
Draw shapes of ‘2s’ and ‘2p’ orbitals.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: An orbital can be defined as a three - dimensional space around the nucleus where the possibility of finding the electron is very high. These orbitals are of 4 types and are distinguished on the basis of their geometries.
Complete step by step answer:
The 4 main types of orbitals are named ‘s’, ‘p’, ‘d’ and ‘f’. Each of these orbitals have unique geometrical structures and are repeated multiple times in a given atom, depending on its electronic configuration.
The shapes of these of the s and p orbitals can be described as follows:
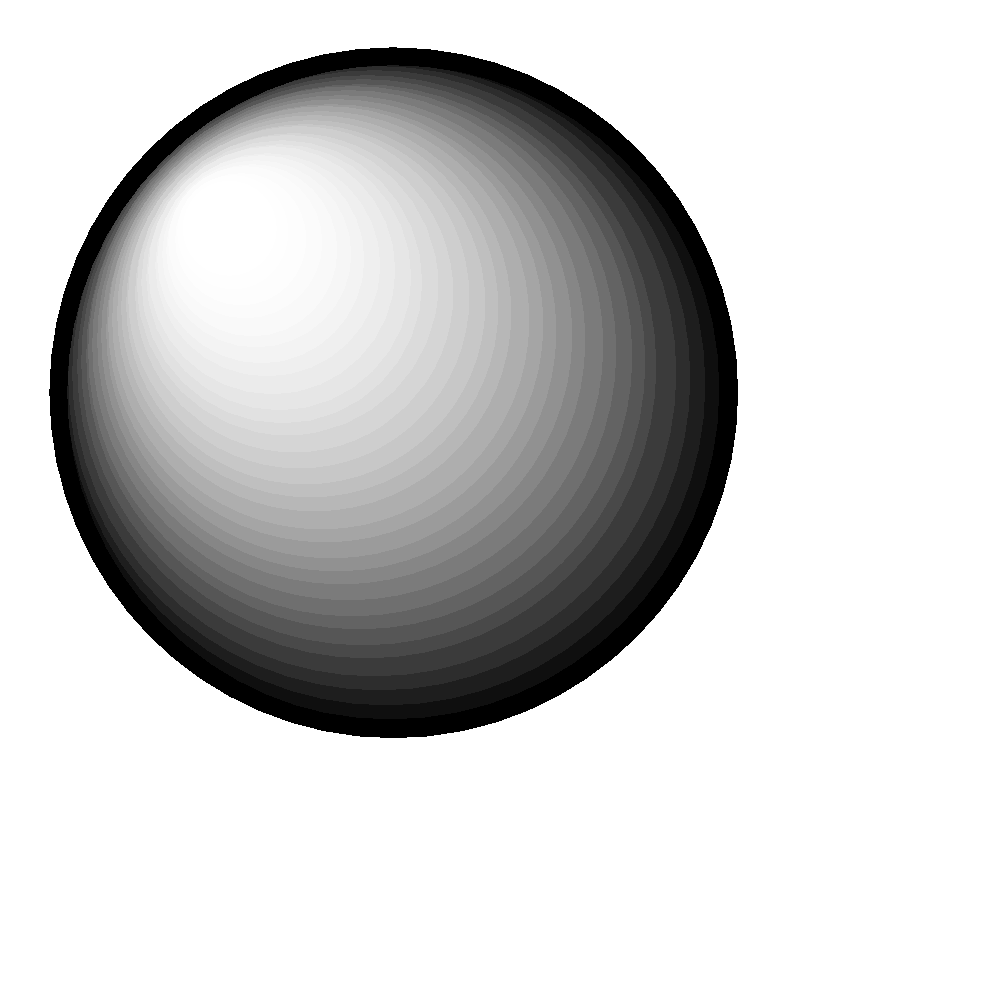
S orbital: spherical in shape. There is only one possible configuration.
