
Draw the structure of $I{{F}_{5}}$ and also explain hybridization of the central atom in $I{{F}_{5}}$.
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint:The fluorine is forming five covalent bonds with iodine. Iodine is the central atom present in $I{{F}_{5}}$. The atomic number of iodine is 53.using valence bond theory structure and hybridization can easily be predicted .
Complete step-by-step answer:So in the question, it is asked to explain about the hybridization of $I{{F}_{5}}$.So here I is the central atom and five fluorine atoms are bonded with Iodine to form the $I{{F}_{5}}$molecule.
First let’s get an idea about what is hybridization.
Hybridization –It is basically the intermixing of the pure atomic orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals with different shape and energy, but which is more favorable and effective than the pure atomic orbitals for the chemical bond formation according to valence bond theory.
Now we have explain about the hybridization involved in $I{{F}_{5}}$molecule.
We know I is the central atom surrounded by the five fluorine monovalent atom.
Chlorine belongs to group 17 and hence it possess valency of 7.
And the electronic configuration of I is,
$Electronic\,configuration=\left[ Kr \right]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{5}}$
There is seven electrons in the outer most shells from which five electrons are used for forming the covalent bond with the F atoms and there is two electrons remaining which forms the lone pair.
Let’s draw the Lewis structure of $I{{F}_{5}}$ molecule,
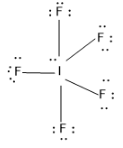
So from the structure it is clear that there is five bonded atoms with I and one lone pair of atoms. Using these data we can calculate the steric number of the compound (Z)
Z= no. of bonded atom + no. of lone pairs =5+1=6
As the steric number is 6, the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization and the expected geometry is octahedral as it is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridized. But there is one lone pair so the geometry of $I{{F}_{5}}$ molecule is square pyramidal.
The structure of $I{{F}_{5}}$ is,
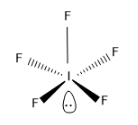
Note:The hybridization can also be found using the formulae,
$Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( v+n-p+m \right)$
Where v is the valency of central atom
n is the negative charge attached, it may also be given as A which is anionic charge
p is the positive charge or given as C which is cationic charge.
m is the number of monovalent atoms which are attached to the central atom.
Here,$Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 7+5 \right)=Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 12 \right)=6$
As m =5, n =0, p=0 and v=7
Z=6 which is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$hybridization
Complete step-by-step answer:So in the question, it is asked to explain about the hybridization of $I{{F}_{5}}$.So here I is the central atom and five fluorine atoms are bonded with Iodine to form the $I{{F}_{5}}$molecule.
First let’s get an idea about what is hybridization.
Hybridization –It is basically the intermixing of the pure atomic orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals with different shape and energy, but which is more favorable and effective than the pure atomic orbitals for the chemical bond formation according to valence bond theory.
Now we have explain about the hybridization involved in $I{{F}_{5}}$molecule.
We know I is the central atom surrounded by the five fluorine monovalent atom.
Chlorine belongs to group 17 and hence it possess valency of 7.
And the electronic configuration of I is,
$Electronic\,configuration=\left[ Kr \right]4{{d}^{10}}5{{s}^{2}}5{{p}^{5}}$
There is seven electrons in the outer most shells from which five electrons are used for forming the covalent bond with the F atoms and there is two electrons remaining which forms the lone pair.
Let’s draw the Lewis structure of $I{{F}_{5}}$ molecule,

So from the structure it is clear that there is five bonded atoms with I and one lone pair of atoms. Using these data we can calculate the steric number of the compound (Z)
Z= no. of bonded atom + no. of lone pairs =5+1=6
As the steric number is 6, the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization and the expected geometry is octahedral as it is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridized. But there is one lone pair so the geometry of $I{{F}_{5}}$ molecule is square pyramidal.
The structure of $I{{F}_{5}}$ is,

Note:The hybridization can also be found using the formulae,
$Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( v+n-p+m \right)$
Where v is the valency of central atom
n is the negative charge attached, it may also be given as A which is anionic charge
p is the positive charge or given as C which is cationic charge.
m is the number of monovalent atoms which are attached to the central atom.
Here,$Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 7+5 \right)=Z=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 12 \right)=6$
As m =5, n =0, p=0 and v=7
Z=6 which is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$hybridization
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




