
Draw the block diagram of Amplitude Modulated (AM) Radio transmitter.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:Draw the functional block diagram of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter or AM radio transmitter. Recall the function of each block in this block diagram. Hence,, explain the working of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter for the transmission of the sound input from one place to the other place.
Complete answer:
The functional block diagram of the Amplitude Modulated (AM) Radio transmitter is as follows:
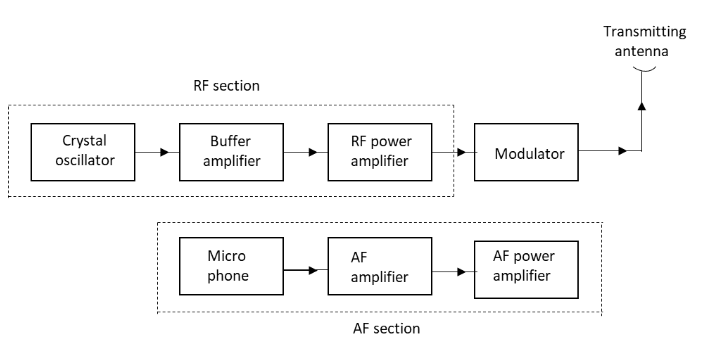
The amplitude modulated radio transmitter is made up of two sections namely audio frequency (AF) section and radio frequency (RF) section.The function of the audio frequency section of the above block diagram is to generate a modulated wave signal.
First the sound input is given to the microphone. The function of a microphone is to convert the input sound energy into electrical energy. The sound energy converted into electrical energy is very small. This electrical energy from the microphone is given to the AF amplifier which amplifies this energy. This amplified energy from the AF amplifier is given to the AF power amplifier which converts the signal into the required audio frequency power. This output from the AF power amplifier is supplied to the modulator.
In the RF section, the crystal oscillator generates a high frequency carrier wave. The RF power amplifier amplifies the output from the crystal oscillator. The buffer amplifier is used to separate the crystal oscillator from the RF power amplifier and the frequency of the crystal oscillator is kept constant using such arrangement in the RF section.The output from the RF section and AF section is mixed to produce the amplitude modulated wave which is then transferred to the transmitting antenna for transmission.
Note: The students should draw the block diagram of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter correctly. If this block diagram is not drawn correctly then one cannot understand the working of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter correctly. Thus, it is important to correctly remember the block diagram.
Complete answer:
The functional block diagram of the Amplitude Modulated (AM) Radio transmitter is as follows:

The amplitude modulated radio transmitter is made up of two sections namely audio frequency (AF) section and radio frequency (RF) section.The function of the audio frequency section of the above block diagram is to generate a modulated wave signal.
First the sound input is given to the microphone. The function of a microphone is to convert the input sound energy into electrical energy. The sound energy converted into electrical energy is very small. This electrical energy from the microphone is given to the AF amplifier which amplifies this energy. This amplified energy from the AF amplifier is given to the AF power amplifier which converts the signal into the required audio frequency power. This output from the AF power amplifier is supplied to the modulator.
In the RF section, the crystal oscillator generates a high frequency carrier wave. The RF power amplifier amplifies the output from the crystal oscillator. The buffer amplifier is used to separate the crystal oscillator from the RF power amplifier and the frequency of the crystal oscillator is kept constant using such arrangement in the RF section.The output from the RF section and AF section is mixed to produce the amplitude modulated wave which is then transferred to the transmitting antenna for transmission.
Note: The students should draw the block diagram of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter correctly. If this block diagram is not drawn correctly then one cannot understand the working of the amplitude modulated radio transmitter correctly. Thus, it is important to correctly remember the block diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




