
What is the electron and molecular geometry for $ BeC{l_2} $ ?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint :In chemistry, the molecular geometry is referred to the arrangement of atoms in relation to a central atom in a three-dimensional space whereas electron geometry is the arrangement of electron groups and it is unaffected by the presence of lone pair and non-bonded pairs of electrons.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) is a theory which states the geometry of a molecule based on the fact that lone pairs and bond pairs are located in such a way that there is minimum repulsion between electrons. It is useful for most compounds which consist of a central atom. In a molecule, whether electrons are bonded or in lone pairs, they will repel each other and due to this, are arranged by maximizing the distance between them.
Electron geometry of a molecule is determined by electron group as per following table:
Now, $ BeC{l_2} $ is a $ A{B_2} $ type molecule which consists of a central beryllium atom which is bonded to two chlorine atoms via a single bond. The atomic number of a beryllium atom is $ 4 $ and its electronic configuration is as follows:
$ Be = 1{s^2}2{s^2} $
As there are only two electrons present in the valence shell of beryllium, it can form only two covalent bonds with chlorine. As per requirement that the electron pairs maximize their distance from one another, the two bonding pairs in the $ BeC{l_2} $ molecule will arrange themselves on directly opposite sides of the $ Be $ atom resulting in the linear geometry of the molecule as shown in the figure below:
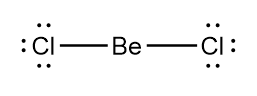
As there are no lone pairs present on the beryllium atom, thus the electron geometry and the molecular geometry for the $ BeC{l_2} $ molecule will be the same i.e., linear.
Thus, we can conclude that the electron and molecular geometry for $ BeC{l_2} $ is Linear.
Note :
Remember that lone pairs have the greatest repelling effect because they are closer to the nucleus of the central atom as compared to bonding pairs and therefore the lone pairs experience greater repulsion as compared to bond pairs. Thus, the presence of lone pairs on the central atom affects the molecular geometry of the molecule while electron geometry remains the same.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) is a theory which states the geometry of a molecule based on the fact that lone pairs and bond pairs are located in such a way that there is minimum repulsion between electrons. It is useful for most compounds which consist of a central atom. In a molecule, whether electrons are bonded or in lone pairs, they will repel each other and due to this, are arranged by maximizing the distance between them.
Electron geometry of a molecule is determined by electron group as per following table:
| Electron group | Electron geometry |
| 2 | Linear |
| 3 | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | Tetrahedral |
| 5 | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | Octahedral |
Now, $ BeC{l_2} $ is a $ A{B_2} $ type molecule which consists of a central beryllium atom which is bonded to two chlorine atoms via a single bond. The atomic number of a beryllium atom is $ 4 $ and its electronic configuration is as follows:
$ Be = 1{s^2}2{s^2} $
As there are only two electrons present in the valence shell of beryllium, it can form only two covalent bonds with chlorine. As per requirement that the electron pairs maximize their distance from one another, the two bonding pairs in the $ BeC{l_2} $ molecule will arrange themselves on directly opposite sides of the $ Be $ atom resulting in the linear geometry of the molecule as shown in the figure below:

As there are no lone pairs present on the beryllium atom, thus the electron geometry and the molecular geometry for the $ BeC{l_2} $ molecule will be the same i.e., linear.
Thus, we can conclude that the electron and molecular geometry for $ BeC{l_2} $ is Linear.
Note :
Remember that lone pairs have the greatest repelling effect because they are closer to the nucleus of the central atom as compared to bonding pairs and therefore the lone pairs experience greater repulsion as compared to bond pairs. Thus, the presence of lone pairs on the central atom affects the molecular geometry of the molecule while electron geometry remains the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




