
Draw the diagram of the chloroplast.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Chloroplast structure is present in the cells of plants and green algae, they are the site of photosynthesis. It is a process where light energy is converted to chemical energy and results in the production of oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds. It uses light energy to synthesize organic compounds.
Complete answer:
Chloroplast
Structure:
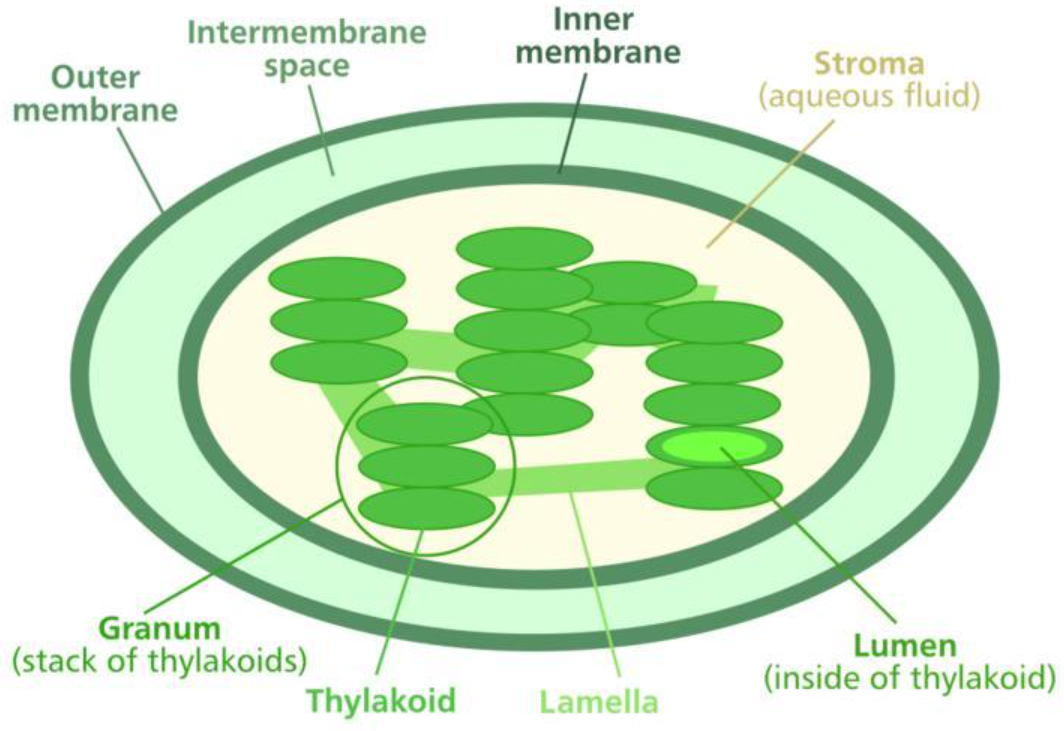
- Chloroplasts are a type of plastid, round, oval, disk-shaped body involved in the synthesis and storage.
- Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green color, by the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and b. These pigments absorb light energy.
- In plants, chloroplasts occur in all green tissues, though they are concentrated particularly in the parenchyma cells of the leaf mesophyll.
- The chloroplast is enclosed in a chloroplast envelope, which consists of a double membrane with outer and inner membrane, between which is a gap called the intermembrane space.
- A third, internal membrane, which is extensively folded and characterized by the presence of thylakoids (closed disks), known as the thylakoid membrane
- In higher plants, the thylakoids are arranged in tight stacks called grana. Grana are connected by stromal lamellae, extensions that run from one granum, through the stroma, into a neighboring granum.
- The thylakoid membrane envelops a central aqueous region known as the thylakoid lumen.
- The space between the inner membrane and the thylakoid membrane is filled with stroma.
- Stroma is a matrix containing dissolved enzymes, starch granules, and copies of the chloroplast genome. It also contains its DNA and ribosomes
- The chloroplast genome typically is circular.
Function:
- Chloroplast synthesizes food by the process of photosynthesis.
- Absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy.
- Chloroplast has chlorophyll which functions by trapping the solar energy and used for the synthesis of food in all green plants.
- It produces molecular oxygen $(O_2)$ and NADPH by photolysis of water.
- It produces ATP by the process of photosynthesis.
Note: The chloroplast is a chlorophyll-containing organelle responsible for photosynthesis. It captures light energy and gives plants a green color. It is essential for the growth and survival of plants. They are thought to be evolved from bacteria, they have a symbiont relationship.
Chloroplast common targets of many plant viruses are exploited for virus propagation and replication.
Complete answer:

Chloroplast
Structure:
- Chloroplasts are a type of plastid, round, oval, disk-shaped body involved in the synthesis and storage.
- Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green color, by the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and b. These pigments absorb light energy.
- In plants, chloroplasts occur in all green tissues, though they are concentrated particularly in the parenchyma cells of the leaf mesophyll.
- The chloroplast is enclosed in a chloroplast envelope, which consists of a double membrane with outer and inner membrane, between which is a gap called the intermembrane space.
- A third, internal membrane, which is extensively folded and characterized by the presence of thylakoids (closed disks), known as the thylakoid membrane
- In higher plants, the thylakoids are arranged in tight stacks called grana. Grana are connected by stromal lamellae, extensions that run from one granum, through the stroma, into a neighboring granum.
- The thylakoid membrane envelops a central aqueous region known as the thylakoid lumen.
- The space between the inner membrane and the thylakoid membrane is filled with stroma.
- Stroma is a matrix containing dissolved enzymes, starch granules, and copies of the chloroplast genome. It also contains its DNA and ribosomes
- The chloroplast genome typically is circular.
Function:
- Chloroplast synthesizes food by the process of photosynthesis.
- Absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy.
- Chloroplast has chlorophyll which functions by trapping the solar energy and used for the synthesis of food in all green plants.
- It produces molecular oxygen $(O_2)$ and NADPH by photolysis of water.
- It produces ATP by the process of photosynthesis.
Note: The chloroplast is a chlorophyll-containing organelle responsible for photosynthesis. It captures light energy and gives plants a green color. It is essential for the growth and survival of plants. They are thought to be evolved from bacteria, they have a symbiont relationship.
Chloroplast common targets of many plant viruses are exploited for virus propagation and replication.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