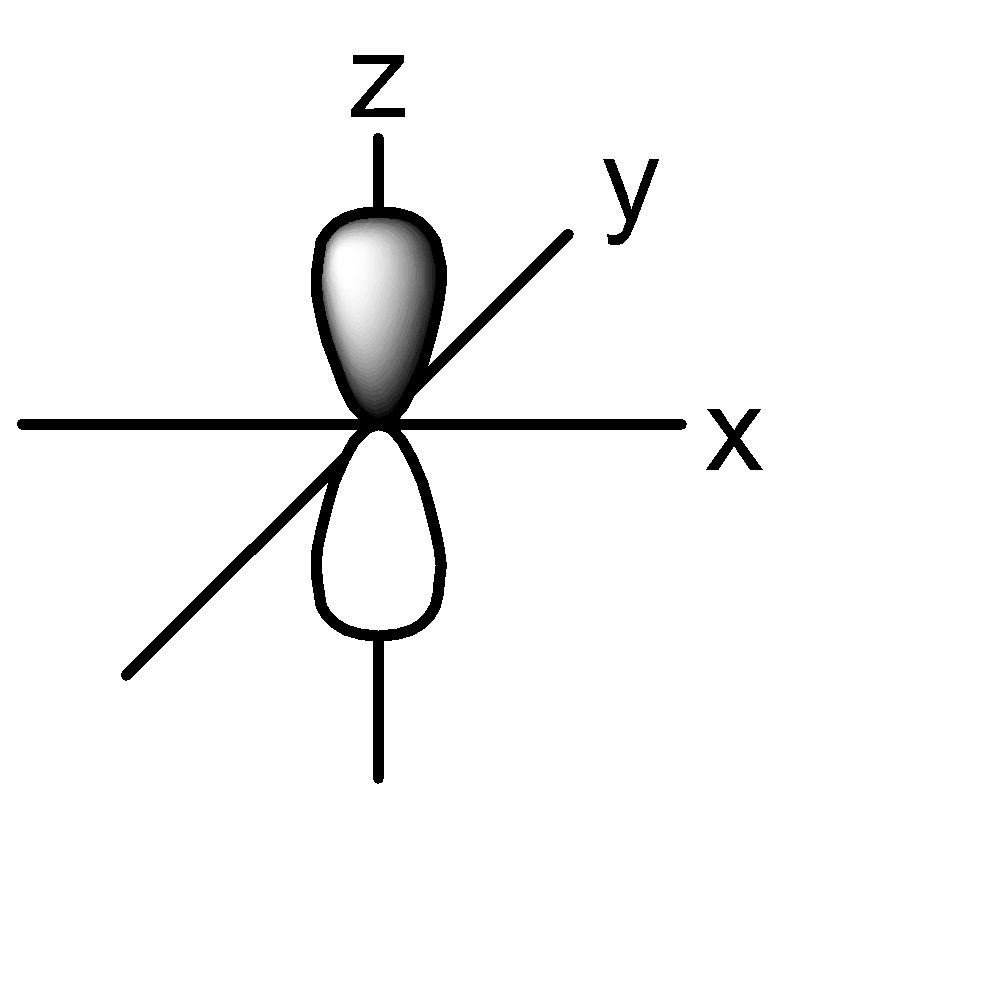
P orbital: consists of two lobes which are lying on either sides of a plane that is passing through a nucleus. There are 3 possible configurations.
The shape of the orbital remains constant irrespective of the shell in which it is present. This means that the shape of 1s, 2s, 3s orbitals are all the same. Same is the case with p, d, f orbitals.
Hence the shape of 2s and 2p orbitals can be given as:
2s:
2p:
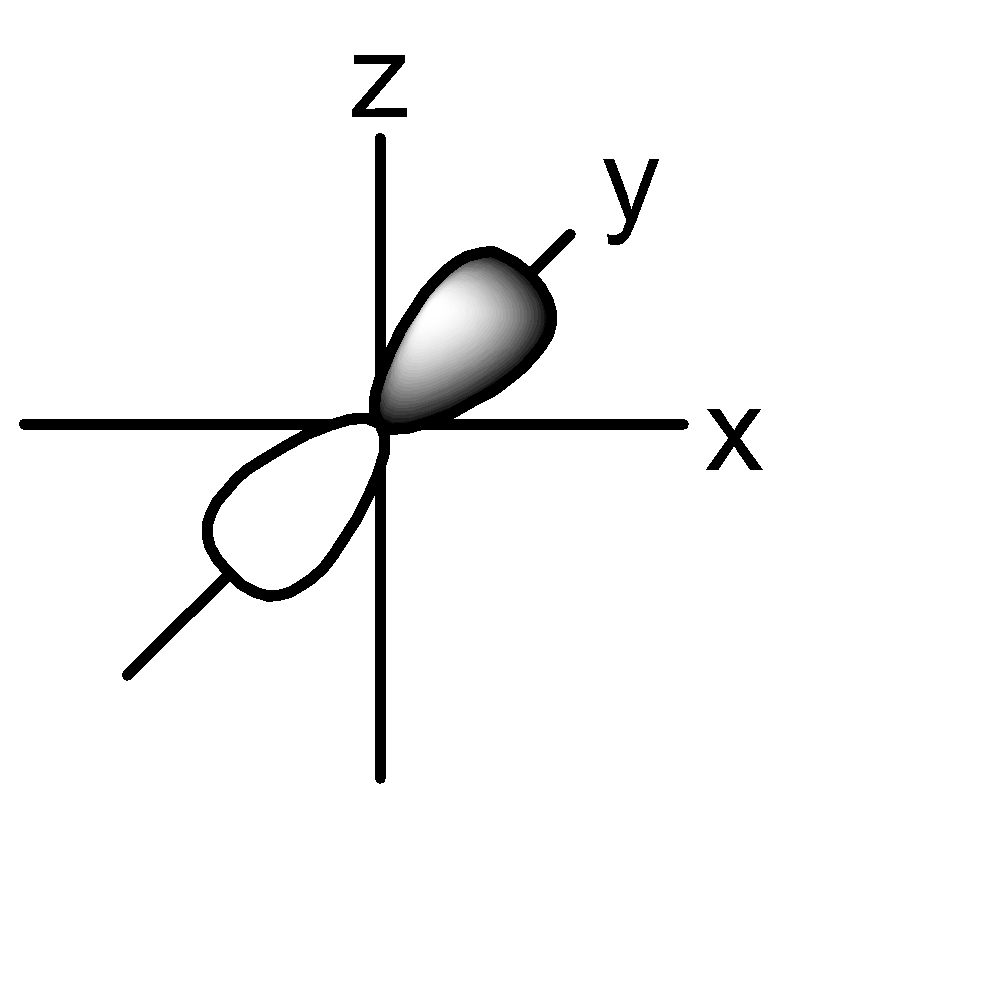
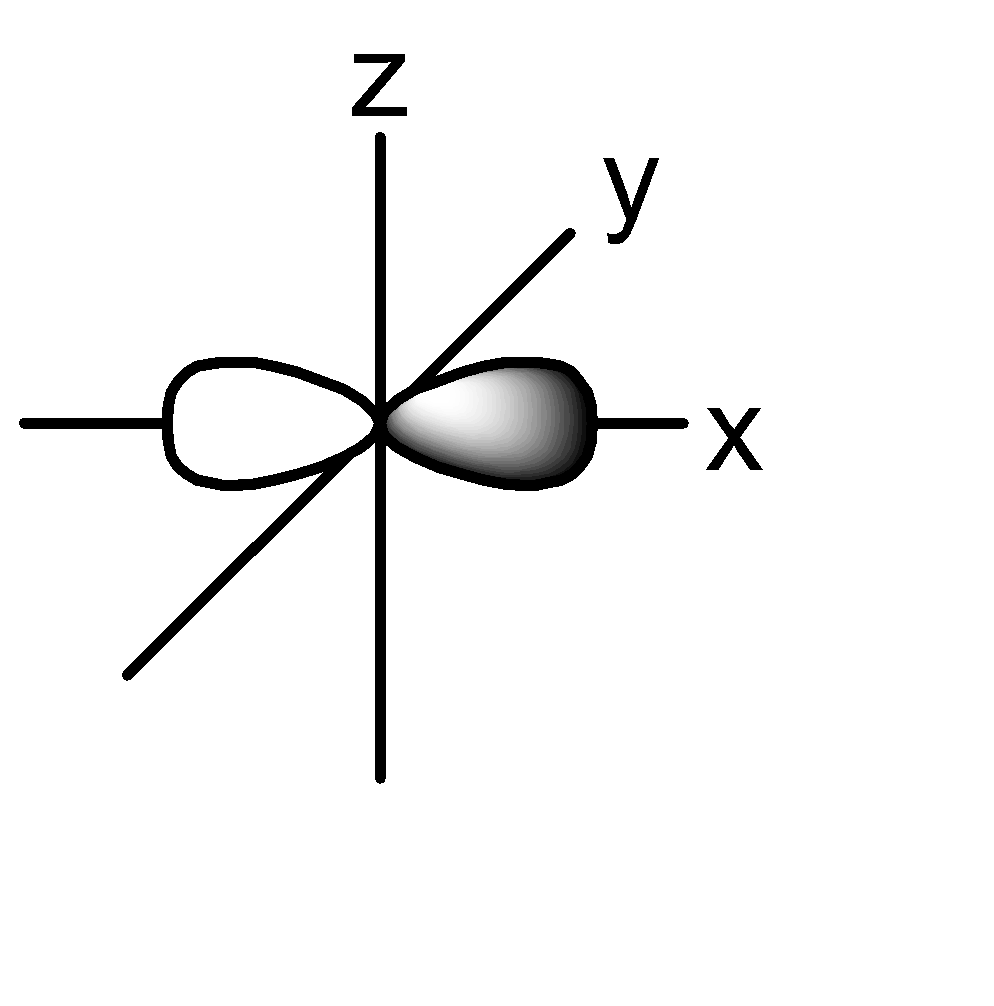


Note:
Another way of explaining an orbital is as a wave function that is capable of describing the characteristic properties of no more than two electrons which are in the vicinity of an atomic nucleus or of a system of nuclei.
Complete step by step answer:
The 4 main types of orbitals are named ‘s’, ‘p’, ‘d’ and ‘f’. Each of these orbitals have unique geometrical structures and are repeated multiple times in a given atom, depending on its electronic configuration.
The shapes of these of the s and p orbitals can be described as follows:
S orbital: spherical in shape. There is only one possible configuration.
P orbital: consists of two lobes which are lying on either sides of a plane that is passing through a nucleus. There are 3 possible configurations.
The shape of the orbital remains constant irrespective of the shell in which it is present. This means that the shape of 1s, 2s, 3s orbitals are all the same. Same is the case with p, d, f orbitals.
Hence the shape of 2s and 2p orbitals can be given as:
2s:

2p:



Note:
Another way of explaining an orbital is as a wave function that is capable of describing the characteristic properties of no more than two electrons which are in the vicinity of an atomic nucleus or of a system of nuclei.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




