
During the propagation of the nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
a) K+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
b) Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
c)K+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
d)Na+ ions from intracellular fluid to extracellular fluid
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: A nerve impulse or the action potential is generated by the movement of the sodium and the potassium ions in and outside the membrane. This movement leads to the generation of the impulse in the neuron.
Complete answer:
The action potential is generated quickly when the negative ions are changed into the positive ions. The movement of the sodium ions into the cell and the movement of potassium ions outside the cell lead to the generation of the nerve impulse. This change takes place in milliseconds. The channels present in the membrane are first to open in order to let in the sodium ions. This starts the nerve impulse. This stage is called the depolarization of the membrane. Then the channels are open in order to move out the potassium ions this leads to the end of the nerve impulse. The inside of the membrane becomes negative again and this stage is known as the repolarization state. After the channels are closed the resting potential is restored and the nerve moves on to the next neuron in the form of a wave. In the presence of the myelinated sheaths on the surface of the neurons, the nerve signals jump from one node to the other. But in the non-myelinated sheath, the flow of nerve impulse is smooth.
So, the answer is ‘Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid’.
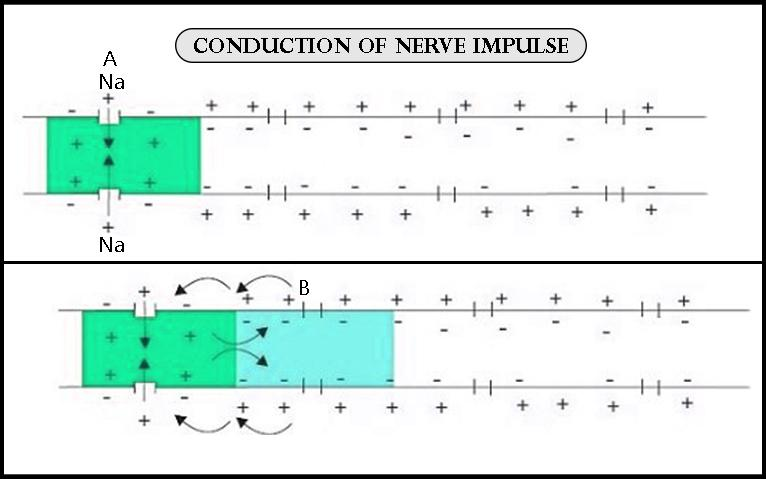
Note: The nerve impulse is generated due to the sodium-potassium pump. The movement of the ions inside and outside the membrane leads to the generation of the nerve impulse. The impulse starts from the movement of sodium ions inside the cell and ends with the movement of the potassium ions outside the cells.
Complete answer:
The action potential is generated quickly when the negative ions are changed into the positive ions. The movement of the sodium ions into the cell and the movement of potassium ions outside the cell lead to the generation of the nerve impulse. This change takes place in milliseconds. The channels present in the membrane are first to open in order to let in the sodium ions. This starts the nerve impulse. This stage is called the depolarization of the membrane. Then the channels are open in order to move out the potassium ions this leads to the end of the nerve impulse. The inside of the membrane becomes negative again and this stage is known as the repolarization state. After the channels are closed the resting potential is restored and the nerve moves on to the next neuron in the form of a wave. In the presence of the myelinated sheaths on the surface of the neurons, the nerve signals jump from one node to the other. But in the non-myelinated sheath, the flow of nerve impulse is smooth.
So, the answer is ‘Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid’.

Note: The nerve impulse is generated due to the sodium-potassium pump. The movement of the ions inside and outside the membrane leads to the generation of the nerve impulse. The impulse starts from the movement of sodium ions inside the cell and ends with the movement of the potassium ions outside the cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




