
Draw the structure of \[S{{O}_{4}}^{2-}\].
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The Sulphur atom is the central atom of the structure of sulphate ion.The outermost orbital of the sulphur contains six electrons, hence, it forms a coordinate bond with the two of the oxygen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
A coordinate bond which is also sometimes termed as a dative covalent bond, can be defined as a covalent bond as in, which has a shared pair of electrons, in which both the involved electrons are coming from the same atom. A covalent bond is when two atoms are sharing a lone pair or a pair of electrons. The atoms are being held together because of the electron pair which is attracted by both of the nuclei.
In order to understand the coordinate bond, we are gonna take an example of carbon monoxide, here two atoms are involved as the name suggests, carbon and oxygen. Since the carbon contains a lone pair of electrons, it will donate its two electrons to carbon in order to form a coordinate bond, and share the rest, to fulfil the valencies.
A lewis dot structural representation is shown below,
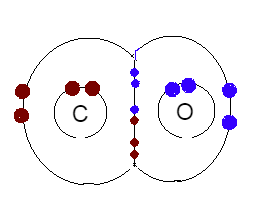
Here as you can see, four electrons are being shared by both of the atoms, which means, it have covalent bonds. And two electrons are donated by the oxygen only, to form a coordinate bond.
Similarly, the structure of sulphate ions has two negative charges, which means it has two electrons. Sulphur has $6$ electrons in its valence shell and Lewis dot structure of sulphur gives it two unshared pairs and two unpaired electrons.
The structure of sulphate ion is shown below.
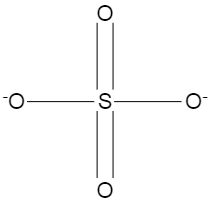
We can see that two of the oxygen atoms are attached to sulphur through double bonds, and the remaining two have single bonds, and those two oxygen atoms have one free bond or electron present in them. In this case the donor atom is sulphur and the acceptor atom is oxygen.
Note: sulfate ions are easily soluble in aqueous solutions. Some of the exceptions which are not soluble are calcium sulfate, strontium sulfate, barium sulfate etc.They have comparatively low solubility. The sulphate ions tend to form white precipitate during reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
A coordinate bond which is also sometimes termed as a dative covalent bond, can be defined as a covalent bond as in, which has a shared pair of electrons, in which both the involved electrons are coming from the same atom. A covalent bond is when two atoms are sharing a lone pair or a pair of electrons. The atoms are being held together because of the electron pair which is attracted by both of the nuclei.
In order to understand the coordinate bond, we are gonna take an example of carbon monoxide, here two atoms are involved as the name suggests, carbon and oxygen. Since the carbon contains a lone pair of electrons, it will donate its two electrons to carbon in order to form a coordinate bond, and share the rest, to fulfil the valencies.
A lewis dot structural representation is shown below,

Here as you can see, four electrons are being shared by both of the atoms, which means, it have covalent bonds. And two electrons are donated by the oxygen only, to form a coordinate bond.
Similarly, the structure of sulphate ions has two negative charges, which means it has two electrons. Sulphur has $6$ electrons in its valence shell and Lewis dot structure of sulphur gives it two unshared pairs and two unpaired electrons.
The structure of sulphate ion is shown below.

We can see that two of the oxygen atoms are attached to sulphur through double bonds, and the remaining two have single bonds, and those two oxygen atoms have one free bond or electron present in them. In this case the donor atom is sulphur and the acceptor atom is oxygen.
Note: sulfate ions are easily soluble in aqueous solutions. Some of the exceptions which are not soluble are calcium sulfate, strontium sulfate, barium sulfate etc.They have comparatively low solubility. The sulphate ions tend to form white precipitate during reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




