
Draw the electron dot structure for an oxygen molecule.
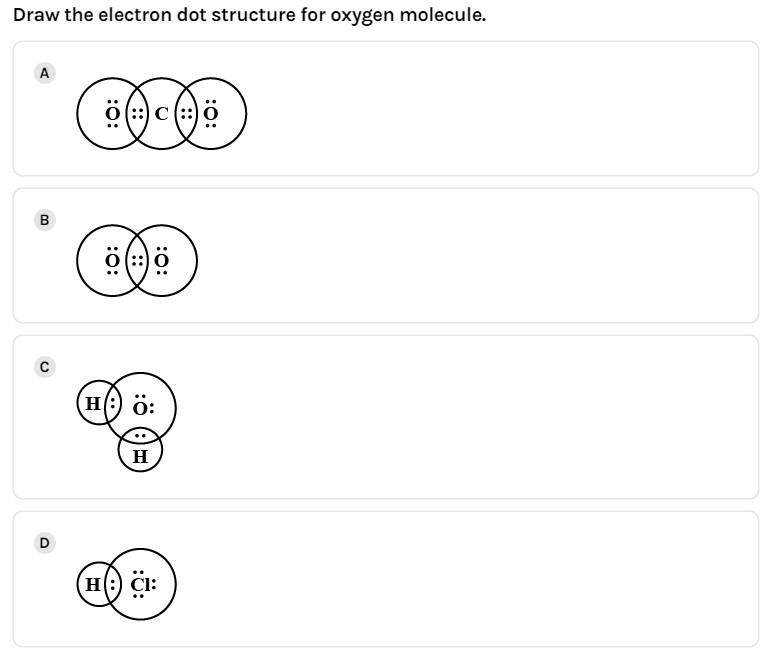
(A)
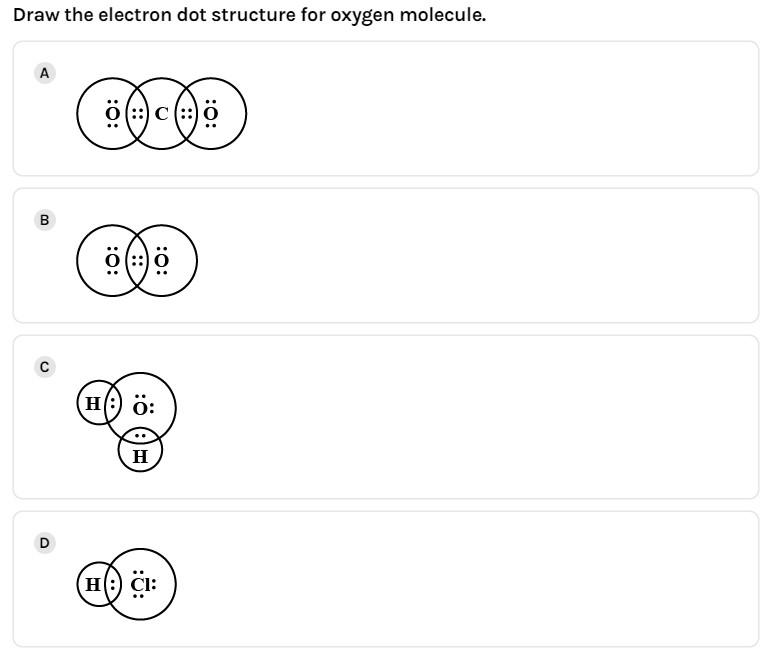
(B)
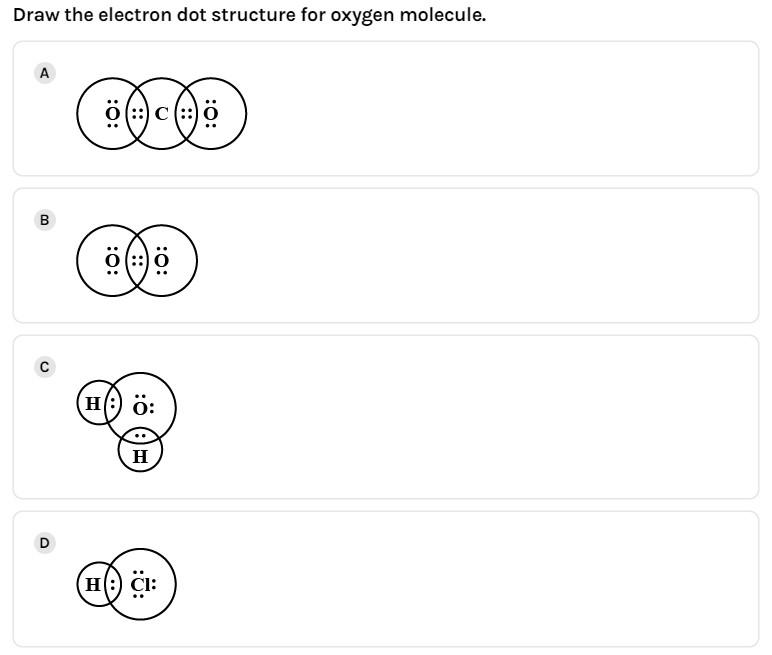
(C)
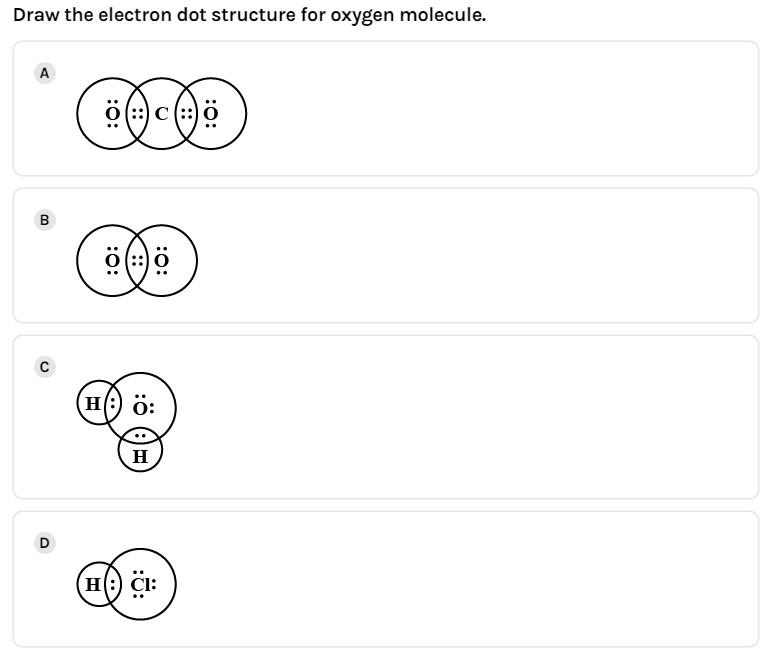
(D)




Answer
530.9k+ views
Hint: While drawing the Lewis dot structure, take only the valence shell electrons into account as they take part in the bonding. Also, consider the octet rule to fulfil the stability of the molecule formed.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to determine the Lewis dot structure of the ${{O}_{2}}$, we use the octet rule, that is, there should be 8 valence electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. An element follows the octet rule to obtain a stable state.
In case of oxygen atoms present in group 16 of the periodic table. It has six valence electrons with configuration $\left[ He \right]2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}$. Thus, each oxygen atom completes its octet by gaining two electrons. Thus, in its diatomic form by sharing electrons with adjacent oxygen atoms forming a covalent bond it tries to satisfy the octet rule.
Then, in the dot structure each oxygen will have six valence electrons. Then, total valence electrons in the ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $(6\times 2=)$12 valence electrons. But the required electrons to complete the octet is $(8\times 2=)$16 electron.
- The number of bonding electrons present will be obtained by subtracting the total valence electrons from the required electrons. We get $(16-12=)$ 4 bonding electrons, that is, two bond pairs.
- The number of unpaired electrons or non-bonding electrons present will be obtained by subtracting the bonding electrons from the valence electrons. We get $(12-4=)$8 non-bonding electrons or 4 lone pairs of electrons.
Thus, we get two bond pairs which form the double bond between the two oxygen atoms and four lone pairs, such a way that each oxygen has a set of two lone pairs each and shares its bond pair with the adjacent oxygen atom.
Thus, completing its octet and the final structure is option (B).
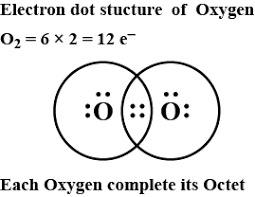
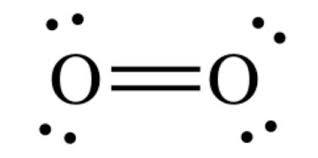
