
During which of the following stages the non-sister chromatids twist around and exchange segments with each other?
A. Diplotene
B. Diakinesis
C. Leptotene
D. Pachytene
E. Zygotene
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint: Diplotene, diakinesis, leptotene, pachytene and zygotene are phases of prophase I of meiosis. The non-sister chromatids refer to chromatid fibres of two homologous chromosomes. Exchange of non-chromatids occurs in the last stage of prophase I.
Complete answer: Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in gamete cells. The cell divides twice to produce four haploid daughter cells called gametes. It occurs in two phases called meiosis I and meiosis II. The meiosis stage I is marked by five sub-stages. These stages are Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I and Cytokinesis I. The pachytene stage is the third stage of meiosis prophase I. Prophase I is characterized by the disintegration of the nuclear envelope followed by condensation of chromosomes. The last step in prophase I is the formation of spindle fibres. The key feature of this stage is the pairing of homologous chromosomes. Crossing over of genetic segments occurs between two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. This occurs in the third stage called pachytene.
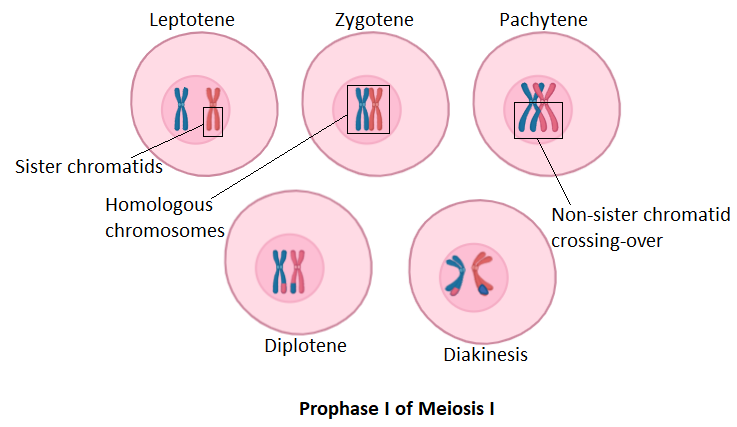
Chromatin segments when they come close in pachytene, they recombine their genetic material. The result of this recombination can be seen in the offspring. When two haploid gametes from two different parents combine they form a diploid zygote. Both of these gametes have been the product of recombination. Further variation occurs due to their fusion with each other. This is the reason why babies look a little different from their parents and have some similar characters resembling either of the parents.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The recombination process is regulated by an enzyme called recombinase. Various other factors determine the crossing-over between chromatid segments. Mutations also occur during this stage. Harmful mutations may lead to diseases.
Complete answer: Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in gamete cells. The cell divides twice to produce four haploid daughter cells called gametes. It occurs in two phases called meiosis I and meiosis II. The meiosis stage I is marked by five sub-stages. These stages are Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I and Cytokinesis I. The pachytene stage is the third stage of meiosis prophase I. Prophase I is characterized by the disintegration of the nuclear envelope followed by condensation of chromosomes. The last step in prophase I is the formation of spindle fibres. The key feature of this stage is the pairing of homologous chromosomes. Crossing over of genetic segments occurs between two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. This occurs in the third stage called pachytene.

Chromatin segments when they come close in pachytene, they recombine their genetic material. The result of this recombination can be seen in the offspring. When two haploid gametes from two different parents combine they form a diploid zygote. Both of these gametes have been the product of recombination. Further variation occurs due to their fusion with each other. This is the reason why babies look a little different from their parents and have some similar characters resembling either of the parents.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The recombination process is regulated by an enzyme called recombinase. Various other factors determine the crossing-over between chromatid segments. Mutations also occur during this stage. Harmful mutations may lead to diseases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




