
Draw the structure of ${{O}_{3}}$ and $N{{O}_{2}}$.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Many theories have been formulated to know the nature of bonds in compounds like Valence bond theory, Molecular orbital theory, Crystal field theory, Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. The geometry of ${{O}_{3}}$ and $N{{O}_{2}}$ molecule is determined by VSEPR theory; i.e; valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Complete step by step solution:
-VSEPR theory states that the electron pairs repel each other, whether they are in the form of lone pair or bond pair. This is done in order to minimise the repulsion, thus increasing the stability of the compound.
-The knowledge of bond pair and lone pair of electrons gives us the idea of the geometry of the molecule. The geometry is found by counting the number of electron pairs and not the lone pairs.
-According to the electron pairs, the geometry can be decided as
-Molecular geometry, on the other hand, also depends on the number of the lone pairs. When there are no lone pairs, the denotation is simply $A{{X}_{n}}$. When lone pairs are added, the denotation becomes $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$
where n=no. of bond pairs
m=no. of lone pairs
-The lone pairs are placed apart from each other while the bond pairs are placed apart from each other to ensure maximum stability.
-The valence electrons of the O atom is 6 and N atom is 5. So oxygen needs 2 more electrons and nitrogen needs 3 more electrons to complete their octet. In ${{O}_{3}}$, the total number of valence electrons will be 6x3=18 which can be arranged keeping 1 atom at the centre and other 2 adjacents to it. 1 atom gets bonded by double bond while the other gets bonded by a single bond. Thus the central oxygen atom has 7 electrons only and so gets a positive charge. Single bonded O atom gets 9 electrons and so it gets a negative charge. Thus overall charge remains neutral.
-There will be 17 valence electrons in $N{{O}_{2}}$. N is the central atom and O is attached adjacent to it. The bonds are drawn so as to complete the octet. While doing so, the N atom gets only 7 electrons and so develops a positive charge and a single bonded O atom develops a negative charge as it gets 9 electrons in total. Thus the overall molecule is neutral.
-Both the molecules are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized and have bent structure. The structures can be drawn as:
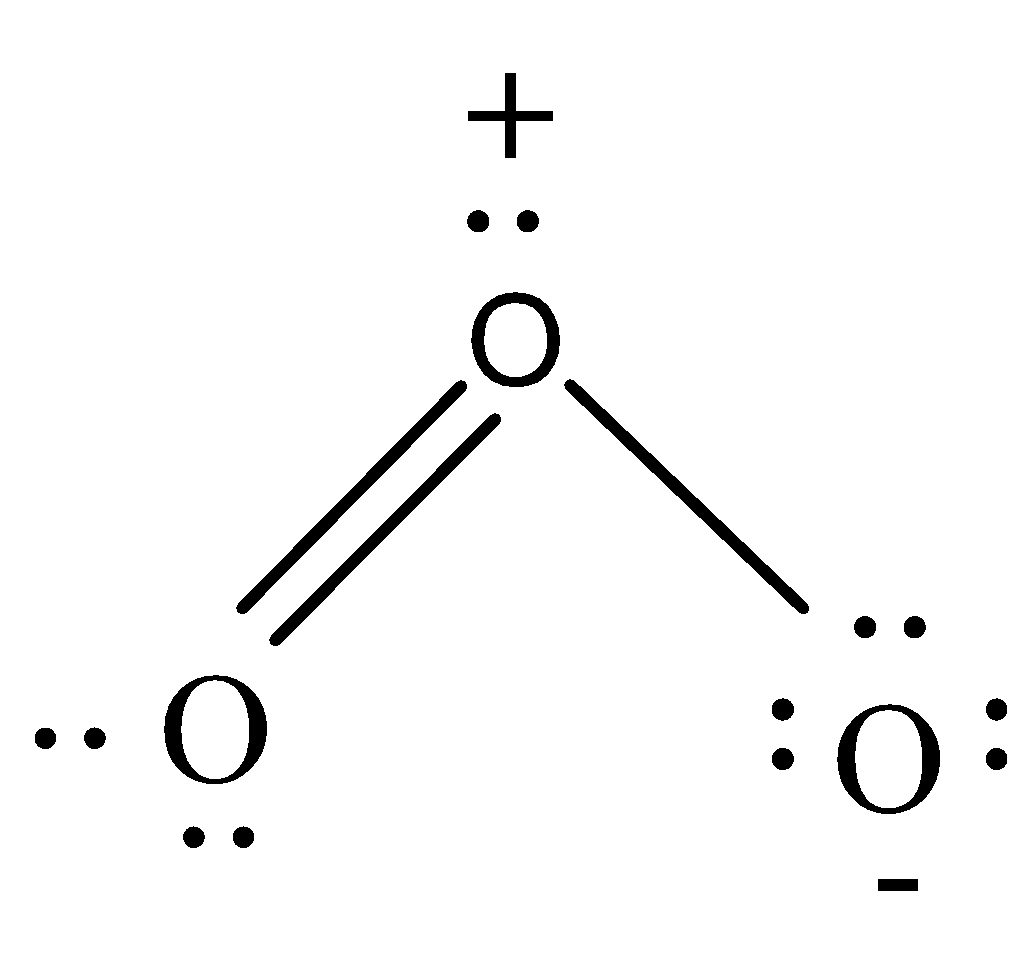
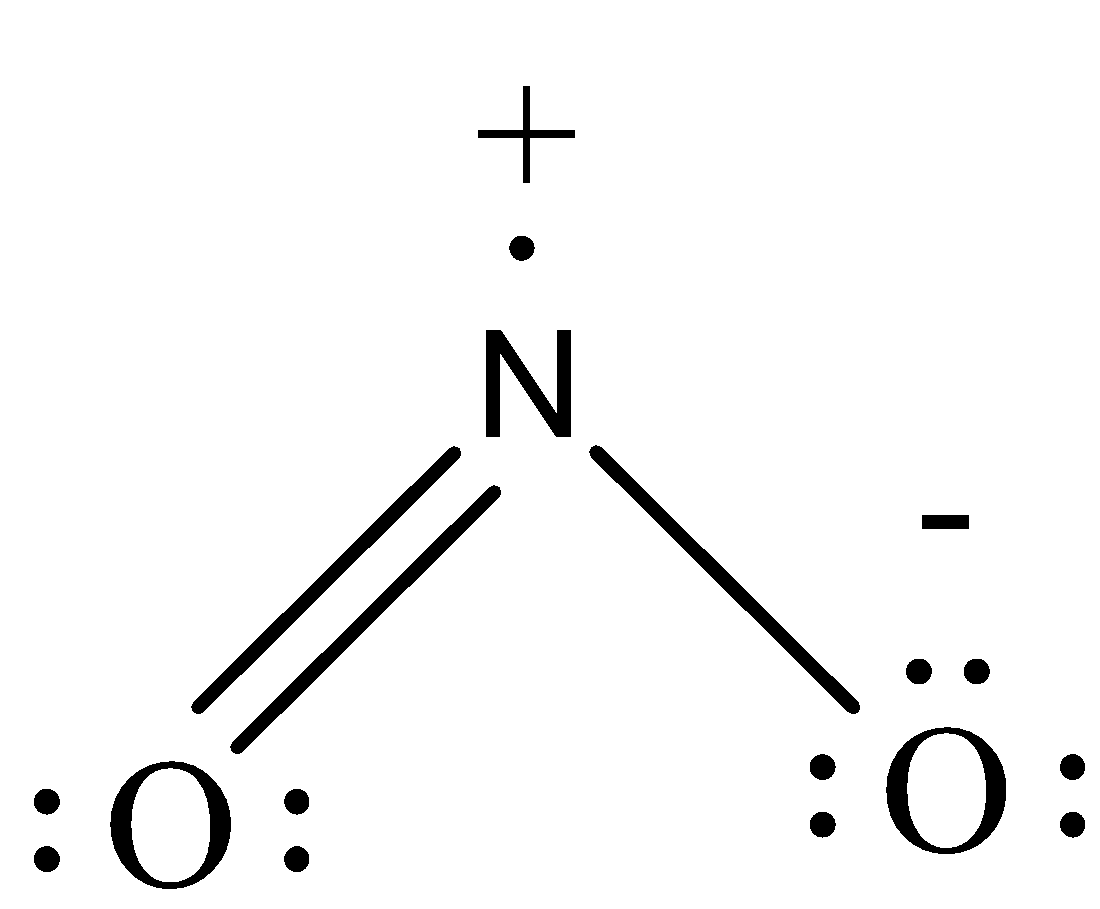
