
During polymerisation of acetylene to benzene, the state of hybridisation of carbon changes from:
[A] $s{{p}^{2}}$to$sp$
[B] $s{{p}^{3}}$to$sp$
[C] $sp$to$s{{p}^{2}}$
[D] $sp$to$s{{p}^{3}}$
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint:
Acetylene is an alkyne. On polymerisation, it gives us benzene which has 6 carbon atoms. Each atom is attached to two other carbon atoms one by a double bond and the other through a single bond. All carbon atoms in an alkane are $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised and that of an alkene and alkyne are $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $sp$ respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that hybridisation of an atom is the number of other atoms it is attached with through a chemical bonding.
For example, if the carbon atom is attached through other carbon atoms through a single bond the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ but when it becomes doubly or triply bonded, the hybridisation becomes $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $sp$ respectively.
We can easily tell the hybridisation of an atom by looking at its substituents.
Here, we have acetylene which is the smallest alkyne, and is a hydrocarbon. We also know it is ethyne.
The chemical formula of ethyne or acetylene is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{\,2}}$. Here, we have a triple bond between the two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom is attached to each of the carbon. We can write acetylene as-
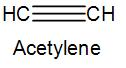
In acetylene, both the carbons have a sp hybridisation.
As we know, polymerisation means repeating a single unit multiple times to attain a network of atoms. Here, acetylene is polymerised to give us benzene.
When acetylene is passed through a red hot iron tube, we get benzene-

3moles of acetylene reacts to form 1 mole of benzene.
As we can see from the above reaction, the formula of benzene is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. Benzene has three carbon-carbon double bonds and three carbon-carbon single bonds and each carbon has a hydrogen atom attached to it. However, each carbon atom forms different bonds (single and double) with two carbon atoms which are again forming two dissimilar bonds with other carbon atoms.
Therefore, the hybridisation of carbon on benzene is $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, polymerisation of acetylene to benzene changes hybridisation from $sp$ to $s {{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $sp$ to $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Note:
Formation of benzene from acetylene is a cyclic polymerisation reaction, which is an intramolecular reaction and it is carried out at a very high temperature of 873 kelvin.
We should not be confused by the two dissimilar bonds formed by benzene. Taking any of the six carbon atoms into consideration, we will get a carbon-carbon double bond and therefore, we can say that the carbons are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised.
Acetylene is an alkyne. On polymerisation, it gives us benzene which has 6 carbon atoms. Each atom is attached to two other carbon atoms one by a double bond and the other through a single bond. All carbon atoms in an alkane are $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised and that of an alkene and alkyne are $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $sp$ respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that hybridisation of an atom is the number of other atoms it is attached with through a chemical bonding.
For example, if the carbon atom is attached through other carbon atoms through a single bond the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ but when it becomes doubly or triply bonded, the hybridisation becomes $s{{p}^{2}}$ and $sp$ respectively.
We can easily tell the hybridisation of an atom by looking at its substituents.
Here, we have acetylene which is the smallest alkyne, and is a hydrocarbon. We also know it is ethyne.
The chemical formula of ethyne or acetylene is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{\,2}}$. Here, we have a triple bond between the two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom is attached to each of the carbon. We can write acetylene as-
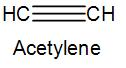
In acetylene, both the carbons have a sp hybridisation.
As we know, polymerisation means repeating a single unit multiple times to attain a network of atoms. Here, acetylene is polymerised to give us benzene.
When acetylene is passed through a red hot iron tube, we get benzene-

3moles of acetylene reacts to form 1 mole of benzene.
As we can see from the above reaction, the formula of benzene is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. Benzene has three carbon-carbon double bonds and three carbon-carbon single bonds and each carbon has a hydrogen atom attached to it. However, each carbon atom forms different bonds (single and double) with two carbon atoms which are again forming two dissimilar bonds with other carbon atoms.
Therefore, the hybridisation of carbon on benzene is $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, polymerisation of acetylene to benzene changes hybridisation from $sp$ to $s {{p}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $sp$ to $s{{p}^{2}}$.
Note:
Formation of benzene from acetylene is a cyclic polymerisation reaction, which is an intramolecular reaction and it is carried out at a very high temperature of 873 kelvin.
We should not be confused by the two dissimilar bonds formed by benzene. Taking any of the six carbon atoms into consideration, we will get a carbon-carbon double bond and therefore, we can say that the carbons are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




