
Draw the circle whose equation is \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 2ay\].
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Before attempting this question, one should have prior knowledge about the circle and also remember that the equation of circle in standard form can easily give the center in form (h, k) and radius r, use this information to approach the solution of the problem.
The general equation is $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: An equation of circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 2ay\], we need to draw the given circle. But we neither have a center or radius. The standard form of circle with center (h, k) and radius is given by the equation, $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
We need to convert the given equation in standard form in order to draw it. Let’s begin with bringing all terms to the left-hand side.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = 2ay\]
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2ay = 0\]
Since, we need to make a square in form $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} $ and $ {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} $ . Add the $ {a^2} $ term to both sides.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} + {a^2} - 2ay = {a^2}\]
Using the algebraic identity $ {\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab $ in the above equation we get
\[{\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {a^2}\]
Hence, on comparing with the standard form we have center (0, a) and radius equal to a.
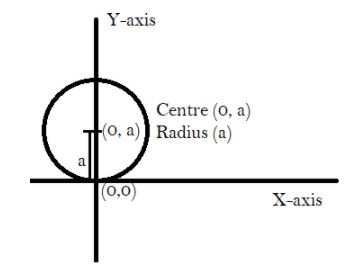
We located the center (0, a) and drew a circle with taking radius ‘a’.
Note: In the above question we came across the term “circle” which can be explained as the collection of points exist in the same plane where every point is equidistant from a point which is named as the center point, in the circle radius is the defined distance from the point on the circumference of the circle. The general form of the equation of circle is given as \[{x^2} + {y^2}{\text{ + }}Dx + Ey + F = 0\], where D, E and F are constants.
The general equation is $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: An equation of circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 2ay\], we need to draw the given circle. But we neither have a center or radius. The standard form of circle with center (h, k) and radius is given by the equation, $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2} $
We need to convert the given equation in standard form in order to draw it. Let’s begin with bringing all terms to the left-hand side.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} = 2ay\]
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2ay = 0\]
Since, we need to make a square in form $ {\left( {x - h} \right)^2} $ and $ {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} $ . Add the $ {a^2} $ term to both sides.
\[{x^2} + {y^2} + {a^2} - 2ay = {a^2}\]
Using the algebraic identity $ {\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab $ in the above equation we get
\[{\left( {x - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {a^2}\]
Hence, on comparing with the standard form we have center (0, a) and radius equal to a.

We located the center (0, a) and drew a circle with taking radius ‘a’.
Note: In the above question we came across the term “circle” which can be explained as the collection of points exist in the same plane where every point is equidistant from a point which is named as the center point, in the circle radius is the defined distance from the point on the circumference of the circle. The general form of the equation of circle is given as \[{x^2} + {y^2}{\text{ + }}Dx + Ey + F = 0\], where D, E and F are constants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




