
Eccentric angle of a point on the ellipse ${{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6$ at a distance $\sqrt 3 $ units from the centre of the ellipse is
A .\[\dfrac{{5\pi }}{3}\]
B. \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
C .\[\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}\]
D .\[\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}\]
Answer
627k+ views
Hint: Proceed the solution of this question by using general parametric coordinates of any point P on ellipse which is (acosθ, bsinθ) then find the distance between center (which is origin) and point P and equalise it with the given distance in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, given equation of ellipse is ${{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6$
On comparing it with standard equation of ellipse which is $\dfrac{{{{\text{x}}^2}}}{{{{\text{a}}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\text{y}}^2}}}{{{{\text{b}}^2}}} = 1$
${\text{Equation of given ellipse is }}{{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6$
Divide by 6 on both side to convert it into standard form
$\dfrac{{{{\text{x}}^2}}}{6} + \dfrac{{{{\text{y}}^2}}}{2} = 1$
so on comparing with standard equation of ellipse
a = $\sqrt 6 $ and b = $\sqrt 2 $
We know that, the parametric coordinate of any point P on the ellipse is
(x=acosθ and y=bsinθ); Where θ is the eccentric angle.
So the parametric coordinate of point P is (√6cosθ, √2sinθ) ($\because $a = $\sqrt 6 $ and b = $\sqrt 2 $) Here θ be the eccentric angle of the point P.
The center of the ellipse is at the point of origin (0,0)
It is given that
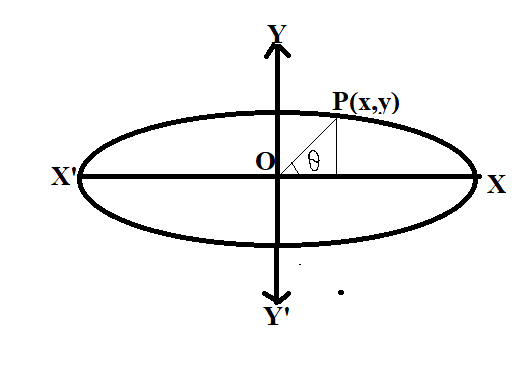
$\therefore {\text{OP = }}\sqrt 3 $
So to find length of OP,
Let the coordinates of point O $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ and P $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$
So Distance between two points O and P will be = \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{{\text{x}}_2} - {{\text{x}}_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
O= (0, 0), P= (√6cosθ, √2sinθ)
Here, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = 0,{{\text{y}}_1} = 0,{{\text{x}}_2} = \sqrt 6 {\text{cos}}\theta ,{{\text{y}}_2} = \sqrt 2 {\text{sin}}\theta \]
So length of side OP = $\sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt 6 \cos \theta - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sqrt 2 \sin \theta - 0} \right)}^2}} {\text{ = }}\sqrt {6{{\cos }^2}\theta + 2{{\sin }^2}\theta } {\text{ }}$
but It is given that ${\text{OP = }}\sqrt 3 $
${\text{so, }}\sqrt {6{{\cos }^2}\theta + 2{{\sin }^2}\theta } {\text{ = }}\sqrt 3 $
On squaring both side
$ \Rightarrow 6{\cos ^2}\theta + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6(1 - {\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta ) + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 6{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 3 = 6{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4} = {\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{sin}}\theta = \pm \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{sin}}\theta = + \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ or sin}}\theta = - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { + \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ }}} \right){\text{or }}\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}{\text{,}}\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}{\text{ or }}\theta = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{5\pi }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{so, eccentric angle }}\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}{\text{ }}$given in option C
Hence, Option A, B and D all are correct.
Note: In such types of particular questions, where we have assumed Parametric coordinates (trigonometric function of eccentric angles θ). In the solution we got 4 values of θ. This happens because we can assume 4 such values in each quadrant. Therefore, exactly we got 4 such values of θ in each quadrant. These 4 values of θ will also be a mirror image of each other about the x and y axis correspondingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, given equation of ellipse is ${{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6$
On comparing it with standard equation of ellipse which is $\dfrac{{{{\text{x}}^2}}}{{{{\text{a}}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\text{y}}^2}}}{{{{\text{b}}^2}}} = 1$
${\text{Equation of given ellipse is }}{{\text{x}}^2} + 3{{\text{y}}^2} = 6$
Divide by 6 on both side to convert it into standard form
$\dfrac{{{{\text{x}}^2}}}{6} + \dfrac{{{{\text{y}}^2}}}{2} = 1$
so on comparing with standard equation of ellipse
a = $\sqrt 6 $ and b = $\sqrt 2 $
We know that, the parametric coordinate of any point P on the ellipse is
(x=acosθ and y=bsinθ); Where θ is the eccentric angle.
So the parametric coordinate of point P is (√6cosθ, √2sinθ) ($\because $a = $\sqrt 6 $ and b = $\sqrt 2 $) Here θ be the eccentric angle of the point P.
The center of the ellipse is at the point of origin (0,0)
It is given that

$\therefore {\text{OP = }}\sqrt 3 $
So to find length of OP,
Let the coordinates of point O $\left( {{{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}} \right)$ and P $\left( {{{\text{x}}_2},{{\text{y}}_2}} \right)$
So Distance between two points O and P will be = \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{{\text{x}}_2} - {{\text{x}}_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{{\text{y}}_2} - {{\text{y}}_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
O= (0, 0), P= (√6cosθ, √2sinθ)
Here, \[{{\text{x}}_1} = 0,{{\text{y}}_1} = 0,{{\text{x}}_2} = \sqrt 6 {\text{cos}}\theta ,{{\text{y}}_2} = \sqrt 2 {\text{sin}}\theta \]
So length of side OP = $\sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt 6 \cos \theta - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sqrt 2 \sin \theta - 0} \right)}^2}} {\text{ = }}\sqrt {6{{\cos }^2}\theta + 2{{\sin }^2}\theta } {\text{ }}$
but It is given that ${\text{OP = }}\sqrt 3 $
${\text{so, }}\sqrt {6{{\cos }^2}\theta + 2{{\sin }^2}\theta } {\text{ = }}\sqrt 3 $
On squaring both side
$ \Rightarrow 6{\cos ^2}\theta + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6(1 - {\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta ) + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 6{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta + 2{\sin ^2}\theta {\text{ = 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 3 = 6{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4} = {\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}\theta $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{sin}}\theta = \pm \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{sin}}\theta = + \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ or sin}}\theta = - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { + \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ }}} \right){\text{or }}\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}{\text{,}}\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}{\text{ or }}\theta = \dfrac{{4\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{5\pi }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{so, eccentric angle }}\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}{\text{ }}$given in option C
Hence, Option A, B and D all are correct.
Note: In such types of particular questions, where we have assumed Parametric coordinates (trigonometric function of eccentric angles θ). In the solution we got 4 values of θ. This happens because we can assume 4 such values in each quadrant. Therefore, exactly we got 4 such values of θ in each quadrant. These 4 values of θ will also be a mirror image of each other about the x and y axis correspondingly.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




