
Draw ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed at infinity.
Answer
539.5k+ views
- Hint: The property of a convex lens is that it converges the light rays passing through them. The nature of image formed by the lens depends on the distance of the object from the lens. Depending on that, the image can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, diminished or magnified.
Complete step-by-step solution -
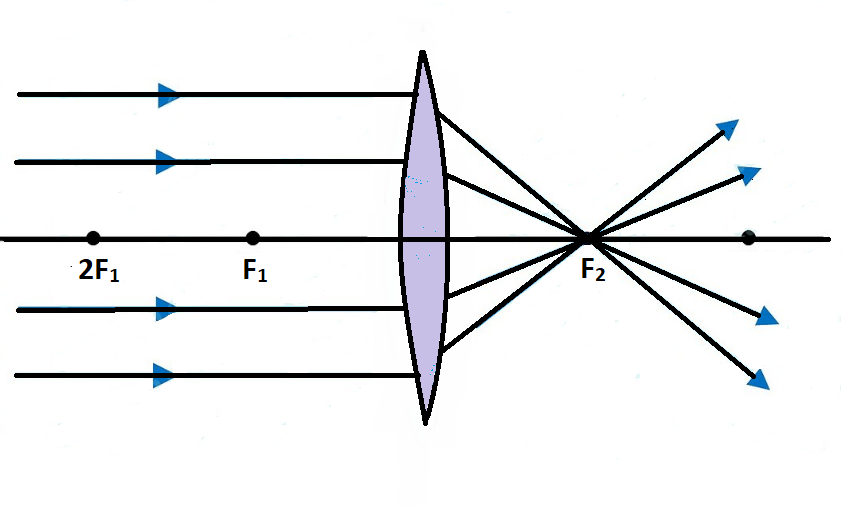
When an object is placed at infinity then its real image will be formed at the focus (${F_2}$).
The image formed in this situation when object is placed at infinity, has the following characteristics:
(1). Real image
(2). Inverted image
(3). Highly diminished image
Additional Information:
A lens is basically a carefully grounded piece of transparent material which refracts light rays in such a way as to form an image.
There are two types of lenses: Convex Lens (Converging) and Concave Lens (Diverging).
A converging lens causes light rays that are parallel to the principal axis to converge or meet, at one point (the principal focus).
A diverging lens causes parallel light rays to diverge or spread apart.
Real image and virtual image:
A real image is formed when light rays pass and diverge from the image point actually. Real images can be displayed on screens.
A virtual image is formed when light rays do not pass through the image point but only appear to diverge from the image point. Virtual images cannot be displayed on screens.
Convex lens always forms a real image except the situation when the object is placed between the optical centre (O) and focus (${F_1}$).
Note: 1. All distances to the left of the lens are taken to be negative while all distances to the right of the lens are taken to be positive.
2. A real image can be obtained on a screen while a virtual image cannot be obtained on a screen.
Complete step-by-step solution -

When an object is placed at infinity then its real image will be formed at the focus (${F_2}$).
The image formed in this situation when object is placed at infinity, has the following characteristics:
(1). Real image
(2). Inverted image
(3). Highly diminished image
Additional Information:
A lens is basically a carefully grounded piece of transparent material which refracts light rays in such a way as to form an image.
There are two types of lenses: Convex Lens (Converging) and Concave Lens (Diverging).
A converging lens causes light rays that are parallel to the principal axis to converge or meet, at one point (the principal focus).
A diverging lens causes parallel light rays to diverge or spread apart.
Real image and virtual image:
A real image is formed when light rays pass and diverge from the image point actually. Real images can be displayed on screens.
A virtual image is formed when light rays do not pass through the image point but only appear to diverge from the image point. Virtual images cannot be displayed on screens.
Convex lens always forms a real image except the situation when the object is placed between the optical centre (O) and focus (${F_1}$).
Note: 1. All distances to the left of the lens are taken to be negative while all distances to the right of the lens are taken to be positive.
2. A real image can be obtained on a screen while a virtual image cannot be obtained on a screen.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




