
Draw the lewis representation of $S{O_2}$ molecule. Define dipole moment. The dipole moment of $B{F_3}$ is zero. Why?
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: A Lewis structure of any molecule is based on the concept of the octet rule, in which atoms share electrons so that each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell.
Complete answer:
Lewis representation of $S{O_2}$ molecule –
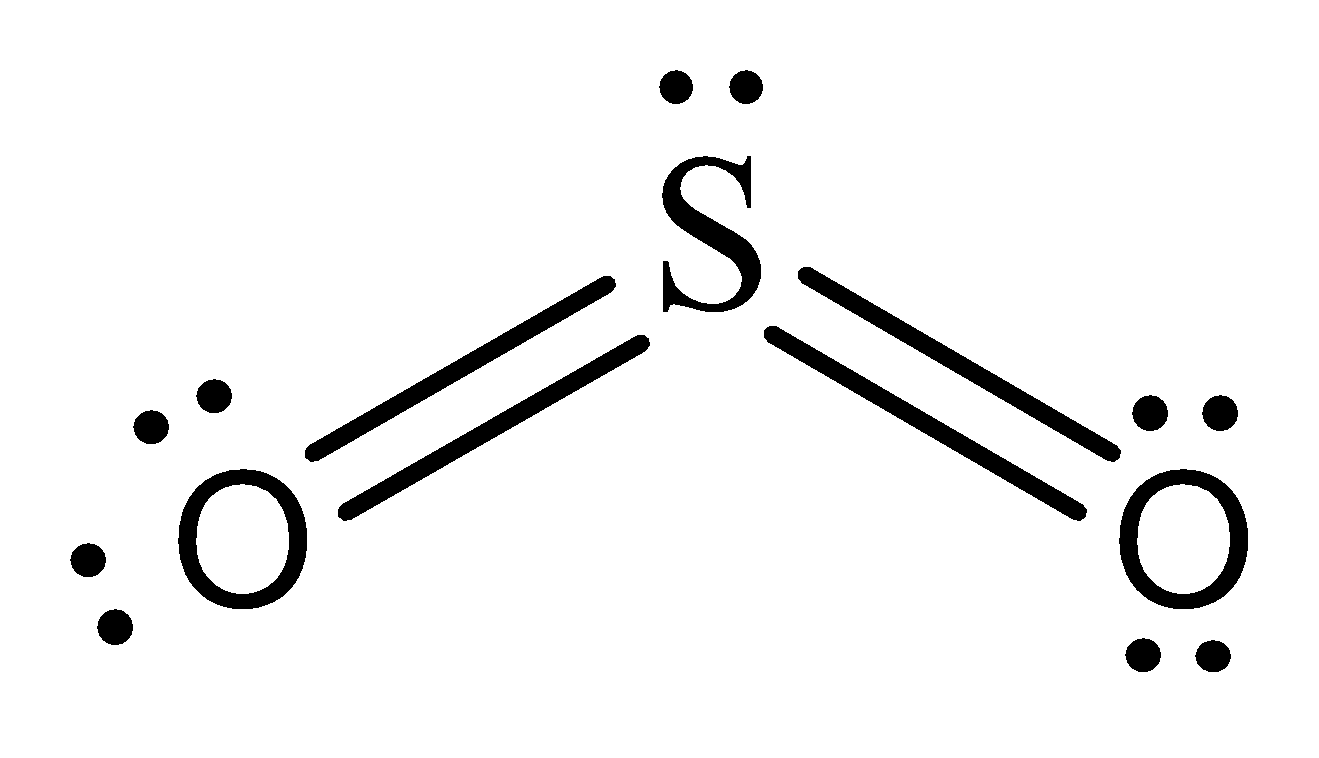
The formal charges of the $S{O_2}$ with the single bond and a double bond is larger than $S{O_2}$ with two double bonds.
A dipole moment arises in any system in which there is a separation of charge. They can, therefore, arise in ionic bonds as well as in covalent bonds. Dipole moments occur due to the difference in electronegativity between two chemically bonded atoms.
A bond dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a chemical bond between two atoms in a molecule. It involves the concept of electric dipole moment, which is a measure of the separation of negative and positive charges in a system.
The $B{F_3}$ molecule has a symmetrical trigonal planar geometry, like the $S{O_3}$ molecule. In such a structure, the resultant moment of any two \[B - F\] dipoles is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the moment of the third one. So, the net dipole moment of the $B{F_3}$ molecule is zero, and it is nonpolar.
In case of $B{F_3}$ the dipole moment is zero because it has a regular geometry and no lone pair of electrons is present on B. All the angles are 120 degrees.
Note: The dipole moment is a vector quantity, that means it has magnitude as well as definite directions. And because of being a vector quantity, it can also be zero as the two oppositely acting bond dipoles can cancel each other. By convention, dipole moment is denoted by a small arrow with its tail on the negative centre and its head on the positive centre.
Complete answer:
Lewis representation of $S{O_2}$ molecule –

The formal charges of the $S{O_2}$ with the single bond and a double bond is larger than $S{O_2}$ with two double bonds.
A dipole moment arises in any system in which there is a separation of charge. They can, therefore, arise in ionic bonds as well as in covalent bonds. Dipole moments occur due to the difference in electronegativity between two chemically bonded atoms.
A bond dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a chemical bond between two atoms in a molecule. It involves the concept of electric dipole moment, which is a measure of the separation of negative and positive charges in a system.
The $B{F_3}$ molecule has a symmetrical trigonal planar geometry, like the $S{O_3}$ molecule. In such a structure, the resultant moment of any two \[B - F\] dipoles is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the moment of the third one. So, the net dipole moment of the $B{F_3}$ molecule is zero, and it is nonpolar.
In case of $B{F_3}$ the dipole moment is zero because it has a regular geometry and no lone pair of electrons is present on B. All the angles are 120 degrees.
Note: The dipole moment is a vector quantity, that means it has magnitude as well as definite directions. And because of being a vector quantity, it can also be zero as the two oppositely acting bond dipoles can cancel each other. By convention, dipole moment is denoted by a small arrow with its tail on the negative centre and its head on the positive centre.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




