
Draw the structure of the following molecules:
(i) $XeO{F_4}$ (ii) ${H_3}P{O_3}$
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: First try and find out the valence shell electronic configuration of the central atom. Then try to give structure to the compound in a way that all the atoms forming the bonds complete their octet.
Complete answer:
In order to draw the structure of the given molecules, we need to know the bonding between the atoms. We will see their structure one by one.
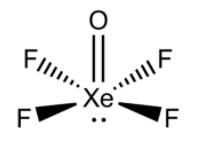
i) $XeO{F_4}$:
- We know that Xe (Xenon) is a noble gas having an atomic number of 54. However, it makes complexes.
- The valence shell electronic configuration of Xe is $[Kr]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}$. So, there are 8 electrons in the valence shell of Xe. There are 6 and 7 electrons in the valence shell of oxygen and fluorine respectively.
- So, Xenon should make four single bonds with four fluorine atoms in order to satisfy the octet of fluorine. Xenon will make a double bond with oxygen as it will complete the octet of oxygen atoms. There will be one lone pair on the Xenon atom.
- Thus, we can say that the hybridization of this atom will be $s{p^3}{d^2}$. So, its shape should be square pyramidal. Its structure can be drawn as below.
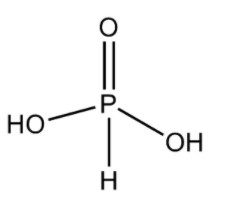
ii) ${H_3}P{O_3}$:
The name of this acid is phosphorus acid. This acid is a diprotic acid. This means that this acid gives two protons upon its full dissociation into ions in water.
- We know that the electronic configuration of P is $[Ne]3{s^2}3{p^3}$.
- From the electronic configuration, we can say that it can make three sigma bonds. It also has a lone pair.
- So, in its structure, it forms a double bond with an oxygen atom in order to complete its octet. It forms a sigma bond with two –OH groups and one H atom. Thus, this structure can explain its dibasic nature. The structure can be drawn as
Note:
Remember that as the formula of phosphorus acid is ${H_3}P{O_3}$, it does not have three –OH groups singly bonded to one P atom. Actually, this structure is not stable and thus ${H_3}P{O_3}$ exists in the structure given just above.
Complete answer:
In order to draw the structure of the given molecules, we need to know the bonding between the atoms. We will see their structure one by one.
i) $XeO{F_4}$:
- We know that Xe (Xenon) is a noble gas having an atomic number of 54. However, it makes complexes.
- The valence shell electronic configuration of Xe is $[Kr]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}$. So, there are 8 electrons in the valence shell of Xe. There are 6 and 7 electrons in the valence shell of oxygen and fluorine respectively.
- So, Xenon should make four single bonds with four fluorine atoms in order to satisfy the octet of fluorine. Xenon will make a double bond with oxygen as it will complete the octet of oxygen atoms. There will be one lone pair on the Xenon atom.
- Thus, we can say that the hybridization of this atom will be $s{p^3}{d^2}$. So, its shape should be square pyramidal. Its structure can be drawn as below.

ii) ${H_3}P{O_3}$:
The name of this acid is phosphorus acid. This acid is a diprotic acid. This means that this acid gives two protons upon its full dissociation into ions in water.
- We know that the electronic configuration of P is $[Ne]3{s^2}3{p^3}$.
- From the electronic configuration, we can say that it can make three sigma bonds. It also has a lone pair.
- So, in its structure, it forms a double bond with an oxygen atom in order to complete its octet. It forms a sigma bond with two –OH groups and one H atom. Thus, this structure can explain its dibasic nature. The structure can be drawn as

Note:
Remember that as the formula of phosphorus acid is ${H_3}P{O_3}$, it does not have three –OH groups singly bonded to one P atom. Actually, this structure is not stable and thus ${H_3}P{O_3}$ exists in the structure given just above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




