
Draw the structure of amino acid Alanine.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Alanine is α-amino acid which is used in biosynthesis of proteins through a process called translation, in which all the amino acids along with alanine polymerise form a polypeptide chain by polypeptide bond between them.
Complete step by step answer:
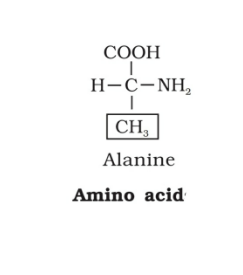
1.Amino acids are the constituent of protein. Although about 300 amino acids occur in nature, only 20 of them enter into the composition of proteins. Each amino acid contains a centrally located carbon atom called α-carbon to which four groups are attached: a basic amino group (-NH+ 3 an acidic carboxyl group (-COOh- , a hydrogen atom and a group of varying chemical structures called a side chain (R-group).
2.With four different groups attached to it, the a-carbon is said to be asymmetric. There are various ways to classify the amino acids :
(i) Common amino acids found in proteins
(ii) Uncommon amino acids
(iii) Amino acids not found in proteins.
3. Common amino acids found in proteins are grouped into:
(i) Nonpolar (hydrophobic) amino acids
(ii) Polar amino acids (neutral amino acids)
(iii) Acidic amino acids and
(iv) Basic amino acids
4.Alanine is one of the non-polar aliphatic amino acid.
In alanine the side-chain is a methyl group (-CH3) which is connected to α-carbon. It is the simplest α-amino acid after glycine.
The methyl group attached at the side-chain of alanine is non-reactive and is therefore hardly ever directly involved in protein function. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be produced by the human body, and does not need to be obtained through the diet. Alanine can be found in a wide variety of foods, but is particularly found in meats.
Note: Some functions of Amino acids are:
Histidine is a precursor to histamines, which work to protect the body from different allergic reactions. It is also important for building haemoglobin and helping to prevent anaemia from occurring.
Leucine assists with muscle recovery and increases mass from exercise. It also helps in the regulation of blood sugar, along with supplying energy to the body.
Isoleucine functions like Leucine for muscle recovery and blood sugar regulation. Additionally, this is needed for haemoglobin to be formed.
Valine combines with Leucine and Isoleucine to make an amino acid group called BCAAs, or branched chain amino acids. It is also needed for muscle metabolism and tissue repair. It is also supposed to help if there are liver or gallbladder problems.
Complete step by step answer:

1.Amino acids are the constituent of protein. Although about 300 amino acids occur in nature, only 20 of them enter into the composition of proteins. Each amino acid contains a centrally located carbon atom called α-carbon to which four groups are attached: a basic amino group (-NH+ 3 an acidic carboxyl group (-COOh- , a hydrogen atom and a group of varying chemical structures called a side chain (R-group).
2.With four different groups attached to it, the a-carbon is said to be asymmetric. There are various ways to classify the amino acids :
(i) Common amino acids found in proteins
(ii) Uncommon amino acids
(iii) Amino acids not found in proteins.
3. Common amino acids found in proteins are grouped into:
(i) Nonpolar (hydrophobic) amino acids
(ii) Polar amino acids (neutral amino acids)
(iii) Acidic amino acids and
(iv) Basic amino acids
4.Alanine is one of the non-polar aliphatic amino acid.
In alanine the side-chain is a methyl group (-CH3) which is connected to α-carbon. It is the simplest α-amino acid after glycine.
The methyl group attached at the side-chain of alanine is non-reactive and is therefore hardly ever directly involved in protein function. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be produced by the human body, and does not need to be obtained through the diet. Alanine can be found in a wide variety of foods, but is particularly found in meats.
Note: Some functions of Amino acids are:
Histidine is a precursor to histamines, which work to protect the body from different allergic reactions. It is also important for building haemoglobin and helping to prevent anaemia from occurring.
Leucine assists with muscle recovery and increases mass from exercise. It also helps in the regulation of blood sugar, along with supplying energy to the body.
Isoleucine functions like Leucine for muscle recovery and blood sugar regulation. Additionally, this is needed for haemoglobin to be formed.
Valine combines with Leucine and Isoleucine to make an amino acid group called BCAAs, or branched chain amino acids. It is also needed for muscle metabolism and tissue repair. It is also supposed to help if there are liver or gallbladder problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




