
Draw the graphs of x-y+1=0 and 3x+2y-12=0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis and shade the triangular area.
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: Draw the graph of the two given equations. To draw the graph of a straight line, we need at least two points. So, choose one of the equations and substitute x = 0, determine y, then substitute y = 0, determine x. Now, apply the same process for the second equation. Plot the graph of the two equations using the points obtained. To determine the vertices of the triangle, solve the given equations algebraically.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the two equations as:
$\begin{align}
& x-y+1=0........................(i) \\
& 3x+2y-12=0..................(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Considering equation (i),
$x-y+1=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& -y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: \[A\left( 0,1 \right)\text{ and }B\left( -1,0 \right)\].
Considering equation (ii),
$3x+2y-12=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2y=12 \\
& \Rightarrow y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3x-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x=12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: $C\left( 0,6 \right)\text{ and }D\left( 4,0 \right)$.
Therefore, the graph of the two functions can be plotted as:
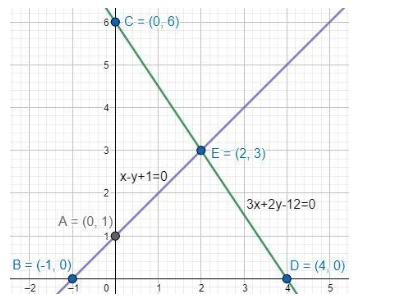
Clearly, we can see that the two lines are intersecting each other at a particular point E. To determine this point of intersection, we have to solve the equations algebraically. Let us solve the two equations.
Multiplying equation (i) by 2 and adding it to equation (i) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-2y+2+3x+2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x-10=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=10 \\
& \Rightarrow x=2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting (x=2) in equation (i), we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2-y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=3 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the intersection point is given by: E(2, 3).
Here, the triangle formed by the given lines and x-axis is triangle DBE. The sides of the triangle are BE (represented by the equation: x-y+1=0), DE (represented by the equation: 3x+2y-12=0) and BD is nothing but the x-axis.
So, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis are: E(2, 3); D(4, 0) and B(-1, 0).
Note: One may note that it is necessary to substitute the value of x and y equal to 0 because we have to determine the vertices of the base of the triangle which lies on x-axis. Also, it is important to solve these equations algebraically to determine the third vertex of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the two equations as:
$\begin{align}
& x-y+1=0........................(i) \\
& 3x+2y-12=0..................(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Considering equation (i),
$x-y+1=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& -y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: \[A\left( 0,1 \right)\text{ and }B\left( -1,0 \right)\].
Considering equation (ii),
$3x+2y-12=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2y=12 \\
& \Rightarrow y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3x-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x=12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: $C\left( 0,6 \right)\text{ and }D\left( 4,0 \right)$.
Therefore, the graph of the two functions can be plotted as:

Clearly, we can see that the two lines are intersecting each other at a particular point E. To determine this point of intersection, we have to solve the equations algebraically. Let us solve the two equations.
Multiplying equation (i) by 2 and adding it to equation (i) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2x-2y+2+3x+2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x-10=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=10 \\
& \Rightarrow x=2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting (x=2) in equation (i), we get,
$\begin{align}
& 2-y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=3 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the intersection point is given by: E(2, 3).
Here, the triangle formed by the given lines and x-axis is triangle DBE. The sides of the triangle are BE (represented by the equation: x-y+1=0), DE (represented by the equation: 3x+2y-12=0) and BD is nothing but the x-axis.
So, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis are: E(2, 3); D(4, 0) and B(-1, 0).
Note: One may note that it is necessary to substitute the value of x and y equal to 0 because we have to determine the vertices of the base of the triangle which lies on x-axis. Also, it is important to solve these equations algebraically to determine the third vertex of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Which are the three major ports of Tamil Nadu A Chennai class 10 social science CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE




