
How can I draw Lewis dot structures for ionic compounds?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:The diagrammatic representation of the electron distribution around the atoms in a molecule is known as a Lewis dot structure. To draw the Lewis dot structures we must know the valence electrons on each atom present in the given ionic compounds. Then calculate the number of total valence electrons of the ionic compounds.
Complete answer:
We know that the diagrammatic representation of the electron distribution around the atoms in a molecule is known as a Lewis dot structure.
The steps to draw the Lewis dot structure of ionic compounds are as follows:
1-Determine the total number of valence electrons.
2-Select the central atom.
3-Draw the skeletal structure.
4-Determine the number of bonds in a molecule.
5-Determine the number of electrons required for an atom to complete its octet.
6-Place the electrons on the outside atoms.
7-Place the remaining electrons around the central atom.
For example consider an ionic compound magnesium chloride i.e. ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The valence electrons of magnesium are 2 and the valence electrons of chlorine are 7. Thus,
Total valence electrons of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 2 + \left( {2 \times 7} \right) = 2 + 14 = 16$
The central atom in ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is magnesium. The two chlorine atoms are around the magnesium atom. The skeletal structure of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
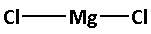
Here, the number of bonds are 2. Thus, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, remaining electrons are,
$16 - 4 = 12$
Now, each chlorine atom requires six electrons to complete its octet. Thus, place six electrons around each chlorine atom. Thus, the Lewis dot structure of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
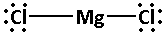
Note: Lewis dot structures are also known as electron dot structures. To draw the Lewis dot structures remember the atomic numbers of the elements in the compounds. This helps in easily determining the valence electrons and thus helps in determining the Lewis dot structures.
Complete answer:
We know that the diagrammatic representation of the electron distribution around the atoms in a molecule is known as a Lewis dot structure.
The steps to draw the Lewis dot structure of ionic compounds are as follows:
1-Determine the total number of valence electrons.
2-Select the central atom.
3-Draw the skeletal structure.
4-Determine the number of bonds in a molecule.
5-Determine the number of electrons required for an atom to complete its octet.
6-Place the electrons on the outside atoms.
7-Place the remaining electrons around the central atom.
For example consider an ionic compound magnesium chloride i.e. ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The valence electrons of magnesium are 2 and the valence electrons of chlorine are 7. Thus,
Total valence electrons of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ $ = 2 + \left( {2 \times 7} \right) = 2 + 14 = 16$
The central atom in ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is magnesium. The two chlorine atoms are around the magnesium atom. The skeletal structure of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
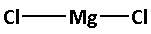
Here, the number of bonds are 2. Thus, four electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, remaining electrons are,
$16 - 4 = 12$
Now, each chlorine atom requires six electrons to complete its octet. Thus, place six electrons around each chlorine atom. Thus, the Lewis dot structure of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
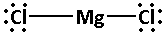
Note: Lewis dot structures are also known as electron dot structures. To draw the Lewis dot structures remember the atomic numbers of the elements in the compounds. This helps in easily determining the valence electrons and thus helps in determining the Lewis dot structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