Note: As the octet rule is fully satisfied, the number of bond pairs formed lead to decrease in the bond distance and thus, the bond strength increases making the diatom formed to be stable.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to determine the Lewis dot structure of the ${{O}_{2}}$, we use the octet rule, that is, there should be 8 valence electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. An element follows the octet rule to obtain a stable state.
In case of oxygen atoms present in group 16 of the periodic table. It has six valence electrons with configuration $\left[ He \right]2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}$. Thus, each oxygen atom completes its octet by gaining two electrons. Thus, in its diatomic form by sharing electrons with adjacent oxygen atoms forming a covalent bond it tries to satisfy the octet rule.
Then, in the dot structure each oxygen will have six valence electrons. Then, total valence electrons in the ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $(6\times 2=)$12 valence electrons. But the required electrons to complete the octet is $(8\times 2=)$16 electron.
- The number of bonding electrons present will be obtained by subtracting the total valence electrons from the required electrons. We get $(16-12=)$ 4 bonding electrons, that is, two bond pairs.
- The number of unpaired electrons or non-bonding electrons present will be obtained by subtracting the bonding electrons from the valence electrons. We get $(12-4=)$8 non-bonding electrons or 4 lone pairs of electrons.
Thus, we get two bond pairs which form the double bond between the two oxygen atoms and four lone pairs, such a way that each oxygen has a set of two lone pairs each and shares its bond pair with the adjacent oxygen atom.
Thus, completing its octet and the final structure is option (B).
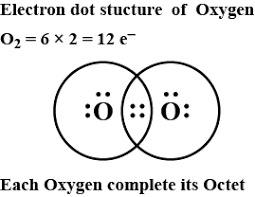
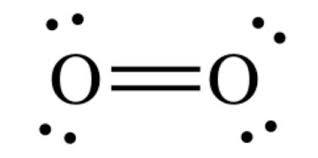
Note: As the octet rule is fully satisfied, the number of bond pairs formed lead to decrease in the bond distance and thus, the bond strength increases making the diatom formed to be stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