Note: Both the molecules are symmetrical and so the single and double bonds get exchanged in the molecule. This is called resonance. Both ozone and nitrogen dioxide show resonating structures and the stability of the resonance hybrid is more than that of the resonating structures.
Complete step by step solution:
-VSEPR theory states that the electron pairs repel each other, whether they are in the form of lone pair or bond pair. This is done in order to minimise the repulsion, thus increasing the stability of the compound.
-The knowledge of bond pair and lone pair of electrons gives us the idea of the geometry of the molecule. The geometry is found by counting the number of electron pairs and not the lone pairs.
-According to the electron pairs, the geometry can be decided as
| Number of electron pairs | Geometry of molecule |
| 2 | Linear |
| 3 | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | Tetrahedral |
| 5 | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | Octahedral |
-Molecular geometry, on the other hand, also depends on the number of the lone pairs. When there are no lone pairs, the denotation is simply $A{{X}_{n}}$. When lone pairs are added, the denotation becomes $A{{X}_{n}}{{E}_{m}}$
where n=no. of bond pairs
m=no. of lone pairs
-The lone pairs are placed apart from each other while the bond pairs are placed apart from each other to ensure maximum stability.
-The valence electrons of the O atom is 6 and N atom is 5. So oxygen needs 2 more electrons and nitrogen needs 3 more electrons to complete their octet. In ${{O}_{3}}$, the total number of valence electrons will be 6x3=18 which can be arranged keeping 1 atom at the centre and other 2 adjacents to it. 1 atom gets bonded by double bond while the other gets bonded by a single bond. Thus the central oxygen atom has 7 electrons only and so gets a positive charge. Single bonded O atom gets 9 electrons and so it gets a negative charge. Thus overall charge remains neutral.
-There will be 17 valence electrons in $N{{O}_{2}}$. N is the central atom and O is attached adjacent to it. The bonds are drawn so as to complete the octet. While doing so, the N atom gets only 7 electrons and so develops a positive charge and a single bonded O atom develops a negative charge as it gets 9 electrons in total. Thus the overall molecule is neutral.
-Both the molecules are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized and have bent structure. The structures can be drawn as:


Note: Both the molecules are symmetrical and so the single and double bonds get exchanged in the molecule. This is called resonance. Both ozone and nitrogen dioxide show resonating structures and the stability of the resonance hybrid is more than that of the resonating structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




