formation of different discrete spectrums for different atoms.
Note:
The emission and the absorption spectra for different gasses are different. Therefore it is one of the most useful ways one can come to know a particular gas by looking at its absorption and emission spectrum. It is to be noted that the emission of the radiation when the gas is heated does not only comprise of radiations in the visible region but it also comprises radiation of wavelengths other than the visible spectrum.
Complete solution:


In the above diagram we can see that when the container containing a gas is heated it emits radiation of a particular wavelength in the visible spectrum. This is because the electrons in their orbits gain energy when heated. But electrons possessing energy are highly unstable. Hence they again come back to their initial orbit thereby releasing energy in the form of visible radiation. The electrons only emit particular radiation of a particular wavelength because the electrons exist only in permitted orbits. Hence when the electrons make transition from one energy state to another they do not give radiations of all the possible wavelengths corresponding to the visible spectrum. They only emit those radiations which correspond to the transitions. This spectrum of light obtained is called the emission spectrum.
Similarly when the source of white light is put on the rarefied gas, the wavelengths of light which were emitted when the gas was heated, the gas now absorbs the energy in the form of the visible radiations. The gas absorbs only those radiations which corresponds to the possible transition due to the permitted orbits of the electrons in an atom. Since the radiations are absorbed by the gas and result in a formation of spectrum, this is termed as absorption spectrum.
The permitted energy state in an atom for an electron is given by,
${{E}_{N}}=\dfrac{-13.6{{\left( Z \right)}^{2}}}{{{N}^{2}}}$ ,where Z is the atomic number of the electrons and N is the permitted energy state for an electron in a particular atom. Since the permitted energy states of individual atoms are different, the corresponding transitions resulting in emission of radiations will be different. This will result in the formation of different discrete spectrums for different atoms.
Note:
The emission and the absorption spectra for different gasses are different. Therefore it is one of the most useful ways one can come to know a particular gas by looking at its absorption and emission spectrum. It is to be noted that the emission of the radiation when the gas is heated does not only comprise of radiations in the visible region but it also comprises radiation of wavelengths other than the visible spectrum.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




